Shock absorber with bidirectional pressure limiting piston
A shock absorber and piston technology is applied in the field of shock absorbers with two-way pressure limiting pistons, which can solve the problem that the damping of shock absorbers cannot be further adjusted, and achieve the effect of improving the buffering effect and improving the applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
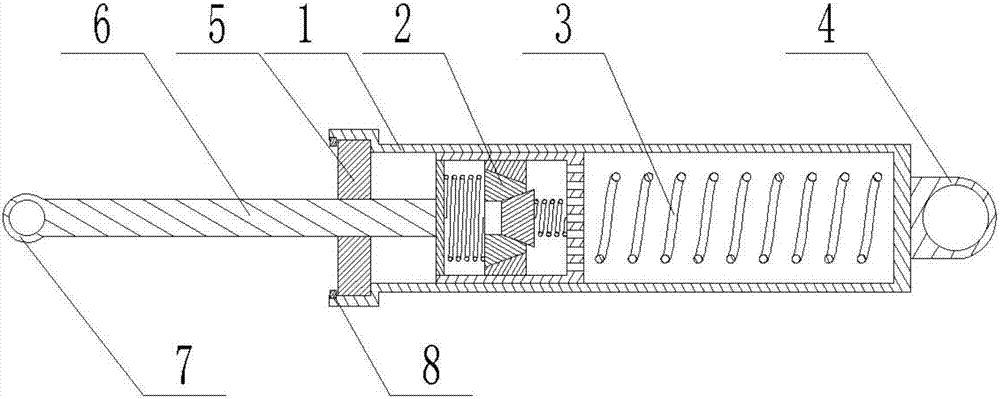
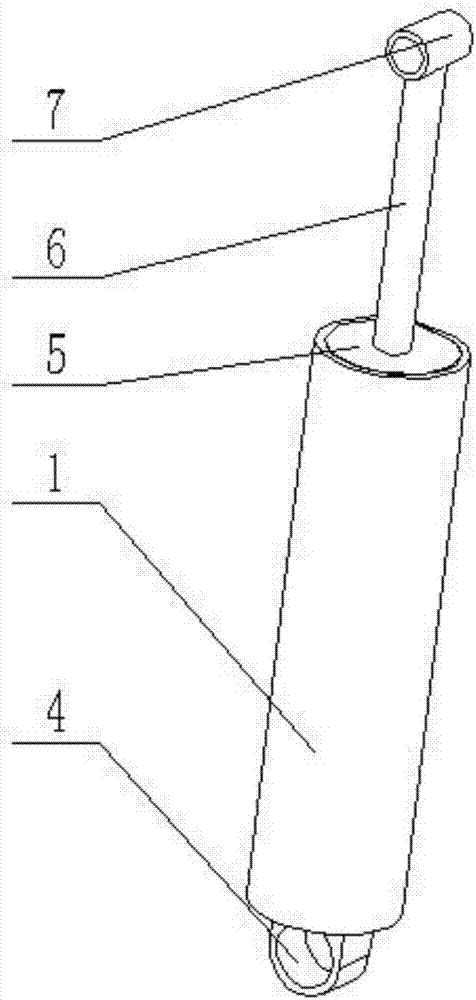
[0030] Combine below Figure 1-9 Describe this embodiment, a shock absorber with a two-way pressure-limiting piston, including a shock-absorbing oil cylinder 1, a two-way pressure-limiting piston 2, a shock-absorbing spring 3, a base suspension ring 4, an oil seal 5, a piston connecting rod 6, and a connecting rod suspension ring 7 and circlip 8, the two-way pressure limiting piston 2 is plugged inside the shock absorbing cylinder 1, a shock absorbing spring 3 is fixedly connected between the shock absorbing cylinder 1 and the two-way pressure limiting piston 2, and the right end of the shock absorbing cylinder 1 is welded to the base The lifting ring 4, the left end of the shock absorbing cylinder 1 is provided with a stepped hole, the oil seal 5 is clamped in the stepped hole, the left end of the stepped hole is provided with a circlip 8, the interior of the shock absorbing cylinder 1 is filled with oil, and the oil seal 5 is used to seal the oil, To prevent oil leakage, the...
