Material for packaging comprising antimicrobial composition
An anti-microbial and anti-microbial agent technology, applied in the field of packaging materials, can solve the problems of affecting efficacy, inefficient coating of anti-microbial agents on the packaging surface, reducing the fluidity of anti-microbial agents, etc., and achieve the effect of maintaining fluidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
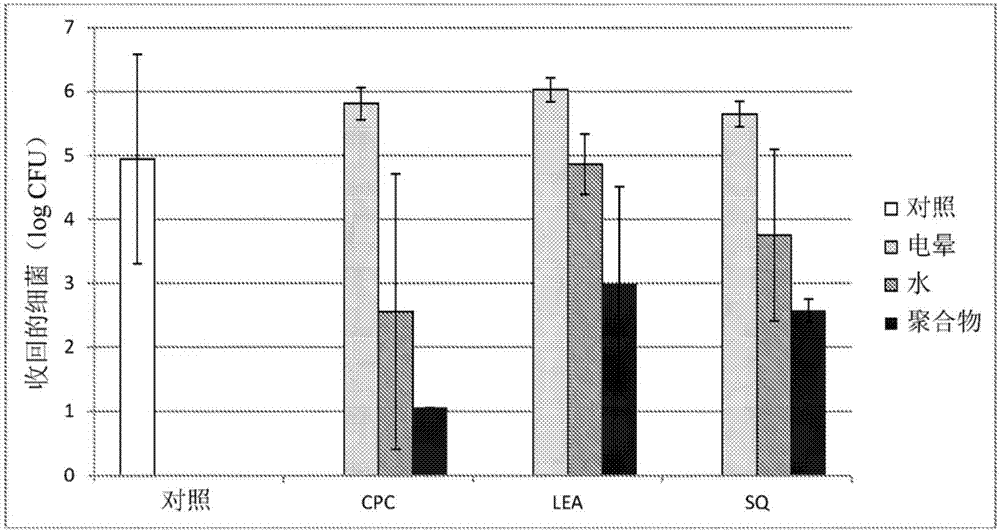
[0070] Chicken skin samples were inoculated with Escherichia coli 11303 and covered with a piece of polyethylene film (DOWLEX TM 2045G) processing:
[0071] ● Control: Polyethylene film without active antimicrobial agent ("control");
[0072] ● Corona: Corona treated and treated with 2% active antimicrobial agent (cetylpyridinium chloride ("CPC"), N α - Lauroyl-L-arginine ethyl ester ("LEA"), or dimethyloctadecyl[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]ammonium chloride (a quaternary silane compound) ( "SQ"), as described below) soak overnight polyethylene film (DOWLEX TM 2045G)("corona CPC", "corona LEA", "corona SQ");
[0073] ● water: 1 ml of aqueous solution (as shown below) with 2% active antimicrobial agent was sprinkled on the surface of the chicken, and polyethylene film (DOWLEX TM 2045 G) placed on the treatment (“CPC Water”, “LEA Water” and “SQ Water”); and
[0074] ● Polymer (antimicrobial composition): A 1 ml solution (prepared as described above) containing 2% by w...
example 2
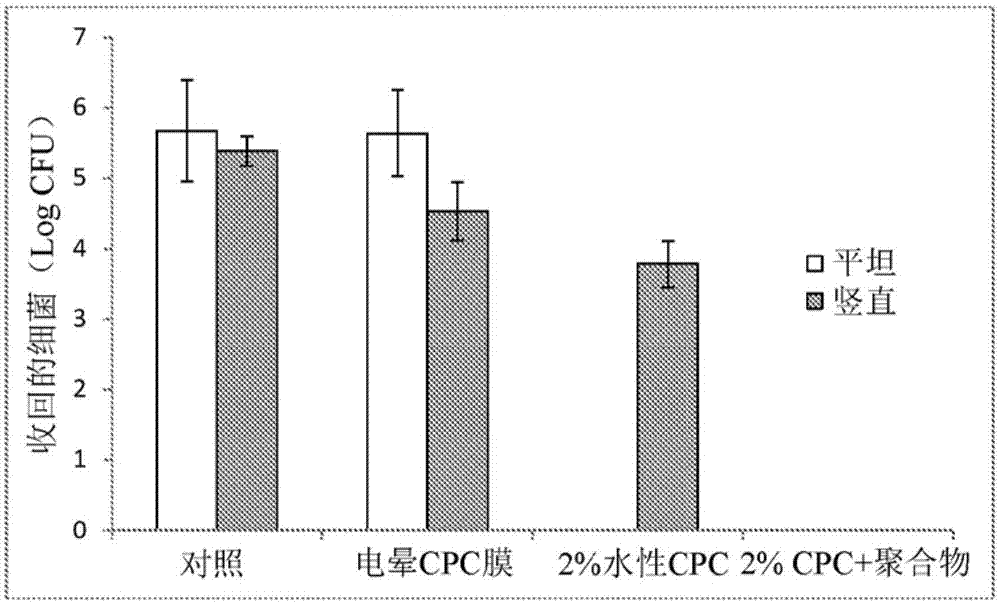
[0080] The method described in Example 1 was further used to assess the effect of instillation on antimicrobial activity. Chicken skin samples inoculated with E. coli were treated using the three treatment techniques described in Example 1 (corona (in figure 2 called "corona