Method for removing tar from biomass thermal conversion gas-phase product
A biomass and conversion gas technology, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, removal of gas pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as hazards, electrostatic precipitator explosion, and separation effects that are difficult to achieve by conventional methods. The effect of strong applicability and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
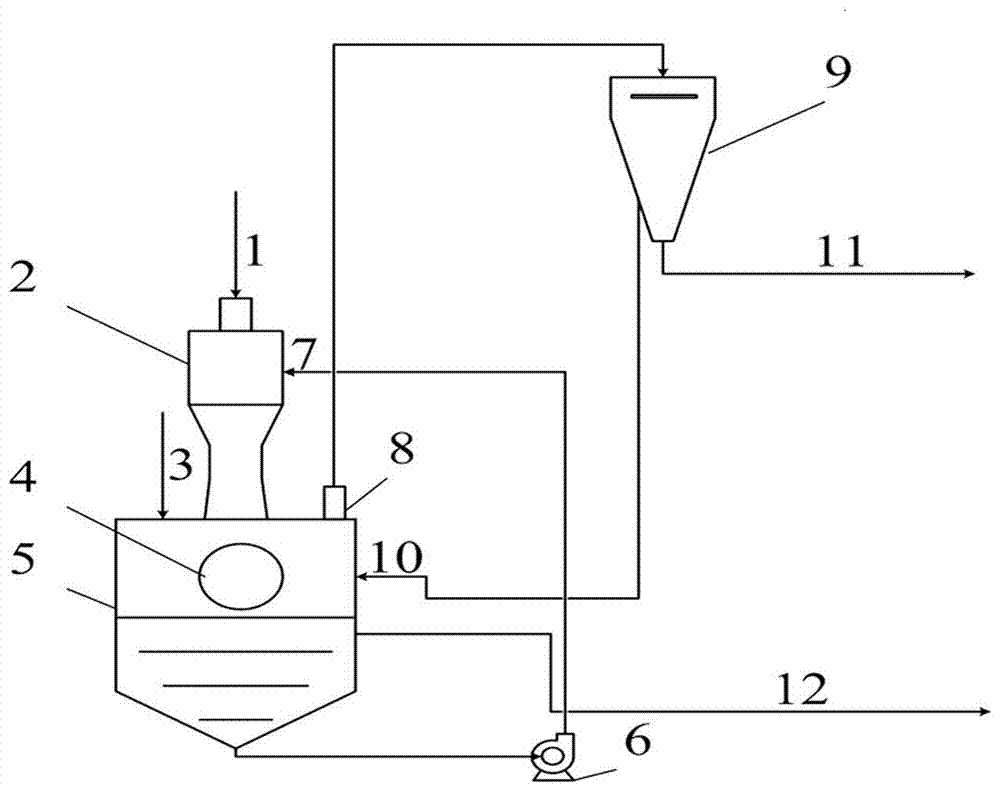
[0024] In a fluidized bed pyrolysis reactor with an annual processing capacity of 1,000 tons of biomass raw materials, the biomass quickly completes the pyrolysis process to form high-temperature gas-phase products and carbon powder. The high-temperature gas-phase products generated include liquid phases that can be condensed at room temperature Products and non-condensable non-condensable gas, high-temperature gas and carbon powder leave the reactor together with the fluidized gas entering the reactor. After gas-solid separation at high temperature to remove most of the carbon powder inside, after multi-stage condensation and cooling Separate the liquid phase product to obtain a non-condensable gas with a lower temperature and remove most of the tar. In this implementation, the gas phase product is cooled by low-temperature water, and the temperature can reach 20 ° C. A part of it is returned to the front of the reactor as fluidizing gas for preheating Part of the system is us...
Embodiment 2
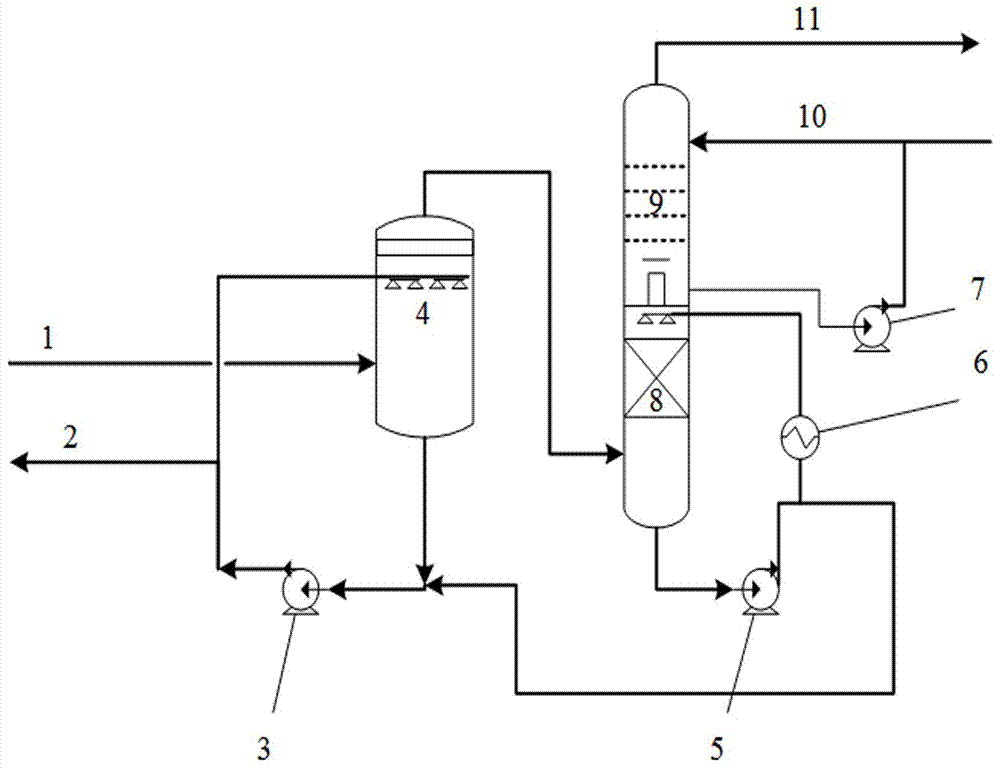
[0028] In the rotary kiln pyrolysis reactor with a processing capacity of 1000 kg of biomass raw material per hour, the biomass completes the pyrolysis process under negative pressure (absolute pressure 30kPa), and the high-temperature gas phase products and carbon powder flow out of the reactor. After gas-solid separation at high temperature to remove most of the carbon powder inside, the liquid phase product is separated after multi-stage condensation and cooling to obtain a non-condensable gas with a lower temperature and most of the tar removed. In this implementation, the gas phase product After cooling with low-temperature water, the temperature can reach 20°C, and white smoke can still be observed in the gas phase product.
