Preparation method and application of α-fe2o3 porous nanorod array photoanode material
A nanorod array, photoanode technology, applied in metal material coating process, electrode, liquid chemical plating and other directions, to achieve the effect of convenient operation, shortened transmission distance and excellent performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
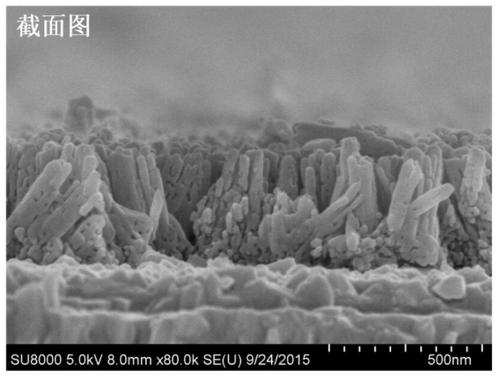
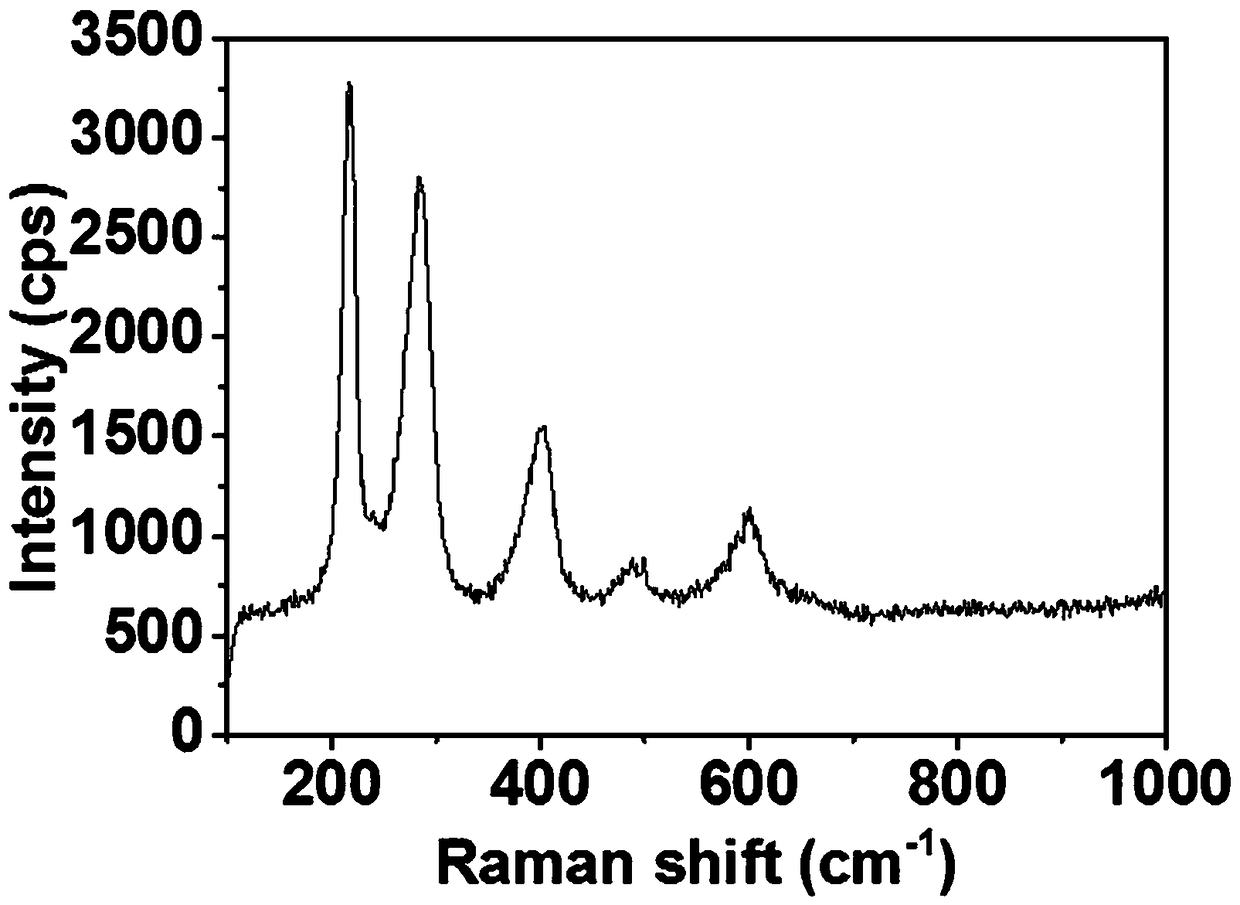
[0030] an α-Fe 2 o 3 Porous nanorod array photoanode material is synthesized and prepared by in-situ liquid-solidification method in two steps. The specific steps are: (1) Immerse the FTO conductive glass into FeCl containing 0.1mol / L 3 and 0.1mol / L dicyandiamide / formaldehyde polycondensate aqueous solution, then use dilute hydrochloric acid to adjust pH=1.5, react at 95°C for 6h, cool, wash, and dry to prepare β-FeOOH nanorod arrays; (2) The β-FeOOH nanorod array prepared in step (1) was placed on the N 2 Under the atmosphere, heat treatment at 550°C for 2h, continue heat treatment at 800°C for 0.1h, and cool naturally to obtain α-Fe 2 o 3 The porous nanorod array photoanode material can be seen from the actual production situation that the prepared material is uniformly covered on the FTO conductive glass substrate and is bright red. The obtained material is used as photoanode material for hydrogen production by photoelectric hydrolysis.
[0031] Figure 1a and Figure...
Embodiment 2
[0038] an α-Fe 2 o 3 Porous nanorod array photoanode material is synthesized and prepared by in-situ liquid-solidification method in two steps. The specific steps are: (1) Immerse FTO conductive glass into FeCl containing 0.05mol / L 3 in the aqueous solution, and then use dilute hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH=1.5, react