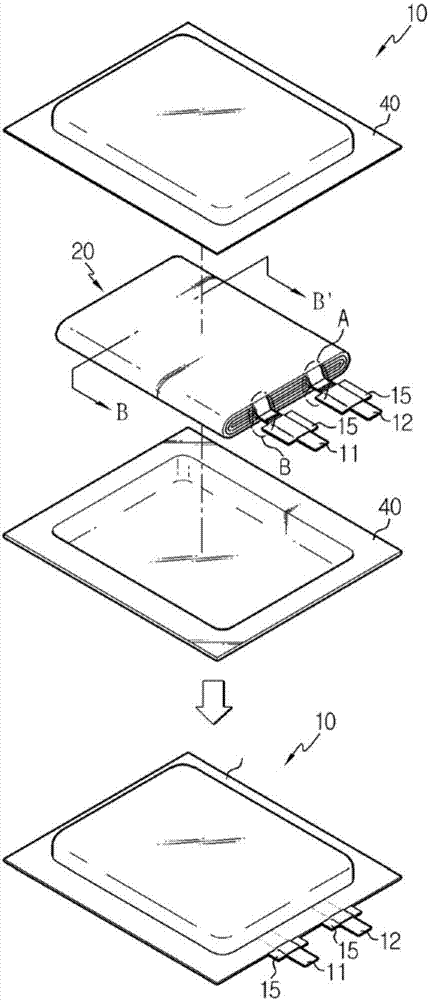
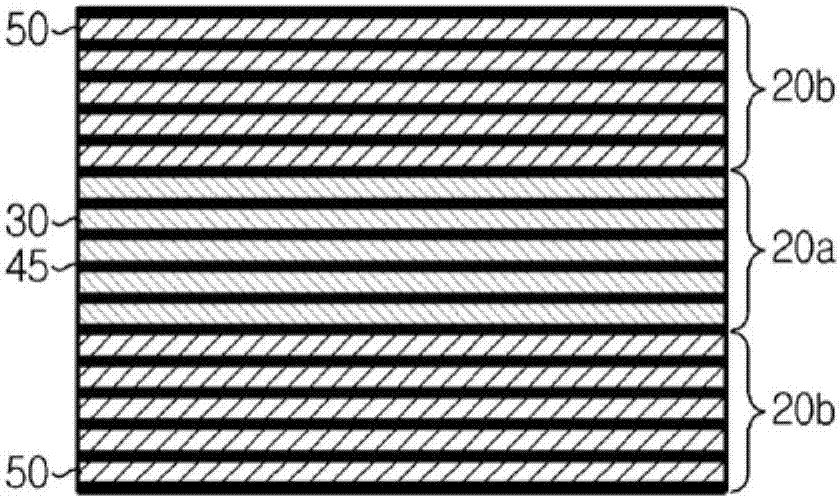
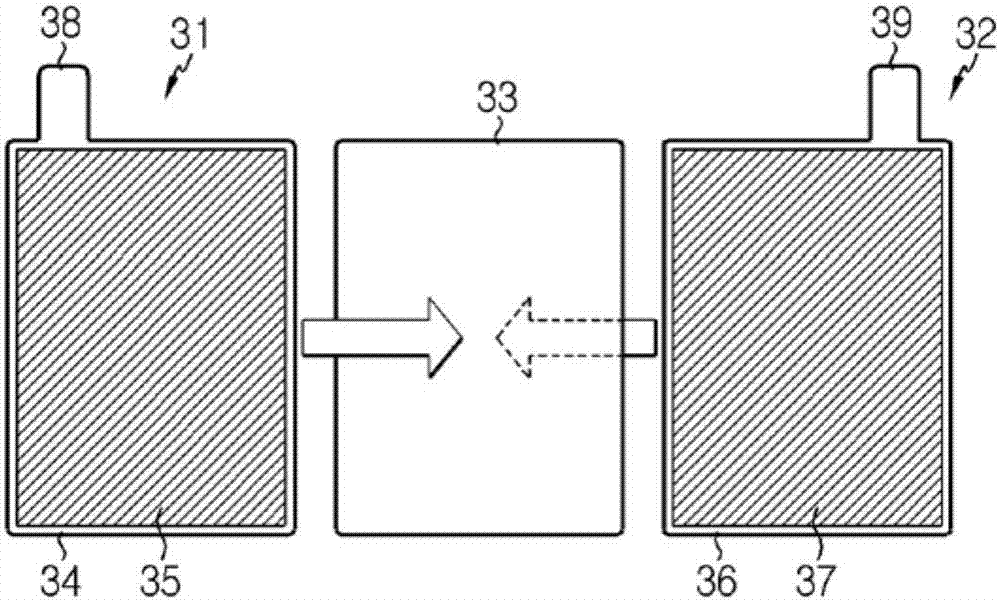
Secondary battery having improved output characteristics
A secondary battery and battery technology, applied in the direction of secondary batteries, secondary battery manufacturing, batteries, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing energy density, improving the effect of high output, and reducing resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-1
[0142] 1.2. Example 1-1: Preparation of a secondary battery with a positive electrode with a high load energy density
[0143] Similar to Comparative Example 1-1, LiNi with an average particle diameter of 10 μm was selected respectively x co y mn z o 2 powder and graphite powder having an average particle diameter of 10 μm were used as the positive electrode active material and the negative electrode active material.
[0144] Then, a process similar to Comparative Example 1-1 was performed to prepare 5 C batteries and 4 A batteries. The same types of electrode separators and battery separators used in Comparative Example 1-1 were also used in the preparation of the respective batteries.
[0145] In Example 1-1, when preparing the battery, compared with the comparative example, the thickness of the positive electrode coating was increased, so that the load energy density of the positive electrode was 3.8mAh / cm 2 . The load energy density as described above corresponds to ...
Embodiment 2-1
[0148] 1.3. Example 2-1: Preparation of a secondary battery with a positive electrode with a low load energy density
[0149] Similar to Example 1-1, respectively select LiNi with an average particle diameter of 10 μm x co y mn z o 2 powder and graphite powder having an average particle diameter of 10 μm were used as the positive electrode active material and the negative electrode active material.
[0150] Then, a process similar to Comparative Example 1-1 was performed to prepare 6 C batteries and 6 A batteries. The same type of electrode separator and battery separator used in Comparative Example 1-1 were also used in the preparation of the battery.
[0151] Unlike Comparative Example 1-1, compared with the positive electrode coating in Comparative Example 1-1, the thickness of the positive electrode coating is reduced, so that the load energy density of the positive electrode is 1.67mAh / cm 2 . The load energy density as described above corresponds to the specificatio...
Embodiment 3-1
[0154] 1.4. Example 3-1: Preparation of a secondary battery according to the present disclosure
[0155] Similar to Example 1-1, respectively select LiNi with an average particle diameter of 10 μm x co y mn z o 2 powder and graphite powder having an average particle diameter of 10 μm were used as the positive electrode active material and the negative electrode active material.
[0156] Then prepare 5 C to be arranged in the central battery block area with the same specifications as in Example 1-1 1 Batteries and 4 A 1 Battery. The only difference is: C set on the leftmost and rightmost of the central battery block 1 The thickness of the outermost negative electrode coating of the battery is as Figure 6 Adjust asymmetrically as shown in . Then prepare 6 C to be arranged in the side battery block with the same specifications as in Example 2-1 2 battery and 6 A 2 Battery. Subscripts "1" and "2" used herein indicate that the corresponding batteries were batteries prep...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| internal resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com