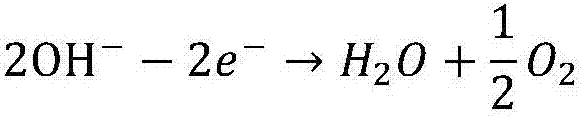Isoelectric protein purification device and method
A purification device and protein technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, peptide preparation methods, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome steps and difficult control, and achieve simple control process, simple composition and structure, and large protein loading Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
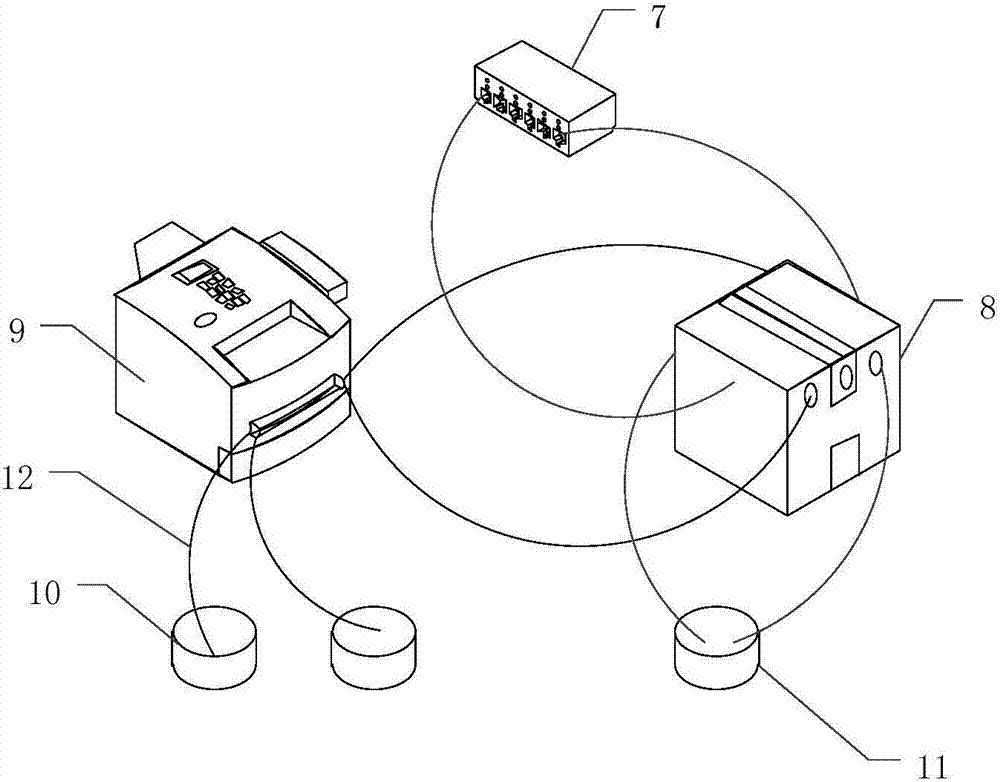
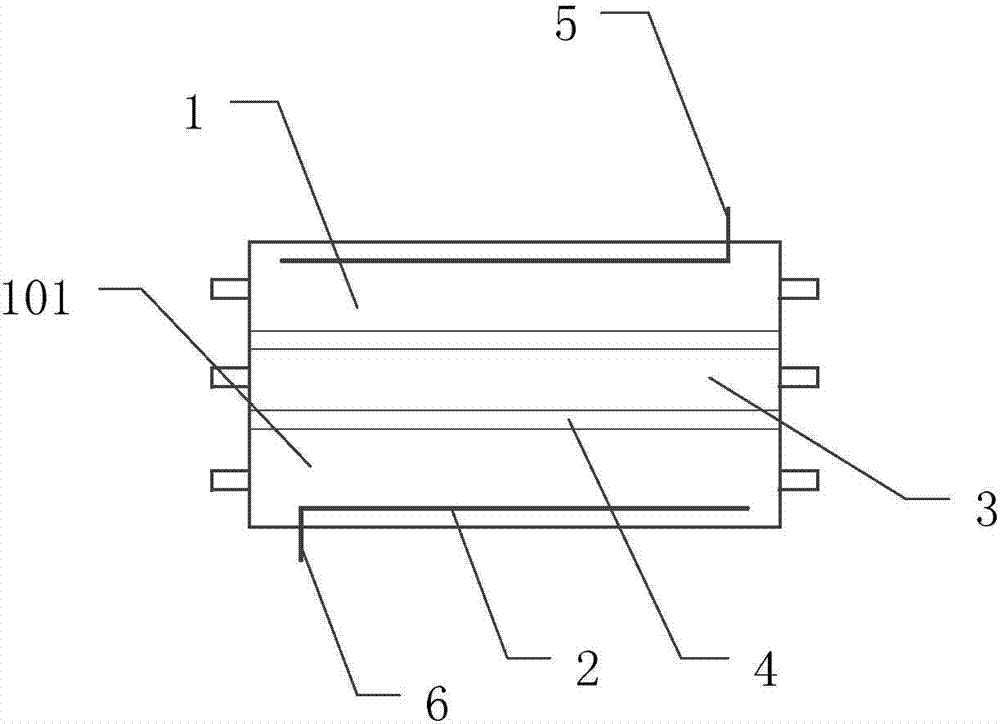
[0057] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, this embodiment discloses a protein isoelectric purification device, which includes an electrophoresis tank 8, a power supply 7, a liquid storage tank 10 and a waste liquid tank 11; the electrophoresis tank 8 is a square straight tank made by splicing organic glass plates, The joints of the plexiglass plates are bonded and sealed with transparent silicone rubber.
[0058] Preferably, the power supply 7 is a 15V voltage regulating switching power supply.
[0059] Preferably, the thickness of the plexiglass plate is 3mm, and the overall size of the electrophoresis tank 8 is 120mm×22mm×30mm.
[0060] The inner surface of the electrophoresis tank 8 is longitudinally provided with two rows of chutes, and the chute is provided with a porous filter membrane 4 made of porous material; the porous filter membrane 4 divides the electrophoresis tank 8 into a sample pool 3, a positive pole electrode pool 101 and a negative pole Electrode cel...
Embodiment 2
[0082] This example discloses a protein isoelectric purification method, and the device used in this example is the same as that in Example 1.
[0083] When using this set of equipment to purify proteins, the specific methods are as follows:
