A nucleic acid aptamer for detecting human uveal melanoma cells
A technology for melanoma cells and nucleic acid aptamers, which can be used in measurement devices, DNA/RNA fragments, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as poor prognosis, and achieve the effects of low preparation cost, small molecular weight, and easy labeling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1: Screening of specific nucleic acid aptamers for human uveal melanoma cells (OCM-1)
[0022] (1) Design of the nucleic acid library and primers used:
[0023] Random nucleic acid library:
[0024] 5'-ATCCAGAGTGACGCAGCA(N25)TGGACACGGTGGCTTAGT-3'
[0025] Upstream primer: 5'-FITC-ATCCAGAGTGACGCAGCA--3';
[0026] Downstream primer: 5'-biotin-TGGACACGGTGGCTTAGT-3'.
[0027] (2) Positive screening:
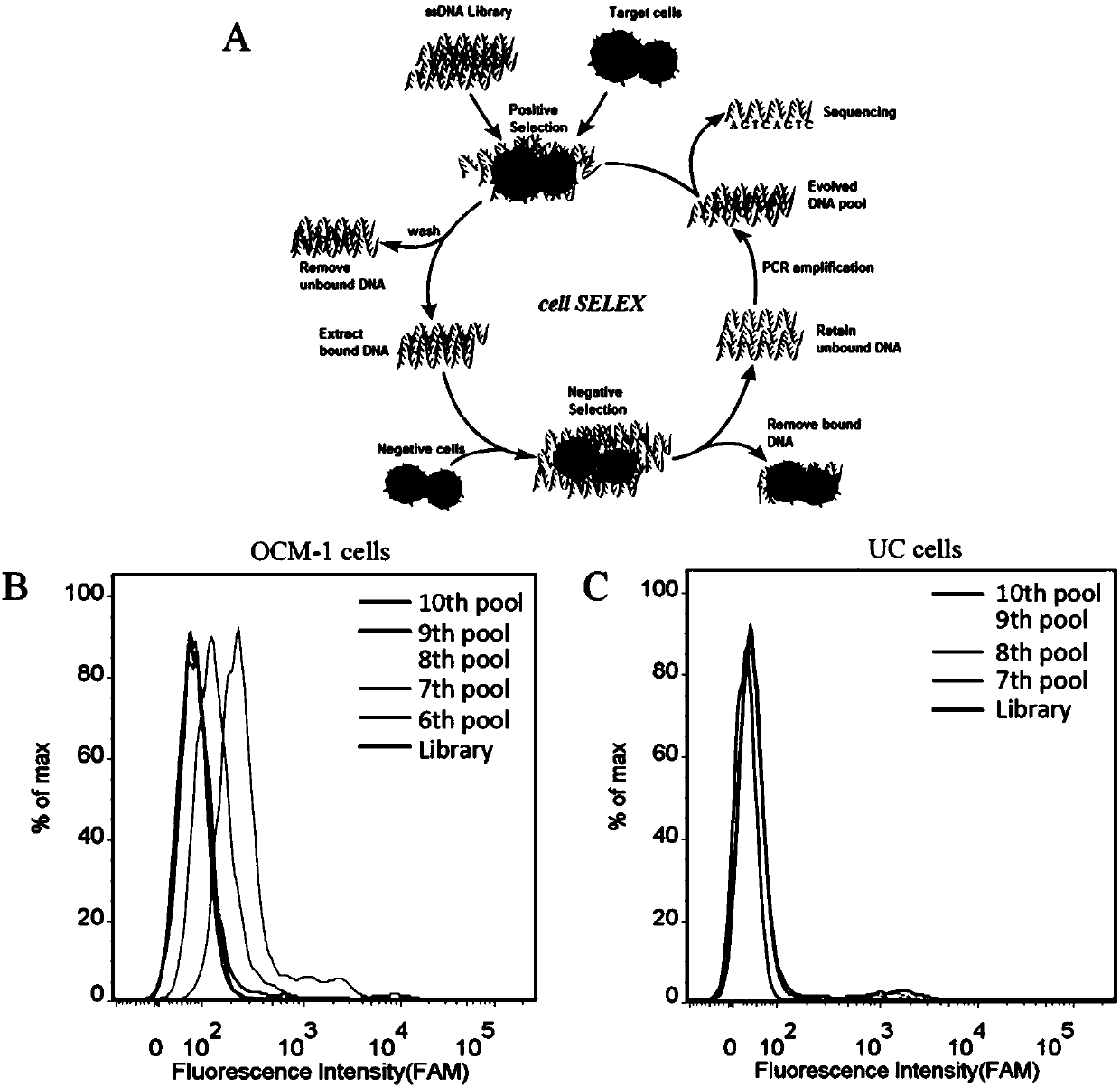
[0028] 2.1 Incubation: Dissolve the above random nucleic acid library with binding buffer (D-PBS, 5 mM magnesium chloride), denature at 95°C for 5 minutes, quickly put it on ice, and let it stand for 10 minutes; then mix with the cultured and pretreated Human uveal melanoma cells (OCM-1) were incubated at 4°C for 1 hour.
