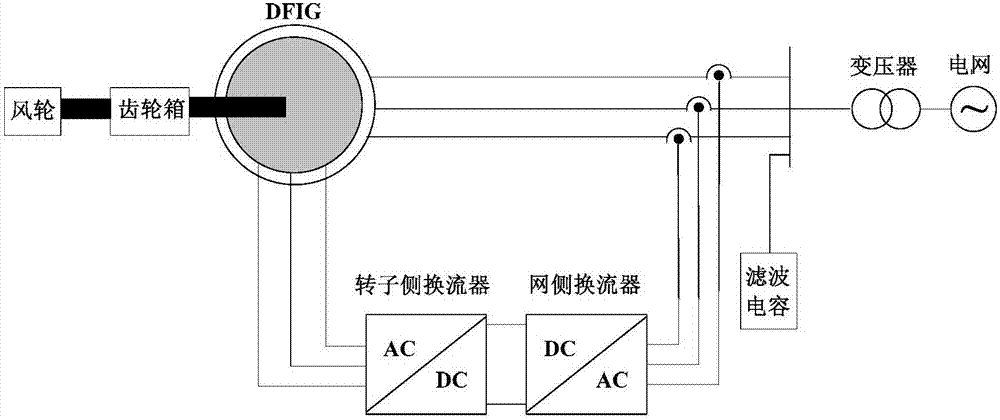
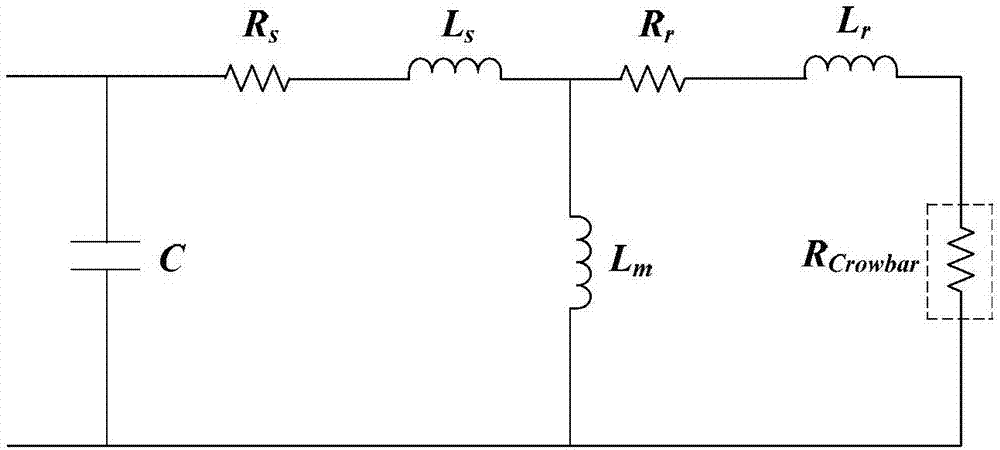
Distributed power supply high frequency impedance equivalence modeling method
A distributed power supply and high-frequency impedance technology, applied in the field of value modeling, can solve the problems of difficult accurate calculation of fault current, difficulty of distributed power supply impedance model, and inability to accurately determine power supply impedance, so as to achieve more certainty and universal adaptive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some of the embodiments of the present invention, not all of them. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
[0045] After a fault occurs in the power system, the voltage and current transients contain information in the full frequency domain. Among them, the energy density in the frequency band within a few thousand Hz is high, and the signal-to-noise ratio is strong, which can be effectively distinguished from noise. When only the high-frequency component network is considered after the fault, the high-frequency equivalent network of the system is observe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com