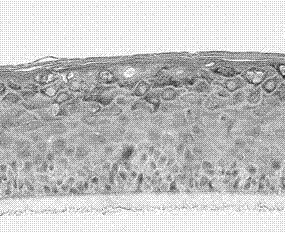
Gingival epithelium model and in-vitro building method thereof
A construction method and gingival technology, applied in the field of tissue engineering biomaterials, can solve the problems of long construction time, poor model stratification, and reduced model application, and achieve the effects of reducing production cost, shortening construction time, and improving barrier function.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: This embodiment emphatically introduces the in vitro construction method steps of a kind of gingival epithelial model:
[0027] Step 1. Primary culture and expansion of human gingival epithelial cells:
[0028] Normal human gingival tissue was washed with 0.01M PBS containing 100IU / mL penicillin and 100μg / mL streptomycin under the condition of pH=7.4. Trim the tissue block, remove the subcutaneous connective tissue, and cut the tissue block into about 10mm 3 Wash with 0.01M PBS containing 100IU / mL penicillin and 100μg / mL streptomycin at pH=7.4, and digest with Dispase solution at 4°C for 16h. The epithelial layer and subcutaneous connective tissue layer were separated, and the separated epithelial layer was transferred to a centrifuge tube pre-prepared with 1.5 mL of 0.25% trypsin, incubated at 37°C for 5 min, and digested to obtain a single-cell suspension. Add keratinocyte serum-free medium to resuspend the cells, transfer them to culture flasks, chang...
Embodiment 2
[0040] This embodiment focuses on the in vitro construction method steps of a gingival epithelial model:
[0041] Step 1. Primary culture and expansion of human gingival epithelial cells:
[0042] Normal human gingival tissue was washed with PBS 0.01M containing 100IU / mL penicillin and 100μg / mL streptomycin at pH=7.4. Trim the tissue block, remove the subcutaneous connective tissue, and cut the tissue block into about 10mm 3 Wash with PBS 0.01M containing 100IU / mL penicillin and 100μg / mL streptomycin at pH=7.4, and digest with Dispase solution at 4°C for 16h. The epithelial layer and subcutaneous connective tissue layer were separated, and the separated epithelial layer was transferred to a centrifuge tube pre-prepared with 1.5 mL of 0.25% trypsin, incubated at 37°C for 5 min, and digested to obtain a single-cell suspension. Add keratinocyte serum-free medium to resuspend the cells, transfer them to culture flasks, change the medium after 12 hours, and change the medium ever...
Embodiment 3
[0054] This embodiment focuses on the in vitro construction method steps of a gingival epithelial model:
[0055] Step 1. Primary culture and expansion of human gingival epithelial cells:
[0056] Normal human gingival tissue was washed with PBS 0.01M containing 100IU / mL penicillin and 100μg / mL streptomycin at pH=7.4. Trim the tissue block, remove the subcutaneous connective tissue, and cut the tissue block into about 10mm 3 Wash with PBS 0.01M containing 100IU / mL penicillin and 100μg / mL streptomycin at pH=7.4, and digest with Dispase solution at 4°C for 16h. The epithelial layer and subcutaneous connective tissue layer were separated, and the separated epithelial layer was transferred to a centrifuge tube pre-prepared with 1.5 mL of 0.25% trypsin, incubated at 37°C for 5 min, and digested to obtain a single-cell suspension. Add keratinocyte serum-free medium to resuspend the cells, transfer them to culture flasks, change the medium after 12 hours, and change the medium ever...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com