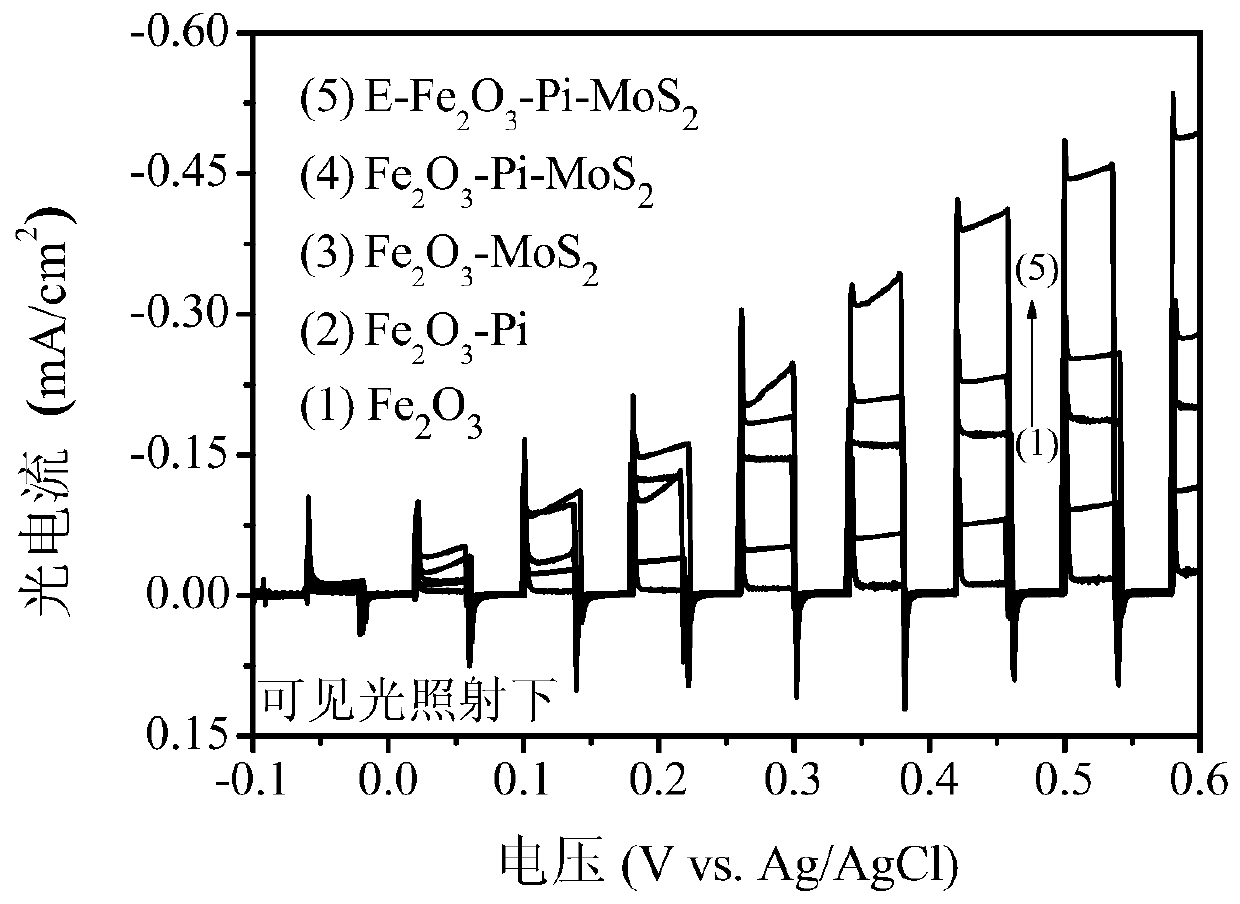
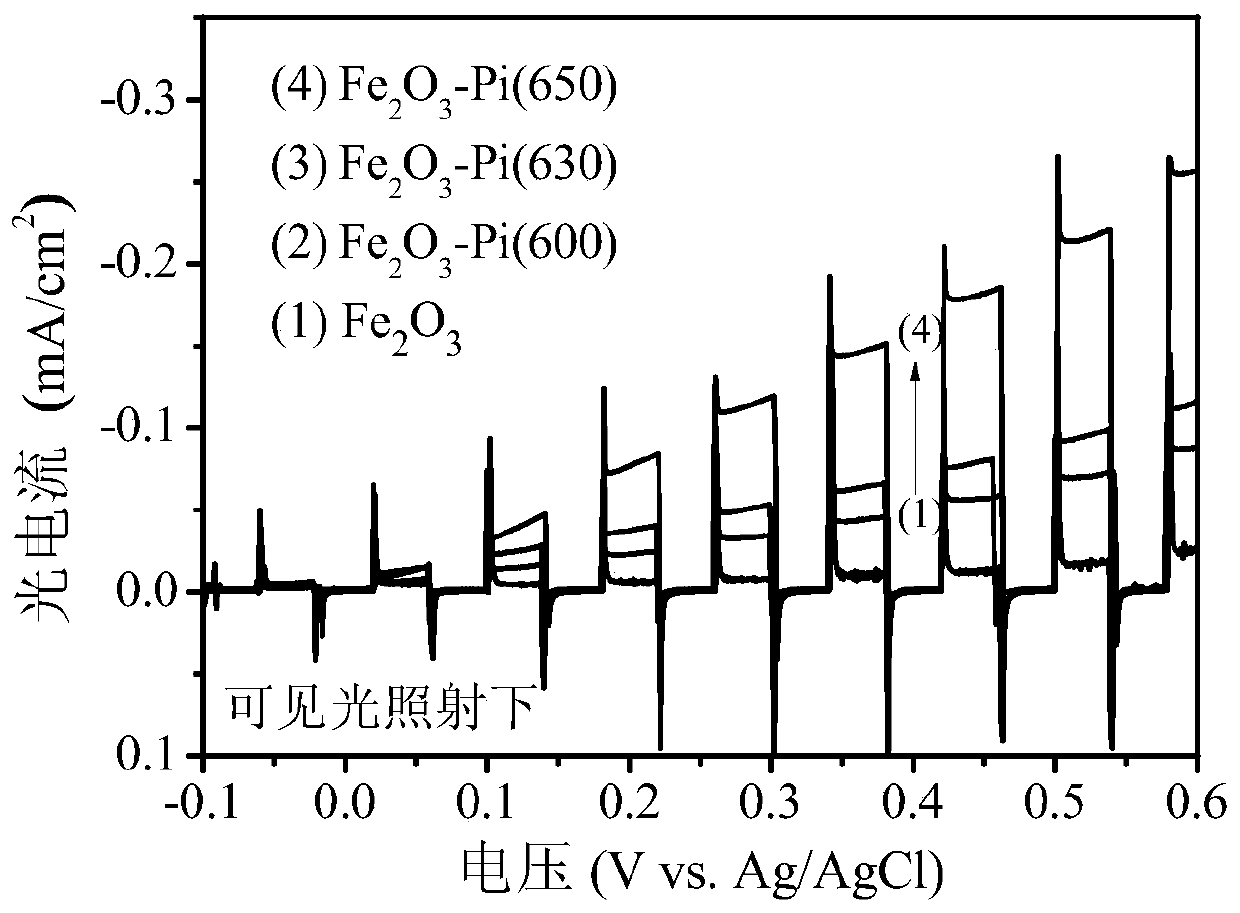
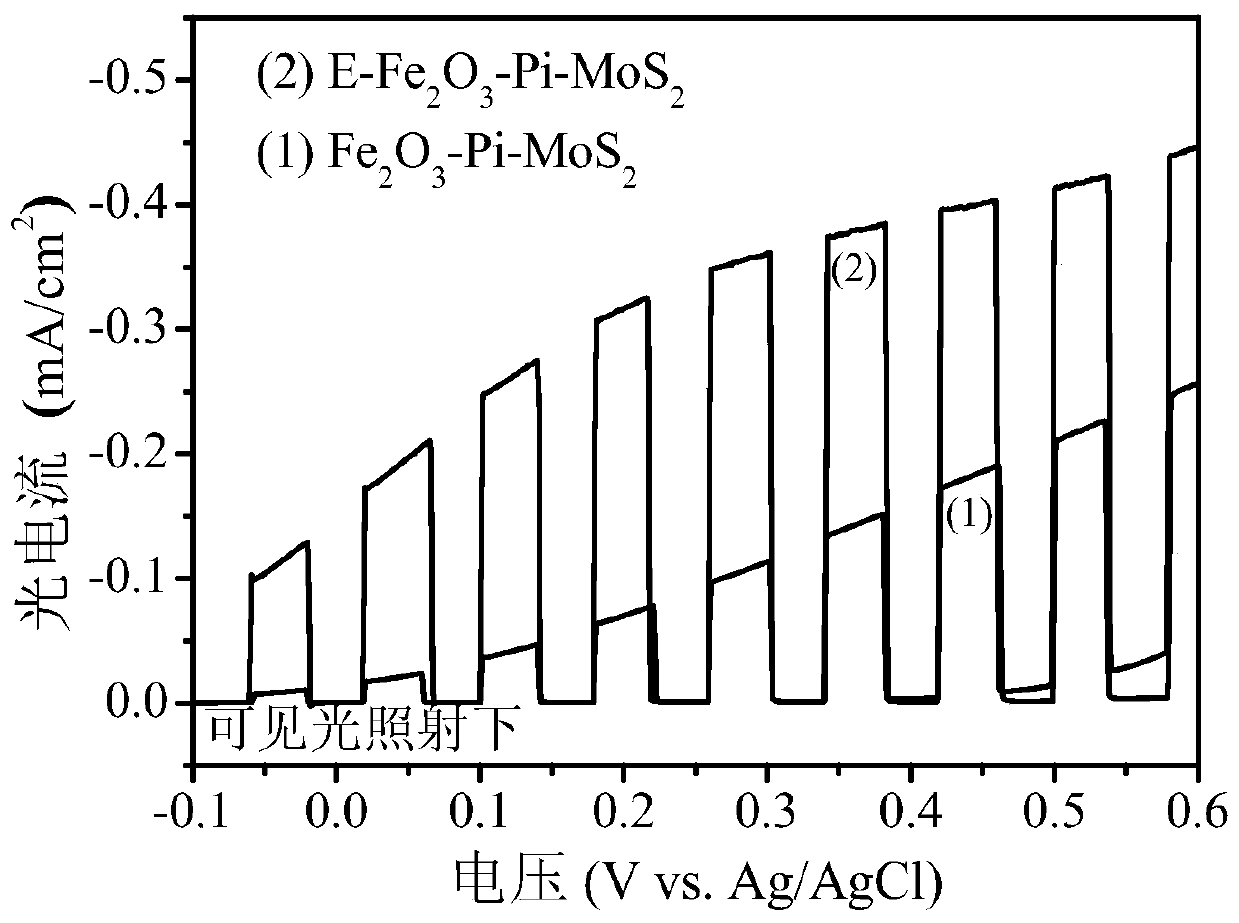
A photocatalytic film for electrochemically treating phosphorus-molybdenum sulfide co-doped iron oxide and its preparation method and application
A photocatalytic thin film, electrochemical technology, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, catalyst activation/preparation, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of poor stability of photocatalytic thin film and limited promotion effect, and achieve low cost, catalytic The effect of excellent performance and simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] E-Fe of this embodiment 2 o 3 -Pi-MoS 2Photocatalytic thin films were prepared by the following methods:
[0064] (1) with Fe 2+ The precursor solution was used as the electrolyte, and the electrochemical workstation was used for electrodeposition with a three-electrode system, that is, the conductive glass (FTO) substrate after cleaning and drying was used as the working electrode, the graphite electrode was used as the counter electrode, and the Ag / AgCl electrode was used. As a reference electrode, it is impregnated in a phosphate buffer solution after electrodeposition, dried in a vacuum oven, and then calcined at a constant temperature to obtain Fe 2 o 3 - Pi film;