[0084] Step 1: Dissolve bovine hemoglobin in Na 2 HPO 4 / NaH 2 PO 4 (50mM, pH6.8) buffer solution to prepare a 5mg / mL solution, and add it to the sample cell 3;
[0085] Step 2: Add Na to the positive electrode pool 101 and the negative electrode pool 1 respectively 2 HPO 4 / NaH 2 PO 4 (50mM, pH6.8) buffer;
[0086] Step 3: Turn on the power supply 7 for 10 minutes of electrophoresis purification;
[0087] In this embodiment, the isoelectric point of bovine hemoglobin is about 6.8, and bovine hemoglobin is almost uncharged at this pH. There was no obvious accumulation of bovine hemoglobin in the positive and negative electrode cells 1 at each time point.
Embodiment 3
[0089] This example discloses a protein isoelectric purification method, and the device used in this example is the same as that in Example 1.
[0090] When using this set of equipment to purify proteins, the specific methods are as follows:
[0091] Step 1: Dissolve bovine hemoglobin in TrisHCl (50mM, pH8.5) buffer solution to prepare a 5mg / mL solution, and add it to the sample pool 3;
[0092] Step 2: adding TrisHCl (50mM, pH8.5) buffer solution to the positive electrode pool 101 and the negative electrode pool 1 respectively;
[0093] Step 3: Turn on the power supply 7 for 10 minutes of electrophoresis purification;
[0094] In this embodiment, the isoelectric point of bovine hemoglobin is about 6.8, and bovine hemoglobin is negatively charged in TrisHCl buffer solution with pH 8.5, and it migrates toward the positive electrode in electrophoresis.
[0095] The result of the electrophoretic purification of the positive electrode pool 101 under the environment of pH 5.0 is:...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com