at 95°C for 9h, cool, wash with water, and dry to obtain the β-FeOOH nanorod array; (2) the β-FeOOH nanorod array prepared in step (1) in N 2 Under the atmosphere, heat treatment at 550°C for 2h, continue heat treatment at 800°C for 0.1h, and cool naturally to obtain α-Fe 2 o 3 The nanorod array material is used as a photoanode material for hydrogen production by photoelectric hydrolysis.
[0039] The test results show that: the prepared α-Fe 2 o 3 It is a smooth nanorod array with a forbidden band width of 2.09eV, a photoelectric hydrolysis reaction onset potential of 0.90 V vs. RHE, and a photocurrent density of 0.65 mA / cm at 1.23 V vs. RHE 2 , the ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] an α-Fe 2 o 3 Porous nanorod array photoanode material is synthesized and prepared by in-situ liquid-solidification method in two steps. The specific steps are: (1) Immerse FTO conductive glass into FeCl containing 0.15mol / L 3 and 0.05mol / L dicyandiamide / formaldehyde polycondensate aqueous solution, then use dilute hydrochloric acid to adjust pH=1.5, react at 95°C for 12h, cool, wash, and dry to prepare β-FeOOH nanorod arrays; (2) The β-FeOOH nanorod array prepared in step (1) was placed on the N 2 Under the atmosphere, heat treatment at 550°C for 2h, continue heat treatment at 800°C for 0.1h, and cool naturally to obtain α-Fe 2 o 3 The nanorod array material is used as a photoanode material for hydrogen production by photoelectric hydrolysis.
[0042] The test results show that: the prepared α-Fe 2 o 3 It is a porous nanorod array with a forbidden band width of 2.03eV, its photoelectric hydrolysis reaction onset potential is 0.80 V vs. RHE, and the photocurrent d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com