[0065] Fe in this example 2+ The preparation method of the precursor solution is as follows: Weigh a certain amount of FeCl 2 4H 2 O dissolved in a certain volume of ethylene glycol and distilled water, Fe 2+ In the precursor solution, Fe 2+ The concentration is 0.02M, and the volume ratio of ...
Embodiment 2
[0094] The wastewater to be treated in this embodiment is wastewater containing phenol, wherein the initial concentration of phenol is 10 mg / L.
[0095] The E-Fe that the present embodiment makes based on embodiment 1 2 o 3 -Pi-MoS 2 The treatment method of the phenol-containing wastewater of the photocatalytic film, the treatment process is as follows:
[0096] (S1) adjusting the pH value of the phenol-containing wastewater to be treated to 7.2;
[0097] by dropwise addition of 1M H 2 SO 4 solution or 1M NaOH solution to adjust the pH value of phenol-containing wastewater.
[0098] (S2) Performing photoelectrocatalytic treatment of the phenol-containing wastewater after adjusting the pH value. The photopositive electrode used in photocatalytic treatment includes a conductive substrate and E-Fe coated on the surface of the conductive substrate. 2 o 3 -Pi-MoS 2 Photocatalytic thin film (the effective area of the film is 2cm×2cm), and the cathode is a titanium sheet w...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Same as Example 2, the difference is that the processing conditions are different. In this embodiment, it is carried out under pure electric and pure light conditions to study the E-Fe 2 o 3 -Pi-MoS 2 Phenol degradation of visible photocatalytic thin films under different light conditions.
[0106] Figure 10 It is the comparison of the removal rate of phenol in the phenol-containing wastewater to be treated under pure electric conditions (EC), pure light conditions (PC) and photoelectric synergistic conditions (PEC), wherein the corresponding curves under the photoelectric synergistic conditions (PEC) conditions are the same as those in the examples 2 the same.
[0107] Such as Figure 10 As shown, after reacting for 5h, E-Fe 2 o 3 -Pi-MoS 2 The effect of thin-film photocatalytic degradation of phenol is significantly better than that of pure photocatalysis (12.81%) or electrocatalysis (26.32%), and the removal rate of phenol by photocatalysis is 93.73%, and th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com