Method for synthesizing N,N'-dialkyl oxalamide by using artificial photosynthesis effect, and derivative thereof
An alkyloxyaldamide and artificial photosynthesis technology, applied in the field of environmental protection, can solve the problems of hindering the industrialization process, high energy consumption and high cost, and achieve the effect of direct resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
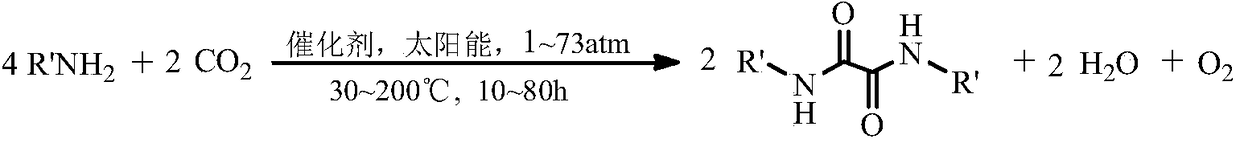
[0022] Using artificial photosynthesis through CO 2 Prepare N, the production method of N '-diethyloxyaldamide:
[0023] Take 10ml (0.103mol) of n-ethylamine and put it into a 100ml sapphire autoclave with a xenon lamp light source and magnetic stirring, and then add 1.2g (0.005mol) of LaFeO 3 Catalyst and 3g molecular sieve dehydrating agent, at room temperature, filled with 1.5MPa of CO 2 , sealed the reaction kettle, turned on the xenon lamp light source, raised the temperature to 120°C, and reacted at constant temperature for 12h. Cool, vent to normal pressure and normal temperature, take out the light yellow reaction liquid, filter the catalyst and dehydrating agent, then rotate the liquid obtained after the reaction, and carry out the gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of the concentrated solution by rotary evaporation and decompression, and measure the concentration of the raw material n-ethylamine. The conversion rate was 82%.
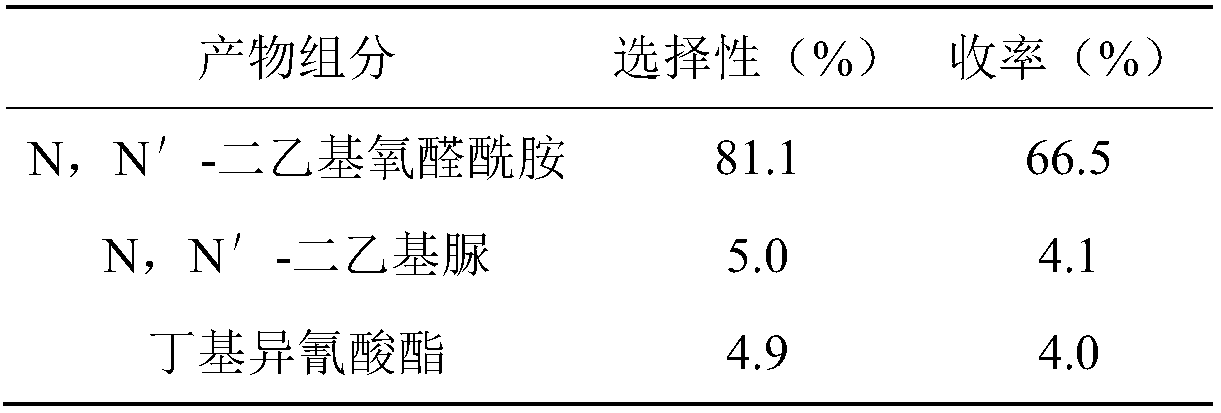
[0024] Product composition...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Using artificial photosynthesis through CO 2 Prepare N, the production method of N '-dibutyloxyaldamide:
[0029] The operation is the same as that of Example 1, and the solvent is the same as that of Example 1, with n-ethylamine being replaced by n-butylamine, and the catalyst LaFeO 3 Change to ZnY 2 o 4 , the reaction temperature is 150°C, and the reaction time is 24h. The rest of the operating conditions remain unchanged. The conversion rate of raw material n-butylamine was measured to be 88%.
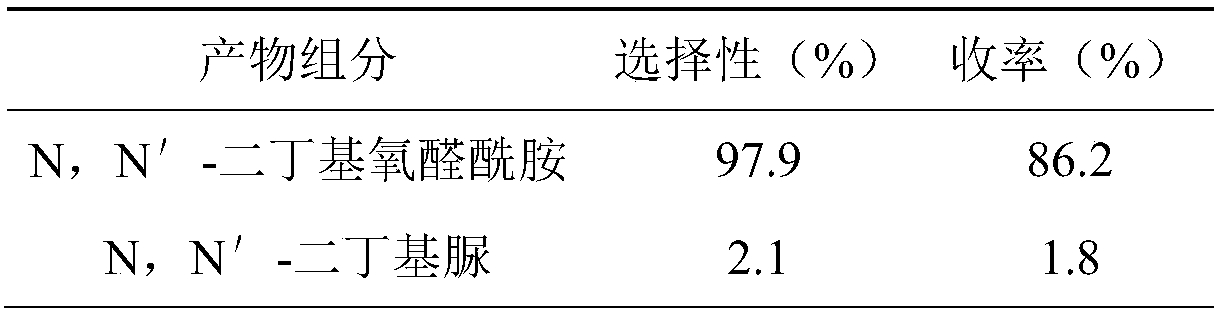
[0030] Product composition, selectivity and yield are shown in Table 2:
[0031] Table 2. Product composition, selectivity and yield
[0032]
Embodiment 3
[0034] Using artificial photosynthesis through CO 2 Preparation N, the production method of N '-dicyclohexyl oxaldamide:
[0035] The operation is the same as in Example 1, and n-ethylamine is replaced by cyclohexylamine, and the catalyst LaFeO 3 Change to In 0.5 Cu 0.5 TaO 4 , the reaction temperature is 120°C, and the reaction time is 36h. The rest of the operating conditions remain unchanged. The conversion rate of the raw material cyclohexylamine was measured to be 78%.
[0036] Product composition, selectivity and yield are shown in Table 3:
[0037] Table 3. Product composition, selectivity and yield
[0038]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com