Y branch waveguide structure based on polymer asymmetric ridge waveguide
A technology of waveguide structure and ridge waveguide, which is applied in light guides, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of poor stability of inorganic materials, increasing the angle and length of branch waveguides, large light energy radiation loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] In order to facilitate a further understanding of the structure and method of the present invention, the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with an example of an M-Z electro-optic modulator.
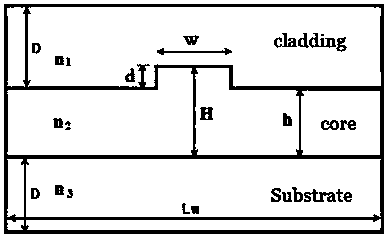
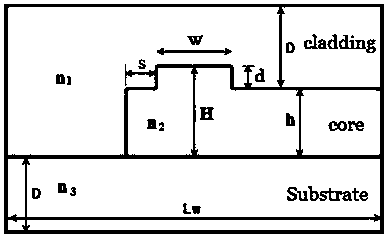
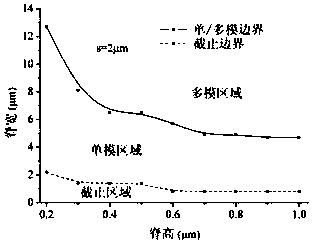
[0025] In this example, the waveguide core layer (core) material containing the ridge waveguide adopts IPC-E / polysulfone (n 2 =1.670), the upper cladding (cladding) material is NOA61 (n 1 =1.55), the lower cladding (substrate) material is UV15 (n 3 = 1.50). In order to ensure single-mode transmission, the parameters of the waveguide are: core layer thickness h = 1.5 μm, waveguide ridge height d = 0.6 μm, waveguide ridge width w = 4 μm, short core width s = 2 μm; upper cladding and lower The thickness of the cladding is D=6μm, and the width is L w = 40 μm. Symmetrically structured waveguide cross-sections such as figure 1 , the waveguide cross-section of the asymmetric structure is as figure 2 , the single-mode conditional curve such as imag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com