Method for guiding crack in edge portion of donor substrate by using inclined laser beam
A donor and substrate technology, applied in laser welding equipment, semiconductor devices, fine working devices, etc., can solve the problem of edge effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
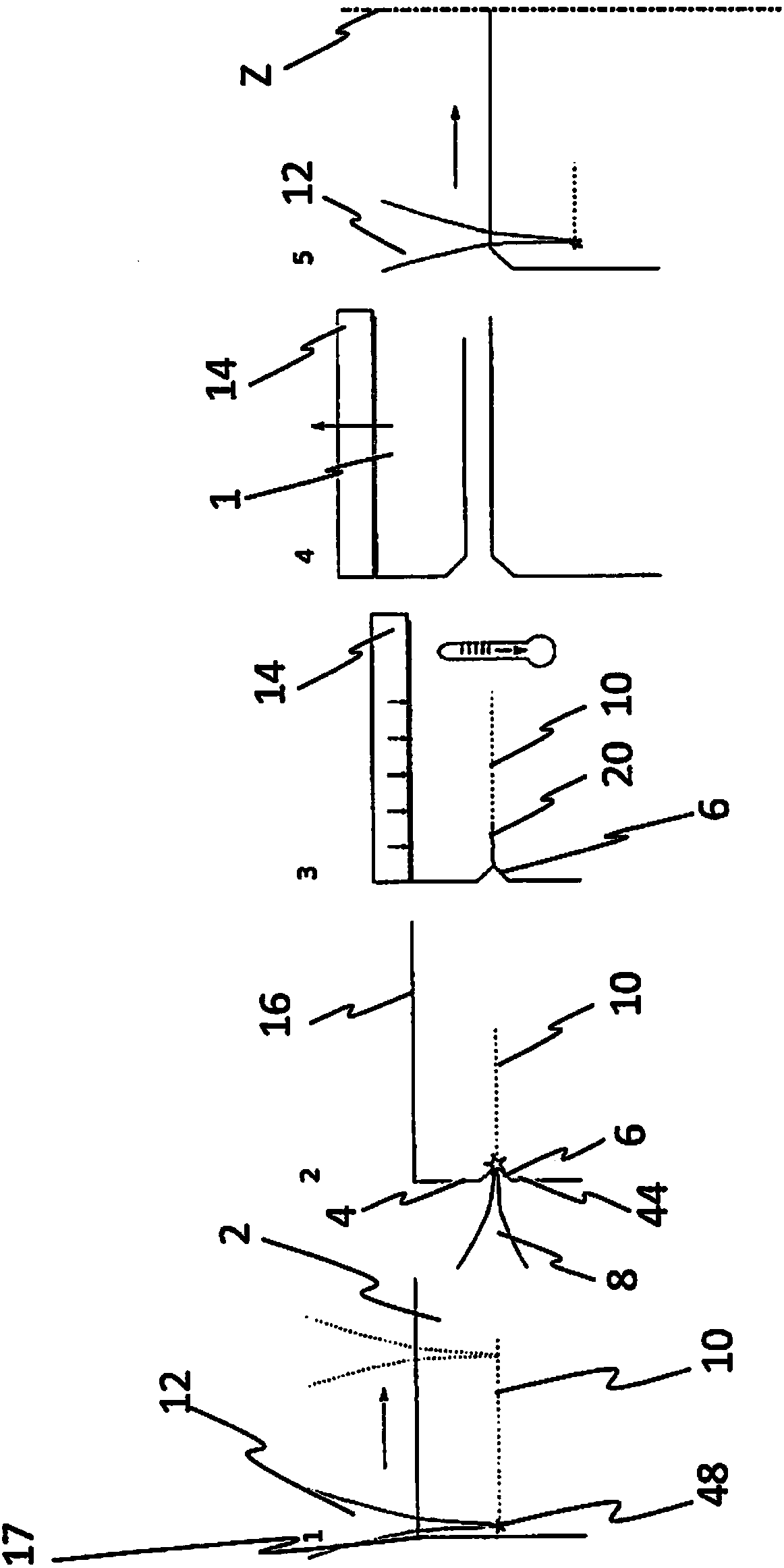
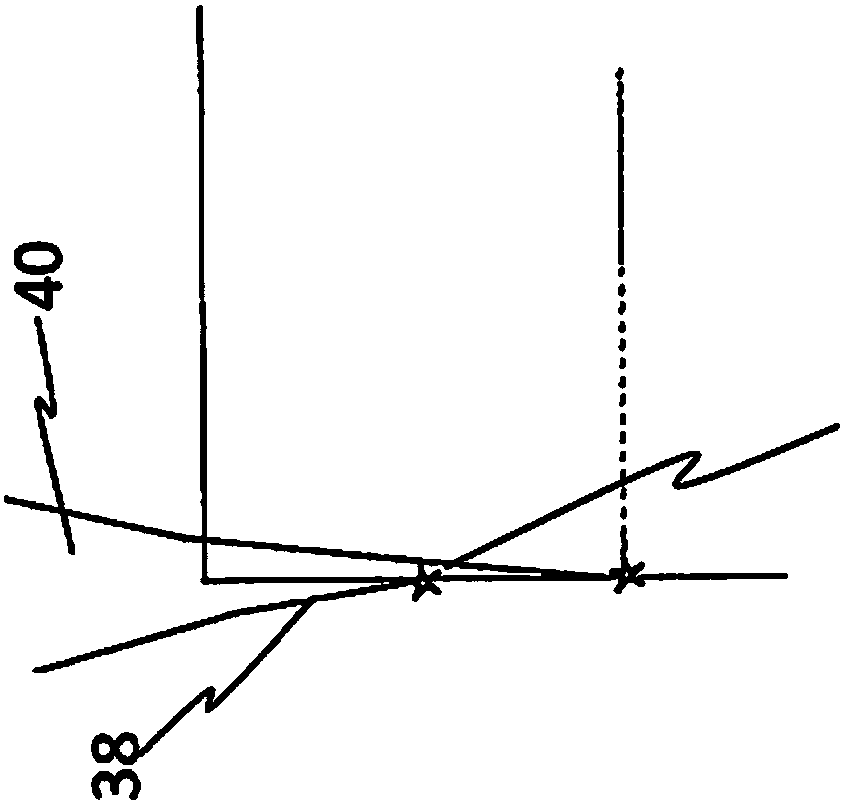
[0048] figure 1 4 views are shown. exist figure 1 In a first view of , a donor substrate 2 is shown, which is loaded with a laser beam 12 . The laser beam 12 is generally inclined relative to the surface 16 via which the laser beam enters the donor substrate 2 such that the inclination is at an angle different from 90°. Preferably, a first portion 36 of the laser beam 12 is aligned at a first angle 38 relative to the surface 16 and a further portion 40 of the laser beam 12 is aligned at a second angle 42 relative to the surface 16 . The laser beam sections 36 and 40 are preferably always inclined at the same angle relative to the surface 16, via which the laser beam sections 36, 40 enter the donor, for the overall generation of the modification 12 for separating a specific solid layer 1. Substrate 2. In addition to being able to Figure 4 It can be seen from the first view of FIG. 2 that the focal point 48 can be directed as far as the edge 44 or directly to the edge 44 i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com