Establishment method of solitary pulmonary nodule malignancy probability prediction model
A technique of probabilistic forecasting and establishment of methods, applied in the medical field, can solve problems such as no objective and quantifiable indicators, and achieve the effect of simple and easy-to-use models and high reference value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1 A method for establishing a predictive model for the malignant probability of solitary pulmonary nodules
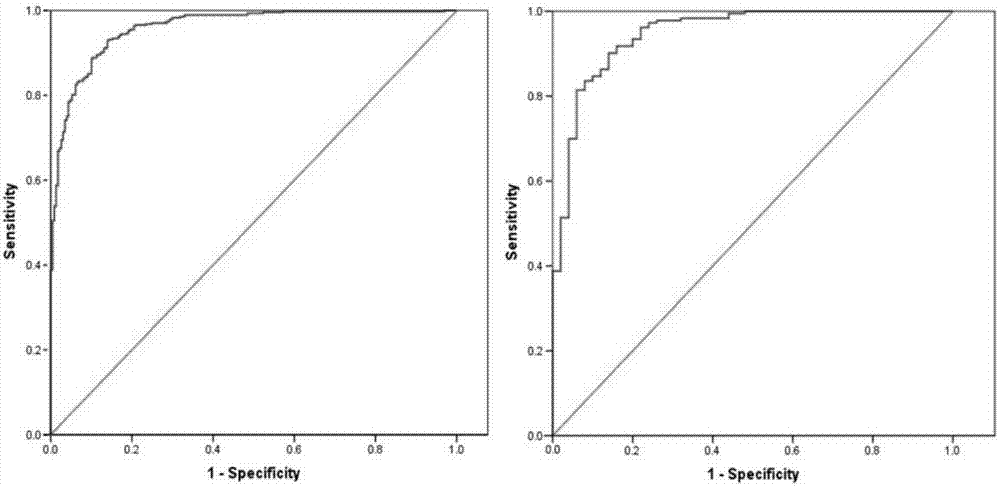
[0021] The applicant used 1234 cases of solitary pulmonary nodules, all of which had a definite pathological diagnosis. The general status of the patients was collected, including age, gender, smoking status (whether smoking, smoking amount, smoking cessation time, etc.), family cancer history, and past cancer history. Serum tumor marker levels were collected 1-7 days before surgery, including serum carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and serum bone collagen (Cyfra21-1) levels. Thoracic surgeons, respiratory physicians, and radiologists jointly reviewed and evaluated CT imaging features, including nodule location, CT maximum diameter (pulmonary window), proportion of ground-glass opacity (GGO), spiculation, Lobulation, calcification, cavity, well-defined borders, and pleural traction.
[0022] Considering that the difference in the proportion of nodules w...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Case 1: Male, 55 years old, physical examination found a nodule in the left lower lobe, the GGO component was less than 50%, the largest CT diameter was 1.8cm, no glitches, calcifications, pleural traction, no previous tumor history, and the serum tumor marker Cyfra21-1 value was 3.34 ng / mL, CEA value 2.82ng / mL.
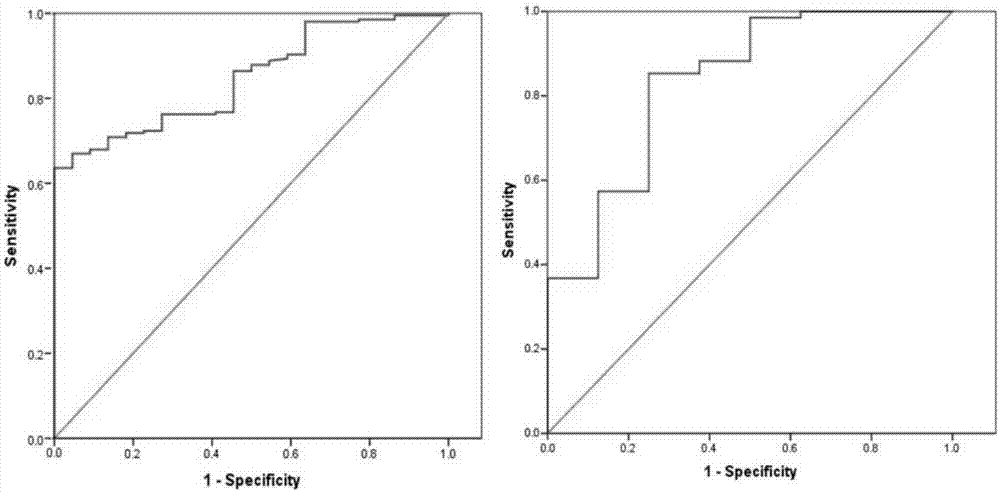
[0030] Bring into the predictive model: P=e X / (1+e X), where X=-10.6+(0.064×age)+(1.358×largest diameter)+(1.698×burr)-(2.492×calcification)+(1.446×pleural traction)+(2.101×tumor history)+(0.639 ×Cyfra21-1)+(0.633×CEA). Calculated P=0.328, less than the cutoff value of 0.521.
[0031] After multiple consultations, the patient was finally operated on. The patient underwent pathological examination after the operation and was diagnosed as granulomatous inflammation. The possibility of old tuberculosis was considered, which was a benign nodule.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Case 2, male, 79 years old, physical examination found a right lower lobe nodule, GGO component greater than 50%, unclear border, serum tumor marker CEA value 5.33ng / mL.
[0034] Bring into the predictive model: P=e X / (1+e X ), where X=-1.180+(0.057*age)-(2.30*clear border)+(1.032*CEA). The calculated P=0.998 was greater than the cutoff value of 0.867.
[0035] On this basis, continued CT-guided puncture pathological diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma, malignant nodules, received follow-up surgical treatment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com