Method for identifying polyamide 6 or polyamide 66 in blended textiles
An identification method, polyamide technology, applied in the field of analysis and detection, can solve the problems of poor reproducibility of test results, low sensitivity, small sampling volume, etc., and achieve the effect of being beneficial to the experimental environment and human health, with less dosage and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] 1. Sample reagent
[0053] Polyamide 6 standard (chip), polyamide 66 standard (fiber), anhydrous formic acid (analytical grade).
[0054] 2. Analysis and determination
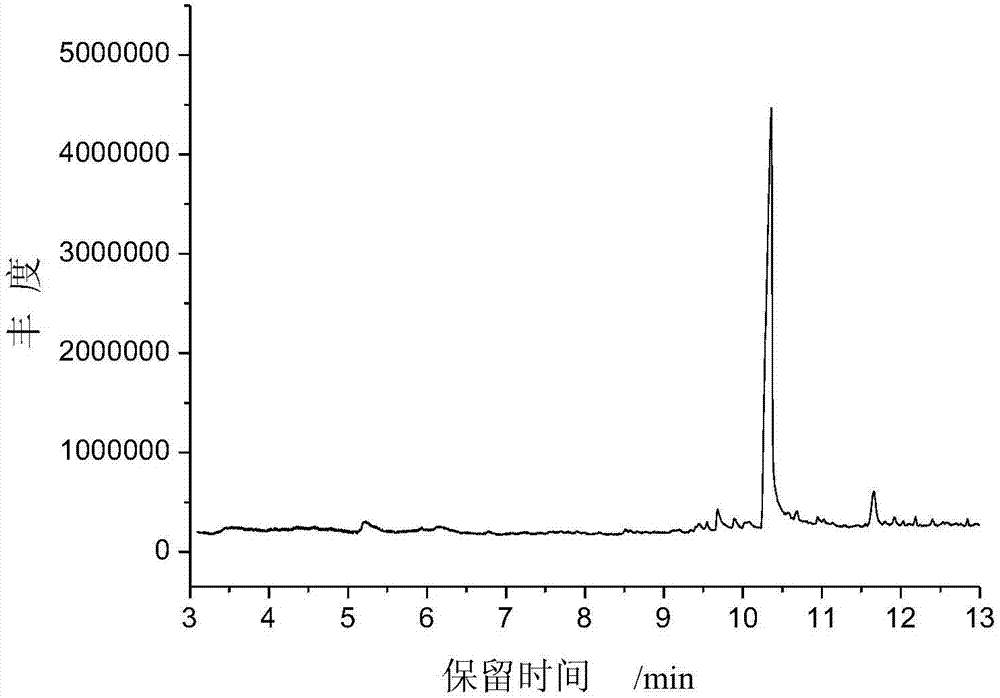
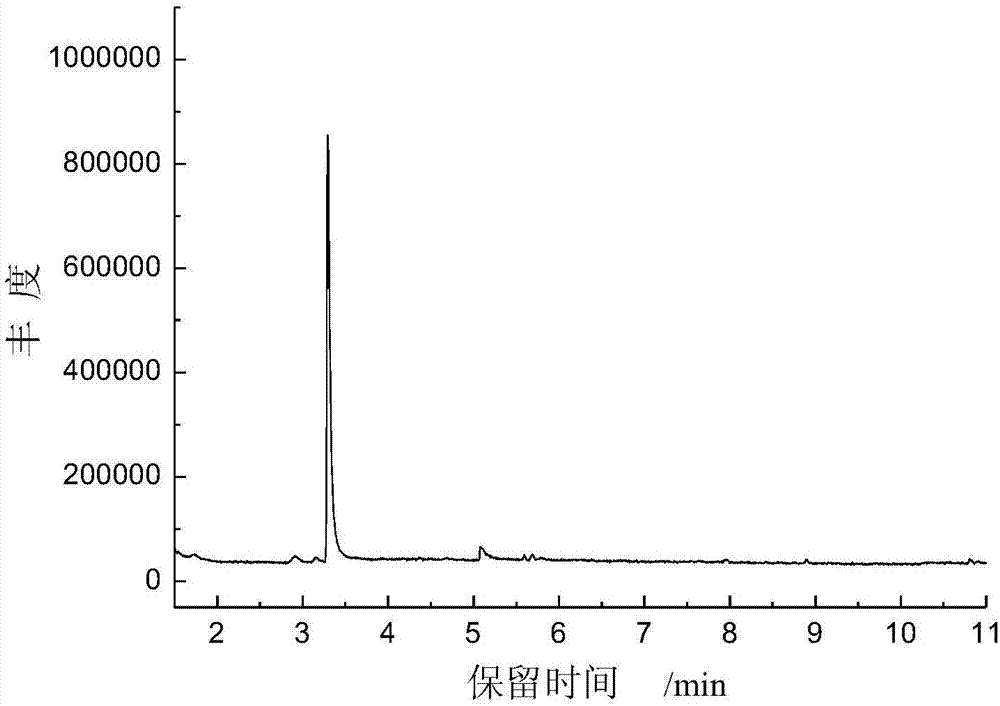
[0055] Weigh 10 mg polyamide 6 standard product or polyamide 66 standard product, dissolve them in 10 mL of anhydrous formic acid, soak for 20 min, take 2 μL into the sample cup, heat at 150 ° C to remove formic acid, and perform pyrolysis chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis to obtain polyamide The standard pyrolysis chromatogram of 6, see attached figure 1 ; The standard pyrolysis chromatogram of polyamide 66, see appendix figure 2 .