[0029] 2.2 Dissociation: After the incubation, remove the solution in the incubation dish, wash the cells in the incubation dish with washing buffer (PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride); scrape the incubation dish with 1mL st...
Embodiment 2
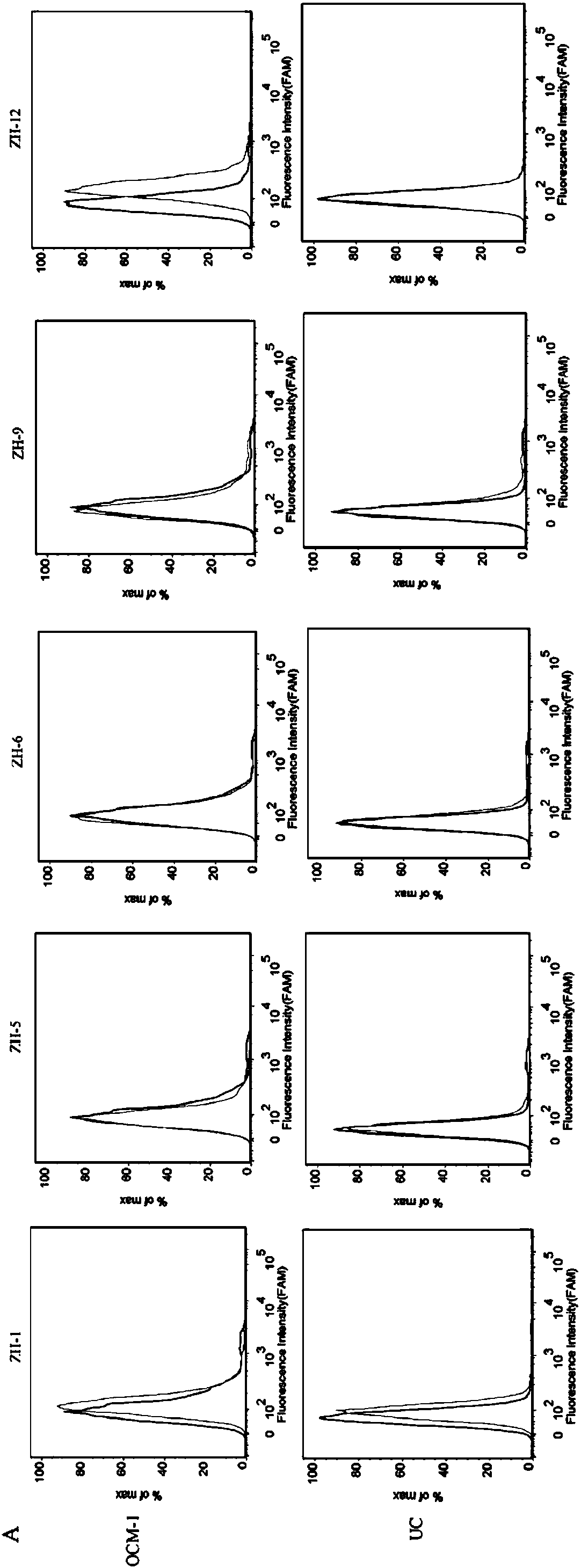
[0037] Example 2: Identification of the sequence with the strongest specific binding ability to the OCM-1 cell line
[0038]First, digest the adherent OCM-1 cells from the culture dish with 0.2% EDTA, collect the cells into centrifuge tubes, and wash them by centrifugation with washing buffer (PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride) Several times; secondly, the final concentration of 200nM of the 5 sequences and the random library were added to the binding buffer (D-PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5mM magnesium chloride, 100mg / L tRNA, 1g / L BSA) soaked OCM -1 cells; then placed on a shaker at 4°C and incubated for 30min; after the incubation was completed, centrifuge and wash once with washing buffer (PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride), and perform fluorescence detection by flow cytometry (results See figure 2 ). The test results showed that ZH-12 had the strongest binding ability to OCM-1 cells.
