Method for synchronously preparing high-F ratio oligopeptide and starch sugar from corn gluten meal as raw material
A corn gluten meal, starch sugar technology, applied in food science, fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems of oligopeptide molecular weight and F value evaluation, high product loss rate and production cost, inability to clarify the characteristics of oligopeptide products, etc., and achieve protein content. High efficiency, low equipment investment, high biological activity and intestinal absorption and utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] 1) Take 10kg of corn gluten powder, add 80L of deionized water to the corn gluten powder, stir in a 90°C reactor for 1.5h, and cool to room temperature to obtain the mixed solution A;
[0036] 2) Add saturated aqueous calcium hydroxide solution to the mixed solution A, adjust the pH of the mixed solution to 5.0, add 100 g of α-amylase to the mixed solution A, stir and react at a constant temperature in a 55°C reactor for 6.0 hours, and then mix Add 100g of α-1,4-glucose hydrolase to solution A, stir and react in a 40°C reactor for 6.0h at a constant temperature. Precipitation A;
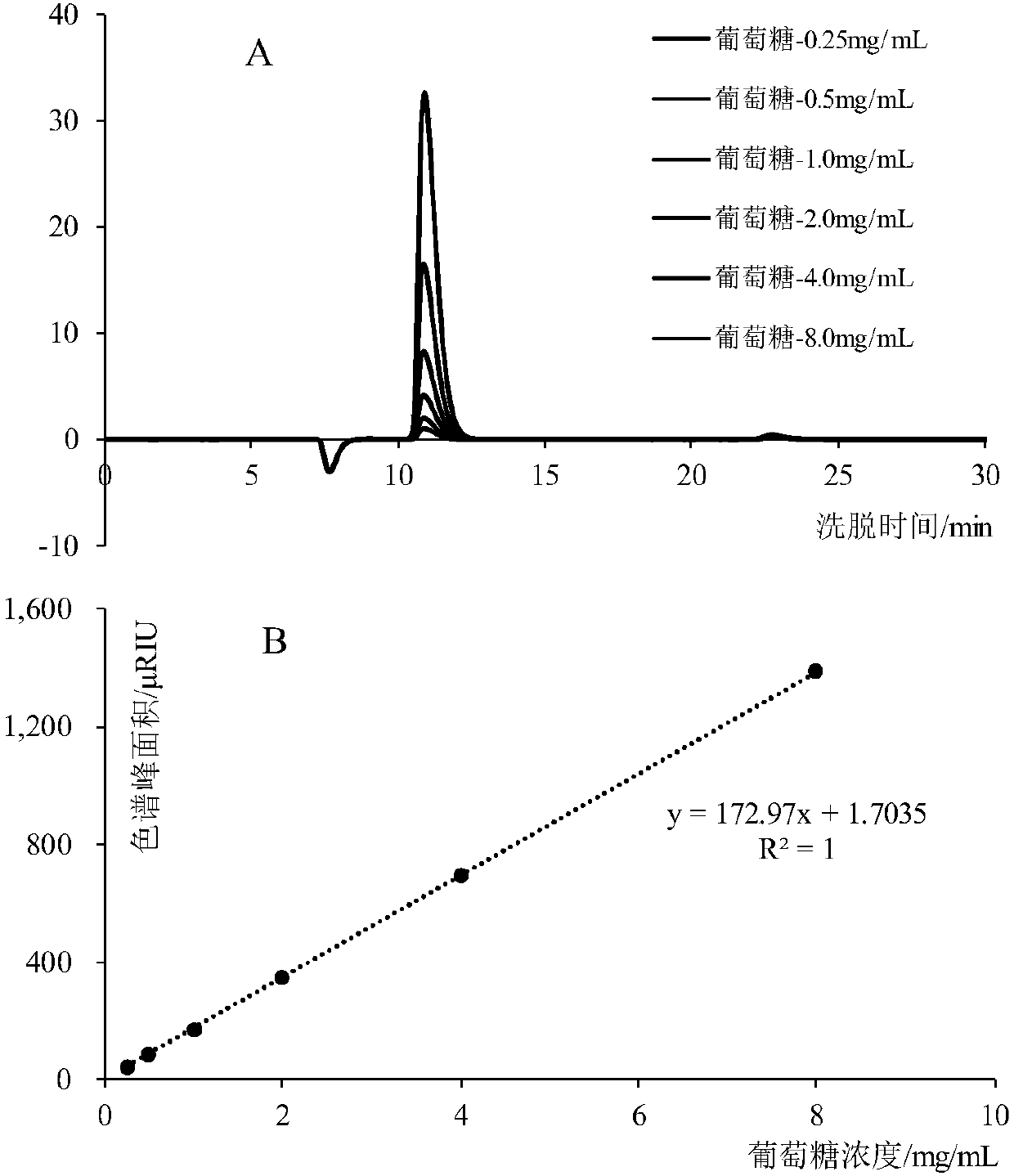
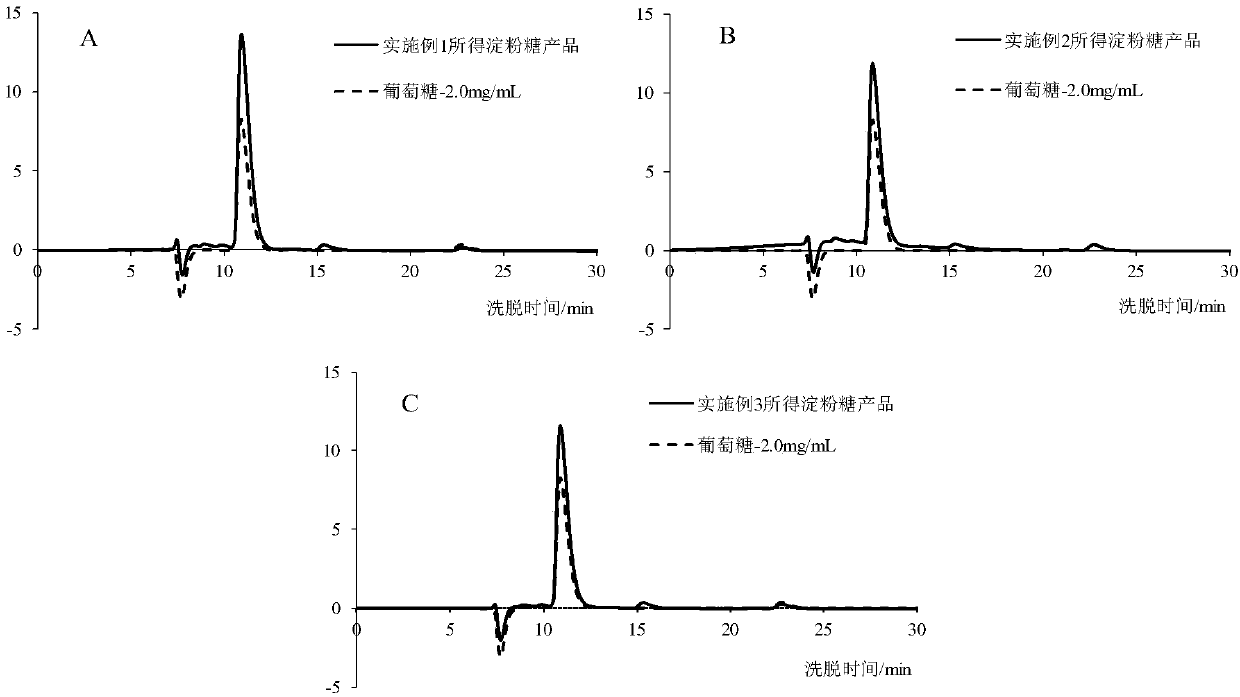