[0056] figure 1 The chromatographic peak with a retention time of 10.33 min is the characteristic cracked substance of the polyamide 6 fiber component, that is, caprolactam, and the relative peak area content is about 89%.
[0057] figure 2 The chromatographic peak with a retention time of 3.28 min is the characteristic cracked substance of the polyamide 66...
Embodiment 2
[0059] 1. Sample reagent
[0060] Polyamide 6 fiber and wool fiber blended sample (mass ratio 21.7:78.3), anhydrous formic acid (analytical pure).
[0061] 2. Analysis and determination
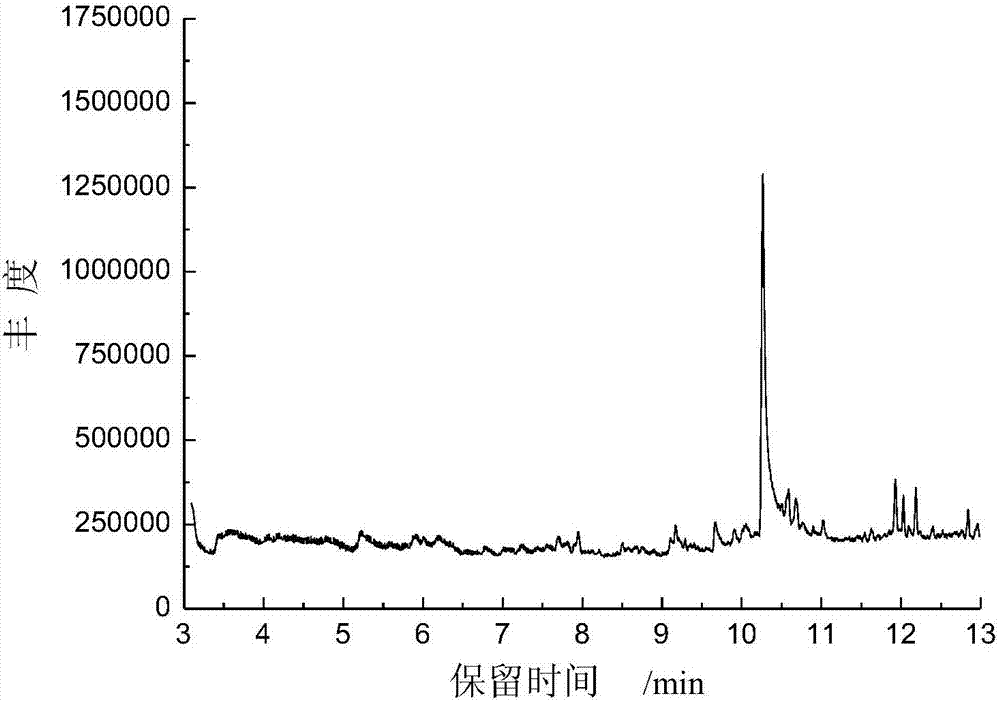
[0062] Weigh 11.53 mg of polyamide 6 fiber and wool fiber blended sample, extract with 10 mL of anhydrous formic acid, soak for 20 minutes, take 2 μL into the sample cup, heat at 155 ° C to remove formic acid, and perform pyrolysis chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. see attached image 3 . The characteristic cracking peak at the retention time of 10.33min is caprolactam, and the relative peak area content is about 76%.
[0063] As a comparison, weigh 0.09 mg polyamide 6 fiber and wool fiber blended sample and add it to the sample cup for pyrolysis chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. The pyrolysis chromatogram obtained is shown in the attached Figure 4 . The characteristic cracking peak at retention time 10.33min is caprolactam, and the relative peak area content is about ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] 1. Sample reagent
[0066] Polyamide 66 fiber and cotton fiber blended sample (mass ratio 39.3:60.7), anhydrous formic acid (analytical grade), first grade pure water.
[0067] 2. Analysis and determination
[0068] Weigh 9.50 mg of polyamide 66 fiber and cotton fiber blended sample, extract with 10 mL of 80% formic acid solution, soak for 30 minutes, take 2 μL into the sample cup, heat at 160 ° C to remove formic acid, and perform pyrolysis chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. See attached chromatogram Figure 5 . The characteristic cracking peak at the retention time of 3.33min is cyclopentanone, and the relative peak area content is about 93%.
[0069] As a comparison, weigh 0.11 mg of polyamide 66 fiber and cotton fiber blended sample and add it to the sample cup for pyrolysis chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. The pyrolysis chromatogram obtained is shown in the attached Figure 6 . The characteristic cracking peak at the retention time of 3.30 mi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com