Molecular marker KB1 for identifying clubroot resistance of brassica rapa pekinensis, primer and application
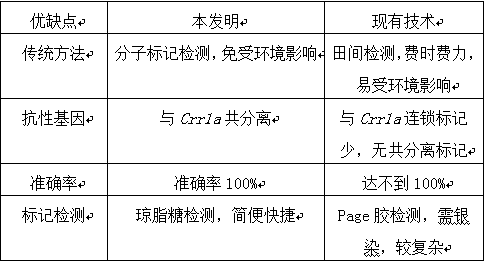
An anti-clubroot, molecular marker technology, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc. The results are easy to confuse and other problems, so as to achieve the effect of simple and fast detection, accurate distinction and good specificity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Chinese cabbage contains clubroot disease resistance gene Crr1a Obtaining of F2 segregating populations
[0032] The Chinese cabbage clubroot disease-resistant material G6 was used as the female parent, and the susceptible material G4 was used as the male parent to obtain the F1 generation. The F1 generation was tested for disease resistance in the field and all of them were disease-resistant materials. The segregation population of F2 generation obtained by selfing of F1 generation was used for phenotype identification and molecular marker detection of Chinese cabbage clubroot.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Phenotypic Identification and Molecular Marker Detection of Clubroot Resistance in F2 Generation Segregation Population of Chinese Cabbage
[0035] 1. Identification of clubroot resistance phenotypes in isolates
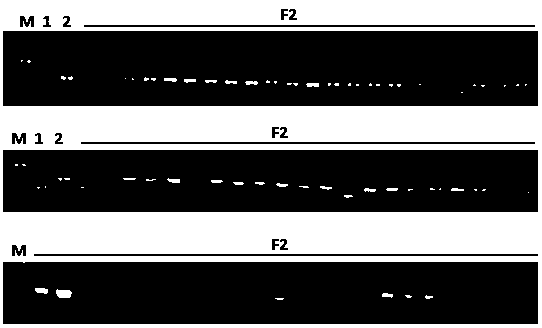
[0036] Taking the F2 population obtained in Example 1 as material, inoculate Physiological race No. 4 of Plasmodium phylloxera after sowing, the inoculation and investigation methods refer to the literature "Wang Weihong et al., Identification of Physiological Races of Cruciferous Vegetable Physiological Races and Resistance Source Screening, Chinese Vegetables, 2013 Vol. 1(12): 55-60". The results showed that among the 66 F2 generation Chinese cabbage plants, 46 were resistant and 20 were susceptible ( figure 1 )
[0037] Molecular Marker Detection of Clubroot Resistance in F2 Population of Chinese Cabbage
[0038]2. Use the CTAB method to extract the genomic DNA of the leaves of the clubroot-resistant material G6, the susceptible material G4, and the F2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com