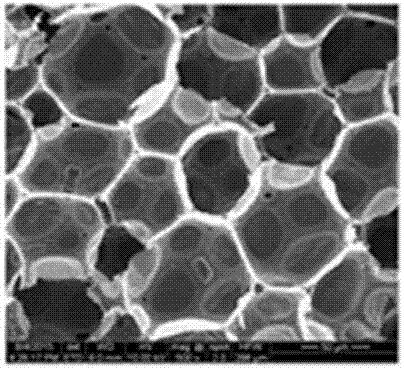
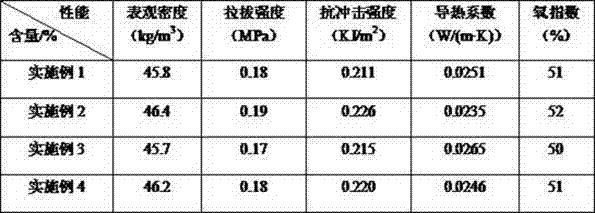
Method for developing low-density high-strength phenolic foam
A phenolic foam, high-strength technology, applied in the field of building exterior wall materials, can solve problems such as brittleness, ineffective toughening effect of phenolic foam, and limited application range of phenolic foam
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Add 94 parts of phenol, 3 parts of catalyst (50% sodium hydroxide solution), 6 parts of urea and 2 parts of modified molybdenum disulfide into the four-necked bottle, raise the temperature to 50~70°C, add 20 parts of formaldehyde, and react for a while Then add 80 parts of paraformaldehyde, react for a period of time and then add 3 parts of catalyst, raise the temperature to 80~85°C and react for 2~3 hours, when the viscosity of the resin reaches 2000~8000 mPa·S, cool down to 70°C, and then add formic acid to adjust pH to neutral, cooled and discharged to obtain the required phenolic resin; in the four-necked bottle, add 100 parts of the phenolic resin modified by the coupling agent grafted molybdenum disulfide in proportion, and then add 4 parts of surfactant, 4 parts of foaming agent and 20 parts of curing agent are mixed evenly and then poured into the mold and placed in a drying oven at 70°C for foaming. After meeting the foaming requirements, take out the mold and c...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Add 90 parts of phenol, 3 parts of catalyst (50% sodium hydroxide solution), 5 parts of urea and 2 parts of modified molybdenum disulfide into a four-necked bottle, raise the temperature to 50~70°C, add 26 parts of formaldehyde, and react for a period of time Finally, add 74 parts of paraformaldehyde, react for a period of time, then add 3 parts of catalyst, raise the temperature to 80~85°C and react for 2~3 hours, when the viscosity of the resin reaches 2000~8000 mPa·S, cool down to 73°C, and then add formic acid to adjust pH to neutral, cooled and discharged to obtain the required phenolic resin; in the four-necked bottle, add 100 parts of the phenolic resin modified by the coupling agent grafted molybdenum disulfide in proportion, and then add 4 parts of surfactant, 5 parts of foaming agent and 22 parts of curing agent are mixed evenly and then poured into the mold and placed in a drying oven at 70°C for foaming. After meeting the foaming requirements, take out the mo...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Add 98 parts of phenol, 4 parts of catalyst (50% sodium hydroxide solution), 7 parts of urea and 3 parts of modified molybdenum disulfide into the four-necked bottle, raise the temperature to 50~70°C, add 30 parts of formaldehyde, and react for a period of time Then add 70 parts of paraformaldehyde, react for a period of time and then add 4 parts of catalyst, raise the temperature to 80~85°C and react for 2~3 hours, when the viscosity of the resin reaches 2000~8000 mPa·S, cool down to 74°C, and then add formic acid to adjust pH to neutral, cooling and discharging to obtain the required phenolic resin; in a four-necked bottle, add 100 parts of the phenolic resin modified by the coupling agent grafted molybdenum disulfide in proportion, and then add 6 parts of surfactant, 5 parts of foaming agent and 25 parts of curing agent are mixed evenly and poured into the mold, and foamed in a drying oven at 70°C. After meeting the foaming requirements, the mold is taken out and cool...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com