[0029] Introduce the method described in the present invention, as attached figure 2 As shown, the pyrolysis gas mixed with a small amount of tar from the condensation section is sprayed from the gas inlet 1 through the atomization pump 3 and the V...
Embodiment 3
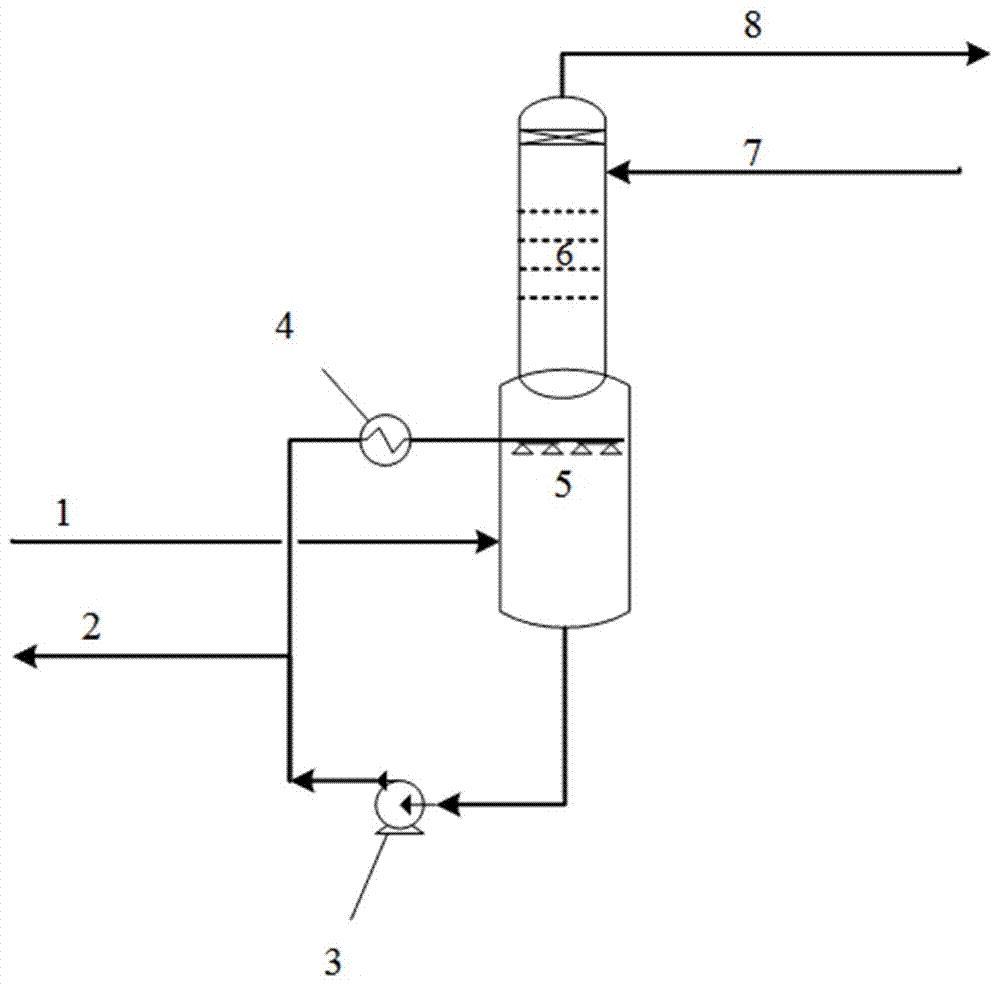
[0032] In a fixed-bed carbonization reactor with a processing capacity of 1 kg of biomass raw material per hour, the biomass completes the thermal cracking process under a slight positive pressure (absolute pressure 2kPa), and forms a high-temperature gas phase product that flows out of the reactor and undergoes multi-stage condensation and cooling. Finally, the liquid phase product is separated to obtain a non-condensable gas with a lower temperature and most of the tar removed. In this implementation, the gas phase product is cooled with low-temperature water, and the temperature can reach 10 ° C. It can still be observed that there is yellowish white in the gas phase product. of soot.
[0033] Introduce the method described in the present invention, as attached image 3 As shown, the pyrolysis gas mixed with a small amount of tar from the condensation section is sprayed from the gas inlet 1 through the atomization pump 3 and the Venturi atomization nozzle 5. After atomizati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com