Embodiment 3
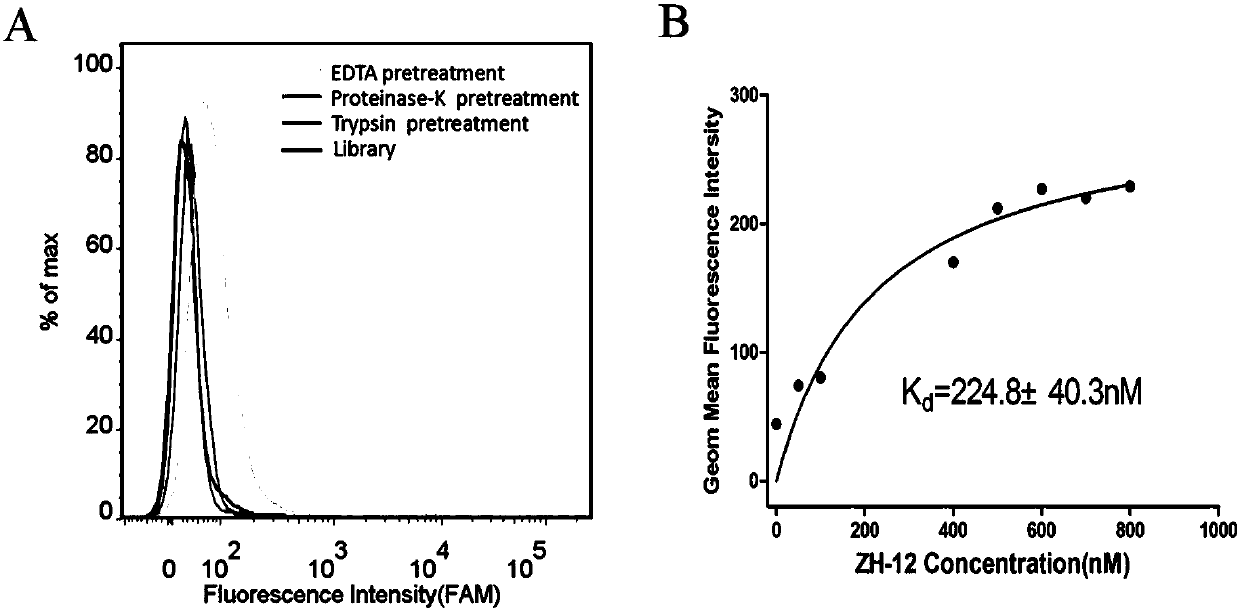
[0039] Example 3: Target type identification and its affinity determination for OCM-1 cells
[0040] First, take 3 OCM-1 cell dishes that have been plated for 24 hours, and digest the cells from the culture dish with 0.2% EDTA, trypsin, and proteinase K respectively (0.2% EDTA was digested for 1 minute, trypsin and proteinase K Digested for 5 minutes), and then collected by centrifuge tubes (2 tubes for EDTA digested cells, one tube for trypsin and proteinase K digested cells), and then washed with washing buffer (PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride), then add 200nM ZH-12 to the cells, add 200nM random library to another tube of EDTA-digested cells, place in a shaker at 4°C and incubate for 30min, and then centrifuge and wash with washing buffer after incubation. Once, and finally use the flow cytometer to detect the fluorescent signal (the results are as follows: image 3 A). The results of flow cytometry showed that the binding amount of ZH-12 to OCM-1 d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com