specific Embodiment approach 2
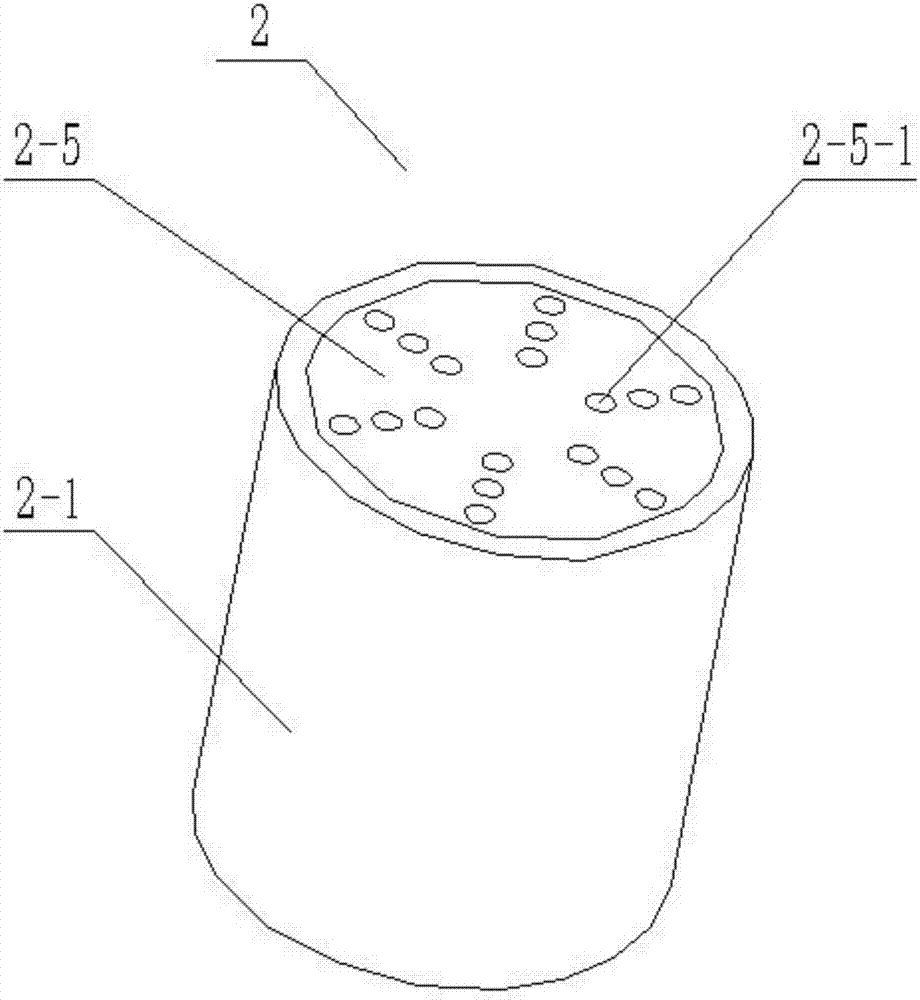
[0031] Combine below Figure 1-9Describe this embodiment, this embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1, the two-way pressure limiting piston 2 includes an outer piston cylinder 2-1, a valve core seat 2-2, a valve core I2-3, a valve core II2-4, a piston The end cover 2-5, the pressure limiting spring I2-6 and the pressure limiting spring II2-7, the outer piston cylinder 2-1 is a cylindrical structure with an open left end and a hollow interior, and the left end of the outer piston cylinder 2-1 is provided with multiple A drain hole I2-1-1, the inner wall of the outer piston cylinder 2-1 is provided with threads, the valve core seat 2-2 is a cylindrical structure, and the valve core seat 2-2 is provided with a valve core hole I2-2 -1, the spool seat 2-2 is coaxial with the spool hole Ⅰ2-2-1, the spool hole Ⅰ2-2-1 is a conical structure with a diameter at the left end larger than that at the right end, and the outer wall of the spool seat 2-2 is provided with thread, the sp...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0032] Combine below Figure 1-9 This embodiment will be described, and this embodiment will further describe the second embodiment, the thread provided on the inner wall of the outer piston cylinder 2-1, the thread provided on the outer wall of the valve core seat 2-2, and the outer wall of the piston end cover 2-5. The threads are all sealed threads, and the position of the valve core seat 2-2 in the outer piston cylinder 2-1 can be adjusted by rotating the valve core seat 2-2, so as to adjust the right end surface of the flow-limiting top column II 2-9 and the outer piston cylinder 2 -1 The distance between the inner right end wall; adjust the distance between the left end face of the flow-limiting top column Ⅰ2-8 and the right end face of the piston end cap 2-5 by rotating the piston end cap 2-5; the sealing thread is used to prevent oil Fluid leaks from threaded connections.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com