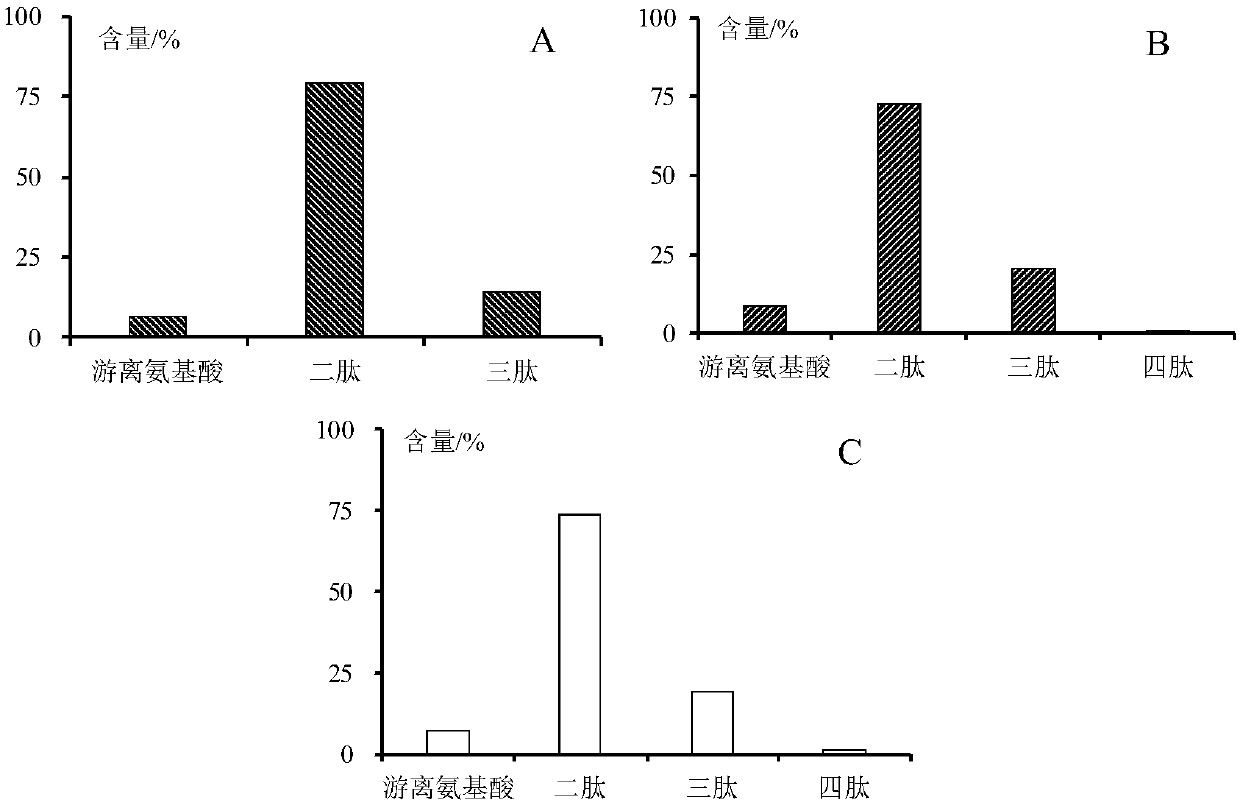
[0037] 3) Supernatant A is identified by the above-mentioned high-performance liquid chromatography, and its main component is starch sugar (see figure 1 and 2 A); after the supernatant A is vacuum freeze-dried, packaged and sterilized, the starch sugar product is obtained;
[0038] 4) Add 80 L of deionized water to the precipitate A, add saturated aqueous calcium hydroxide solution to the ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] 1) Take 10 kg of corn gluten powder, add 50 L of deionized water to the corn gluten powder, stir in an 80°C reactor for 2.0 hours, and cool to room temperature to obtain the mixed solution A;
[0064] 2) Add saturated calcium hydroxide aqueous solution to the mixed solution A, adjust the pH of the mixed solution to 6.0, add 50 g of α-amylase to the mixed solution A, stir and react at a constant temperature in a 65 ° C reactor for 3.0 h, and then mix Add 50g of α-1,4-glucose hydrolase to solution A, stir and react in a 45°C reactor for 0.5h at a constant temperature. Precipitation A;
[0065] 3) Supernatant A is identified by the above-mentioned high-performance liquid chromatography, and its main component is starch sugar (see figure 1 and 2 B); after the supernatant A is spray-dried (the temperature of the air inlet is 180° C., and the temperature of the outlet air is 90° C.), packed and sterilized, the starch sugar product is obtained;
[0066] 4) Add 50 L of deion...
Embodiment 3
[0072] 1) Take 10kg of corn gluten powder, add 150L of deionized water to the corn gluten powder, stir in a 95°C reactor for 0.5h, and cool to room temperature to obtain the mixed solution A;
[0073] 2) Add saturated calcium hydroxide aqueous solution to the mixed solution A, adjust the pH of the mixed solution to 5.5, add 200 g of α-amylase to the mixed solution A, stir and react at a constant temperature in a 75°C reactor for 0.5h, and then mix Add 200g of α-1,4-glucose hydrolase to solution A, stir and react in a 60°C reactor for 3.0h at a constant temperature. Precipitation A;
[0074] 3) Supernatant A is identified by the above-mentioned high-performance liquid chromatography, and its main component is starch sugar (see figure 1 and 2 C); after the supernatant A is spray-dried (inlet air temperature is 195° C., and air outlet temperature is 80° C.), packed and sterilized, the starch sugar product is obtained;
[0075] 4) Add 150 L of deionized water to the precipitate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com