Nanocellulose utilizing non-lignocellulosic biomass, and cosmetic composition and superabsorbent material containing same
A nanocellulose, biomass technology, applied in cosmetics, cosmetic preparations, cosmetic preparations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1. Utilize corn stover to prepare nanocellulose (nanocellulose)
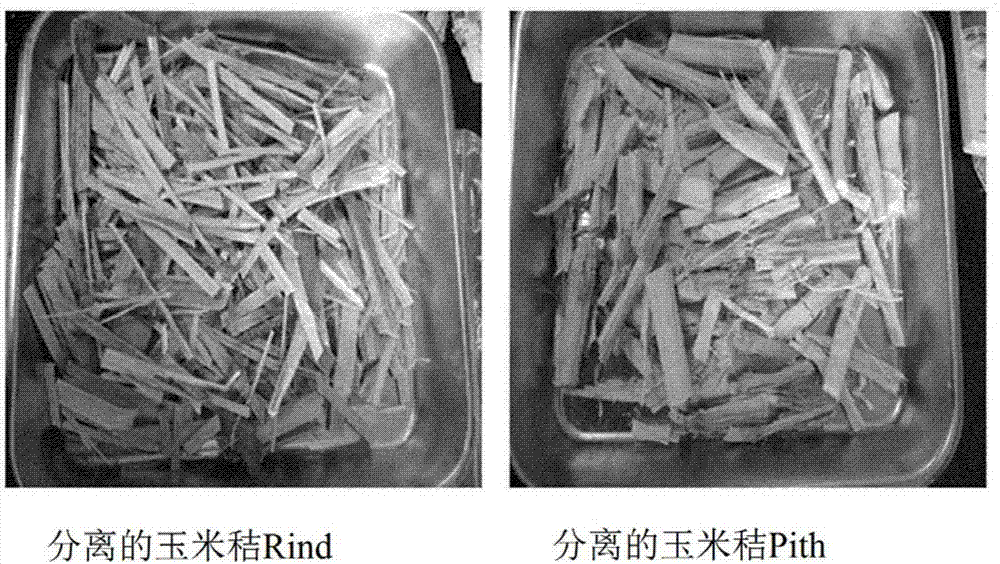
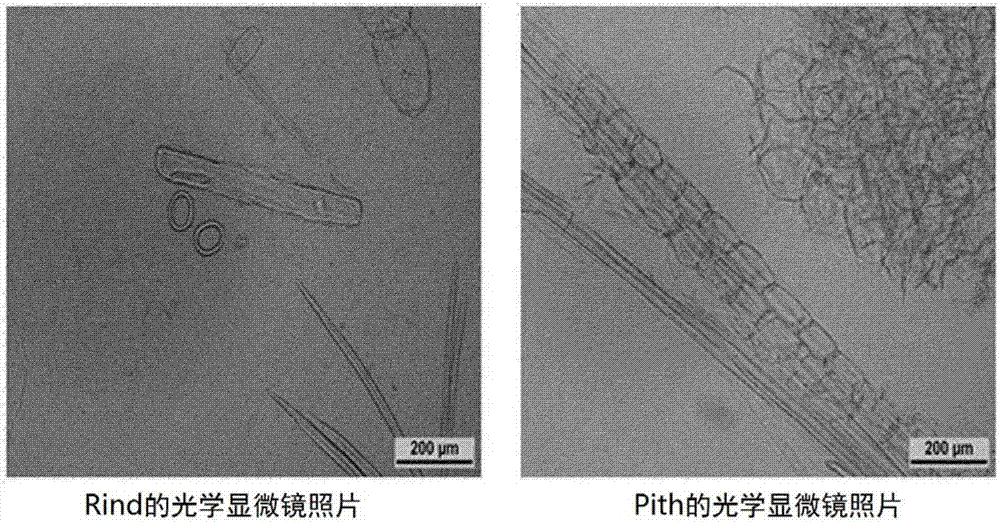
[0043] Corn stalks consist of a hard rind (husk) on the outside and a pith (core) on the inside.
[0044] Rind and pith are composed of different tissues. Before using corn stalks to prepare nanocellulose, the Rind and Pith of corn stalks were separated. figure 1 Show the separated corn stalk Rind and Pith, the optical microscope photos of Rind and Pith are as figure 2 shown.
[0045] In order to prepare nanocellulose using the separated Rind and Pith of corn stalks, a lignin removal step was first performed. The lignin removal process can be removed through a pulping process and a bleaching process.
[0046] In the present invention, lignin (lignin) is removed by the following bleaching process, and the specific process is as follows.
[0047] After adding 1000 mL of distilled water to rind and pith of 30 g of oven dry corn stalks, 15.5 g of NaClO2 and 1.0 mL of acetic acid were added, a...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2. Utilize oil palm trunk (oil palm trunk) to prepare nanocellulose (nanocellulose)
[0051] (1) Oil palm trunk fibers are composed of vascular bundles and parenchyma cells at a ratio of 50:50. Although the vascular bundles are linear and elongated similar to other woody fibers, the parenchyma cells are short and round. Therefore, when oil palm trunks are made into pulp for papermaking, inter-fiber bonding is disturbed due to parenchyma cells, so the parenchyma cells are separated before or after pulping.
[0052] The separation of parenchyma cells before pulping can be carried out by using the density difference between parenchyma cells and vascular bundles, and the separation of parenchyma cells after pulping can be carried out by Bauer Mcnett et al. After pulping, the process of using Bauer Mcnett to separate parenchyma cells is as follows. Each part uses 28, 48, 100, and 200 mesh steel wire mesh to separate long rod-shaped vascular bundles and short roun...
experiment example 1
[0068] Experimental Example 1. Confirmation of nanocellulose (nanocellulose) prepared from corn stalks
[0069] According to Example 1, the nanocellulose prepared from the rind and pith of corn stalks was confirmed by TEM analysis. TEM imaging conditions were diluted to 0.001%, put on a grid, and stained with uranyl acetate. Shooting was carried out under the condition of accelerating voltage 120KW.
[0070] The result is as Figure 10 As shown, it was confirmed that the prepared nanocellulose showed a difference in shape depending on rind and pith, and the nanocellulose prepared by rind showed a linear rod shape similar to nanocellulose of wood-derived fibers. However, it was confirmed that the nanocellulose made of pith is not in the shape of a linear rod, but in the shape of a sphere. This was judged to be due to the production of spherical nanocellulose due to parenchyma cells in the pith of corn stalks.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com