Stable fungal blastospores and methods for their production, stabilization and use
A technology of blastospores and fungi, applied in the field of stable fungal blastospores and their production, stabilization and use, can solve the problems that the production of blastospores resistant to drying has not been realized, commercial use does not exist, long fermentation time and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0070] Fungi and inoculum preparation
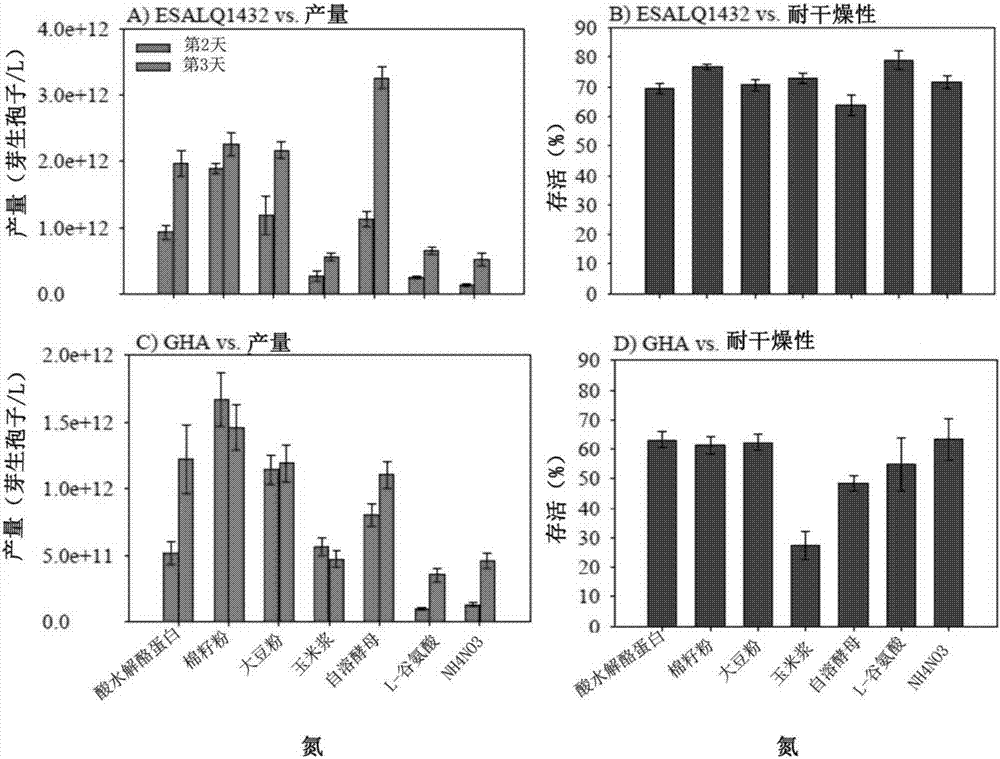
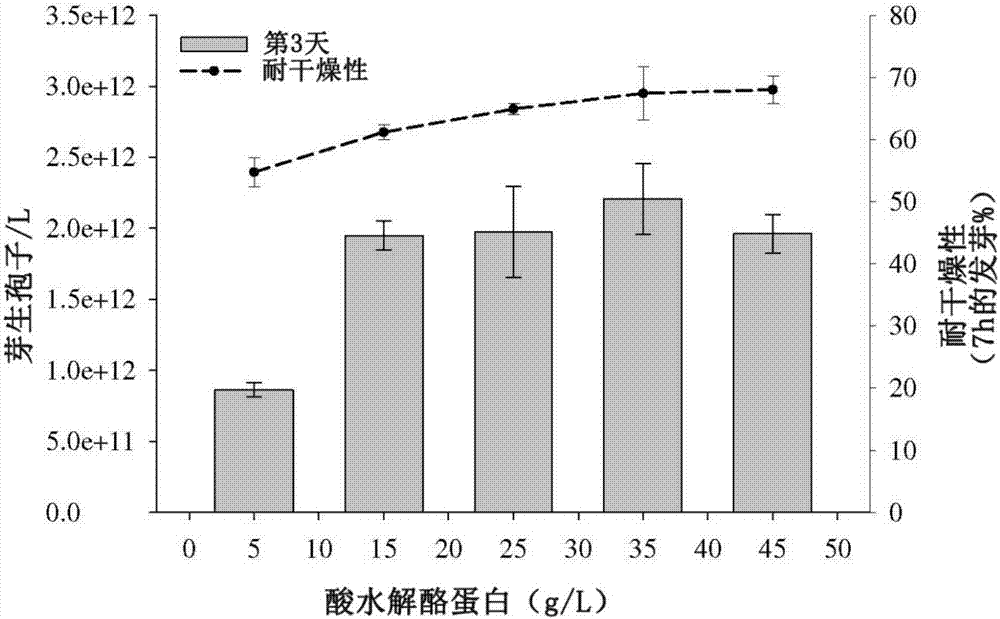
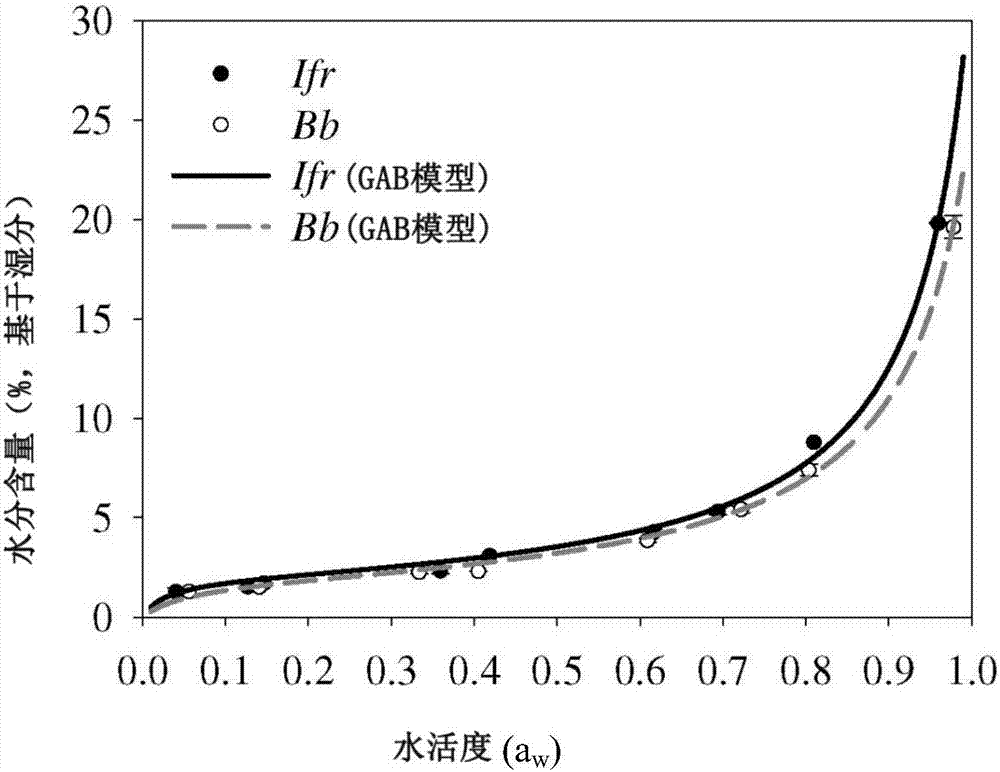
[0071] Five isolates of B. bassiana and five isolates of I. fumosorosea were tested in this study. Most of the fungal isolates originated from Brazil, details are shown in Table 1. The isolate ARSEF 3581 of I. fumosorosea and the GHA of B. bassiana (ARSEF 6444) are currently designated as (Laverlam, Butte, MT, USA) as the active ingredient of a commercial biopesticide as the US standard for liquid culture studies. Brazilian fungal isolates were previously identified using molecular techniques based on domain gene sequencing. Stock cultures of these fungi were grown on potato dextrose agar ([PDA] Detroit, MI, USA) were grown in Petri dishes at 22±2°C with a 12:12 hr (L:D) photoperiod for 2–3 weeks until sporulation and cut into 1 mm sections. 2 Agar plugs and store in 10% glycerol at -80 °C in sterile cryovials. To generate conidial inoculum, use frozen stock cultures to inoculate PDA plates and incubate for 2-3 weeks until the cul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com