Method and structure for removing multi-screen splicing black seams
A multi-screen, black seam technology, applied to instruments, identification devices, etc., can solve problems such as black seams that are easily misunderstood as images, high-end monitoring misjudgments, image splits, etc., to protect acrylic panels, reduce seams, and shrink The effect of splicing gaps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A method for removing black seams for multi-screen splicing, comprising the following steps:
[0029] Step 1: Use thermoplastic technology to mold the acrylic plate into a trapezoid structure, specifically: firstly arrange the low-refractive index material and high-refractive index material in the mold, and then heat and hot-press to form the trapezoid body. Then carry out edge cleaning and surface treatment on the composite ground glass formed by composite; the surface and surrounding of the composite ground glass formed by hot pressing should be ground and polished to above 400 mesh, and then surface treatment agent and composite glass surrounding treatment agent should be sprayed. The number of plates is 9, arranged in a 3×3 matrix.
[0030] Step 2, tile and bond the two acrylic sheets together;
[0031] Step 3: Lay the glass on the front of the two acrylic sheets that are tiled and bonded together in Step 2;
[0032] In step 4, the glass-coated acrylic sheet that ...
Embodiment 2
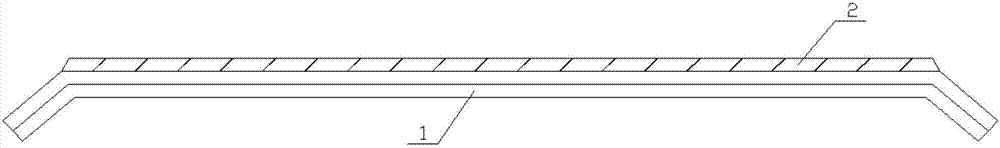
[0034] like figure 1 As shown, a structure for removing black seams for multi-screen splicing includes two acrylic boards 1 that are fixed and stacked together, and the shape of the acrylic boards 1 is a trapezoidal structure. The glass 2 is also included, and the glass 2 is attached to the front surface of the acrylic plate 1 . The acrylic plate 1 contains high refractive index material and low refractive index material. The shape of the low-refractive-index material is sheet-like; its thickness is not greater than one-tenth of the pixel pitch of the applicable display screen. The shape of the high-refractive-index material is sheet-like; the high-refractive-index material is a highly transparent material, and its light transmittance should be greater than 85%; when the high-refractive-index material is sheet-like, its thickness is not greater than the pixel of its applicable display screen point spacing. The glass 2 is a touch screen.
Embodiment 3
[0036] like figure 1 As shown, a structure for removing black seams for multi-screen splicing includes two acrylic boards 1 that are fixed and stacked together, and the shape of the acrylic boards 1 is a trapezoidal structure. The glass 2 is also included, and the glass 2 is attached to the front surface of the acrylic plate 1 . The acrylic plate 1 contains high refractive index material and low refractive index material. The shape of the low-refractive-index material is honeycomb; its thickness is not greater than one tenth of the pixel pitch of the applicable display screen. The shape of the high-refractive-index material is a granular shape smaller than the diameter of the honeycomb hole of the low-refractive-index material; the high-refractive-index material is a highly transparent material, and its light transmittance should be greater than 85%; when the high-refractive-index material is a flake, its The thickness is not greater than the pixel pitch of the display scree...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| transmittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com