film"), water (in figure 2 referred to as "CPC-water") and polymers (antimicrobial compositions) (in figure 2 , referred to as "CPC-polymer" and prepared as described in Example 1) was treated with CPC. One set of chicken skin samples was kept flat during overnight storage, and the other set was stored vertically (upright) during overnight storage to induce instillation. image 3 Shows the observed reduction in bacterial levels. The samples treated with the corona-treated film ("corona film") showed little reduction in bacteria, while the polymer (antimicrobial composition) treatment technology ("CPC-polymer") samples showed little reduction in both sample groups All showed a significant reduction i...
example 3
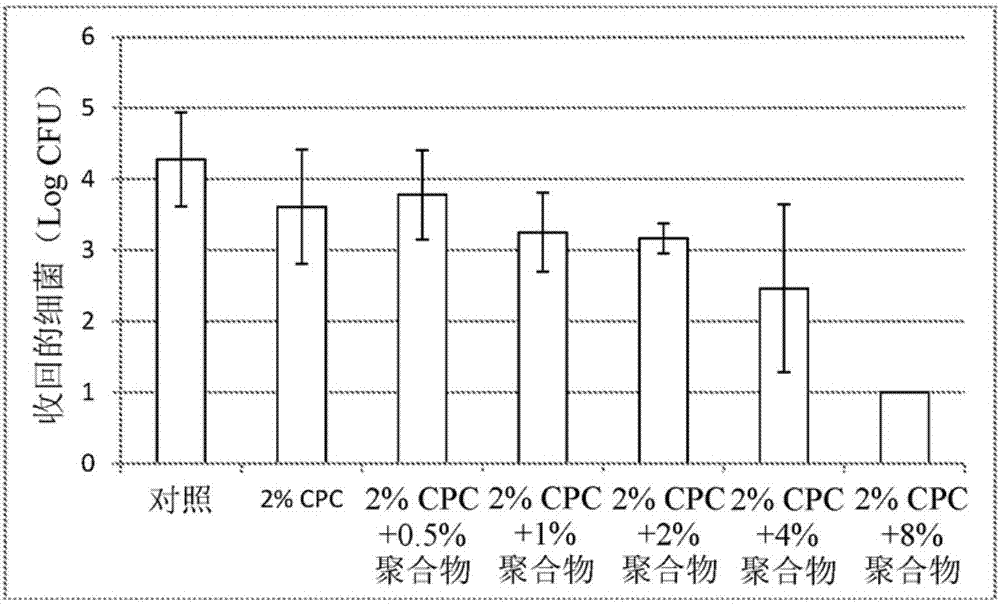
[0082] This example evaluates the effect of viscosity of an antimicrobial composition on antimicrobial efficacy. Each treatment technique was evaluated as described in the "Efficacy Testing" section above. A control sample contained no rheology modifier and no active antimicrobial ("control"). Includes CPC and a range of rheology modifier levels (a methylcellulose, available in METHOCEL TM An antimicrobial composition of E50 (commercially available from The Dow Chemical Company) was compared with an aqueous solution of CPC. image 3 Each result is displayed. An aqueous solution of CPC ("2% aqueous CPC") did not result in a significant reduction in bacteria. Similarly, with 0.5% rheology modifier ("2% CPC; 0.5% polymer"), 1% rheology modifier ("2% CPC; 1% polymer") and 2% rheology modifier ("2% CPC; 2% polymer") solutions (viscosity about 74 cP) also did not show significant reduction in bacteria. A solution at 4% rheology modifier ("2% CPC; 4% polymer") (viscosity about 7...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com