Method for preparing molybdenum disulfide/carbon composite multi-grade porous material
A technology of molybdenum disulfide and multi-level pores, which is applied in the direction of secondary batteries, electrochemical generators, hybrid capacitor electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of unseen supercapacitor applications and complicated preparation methods, and achieve avoidance of damage and simple preparation methods , the effect of multiple expansion spaces
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
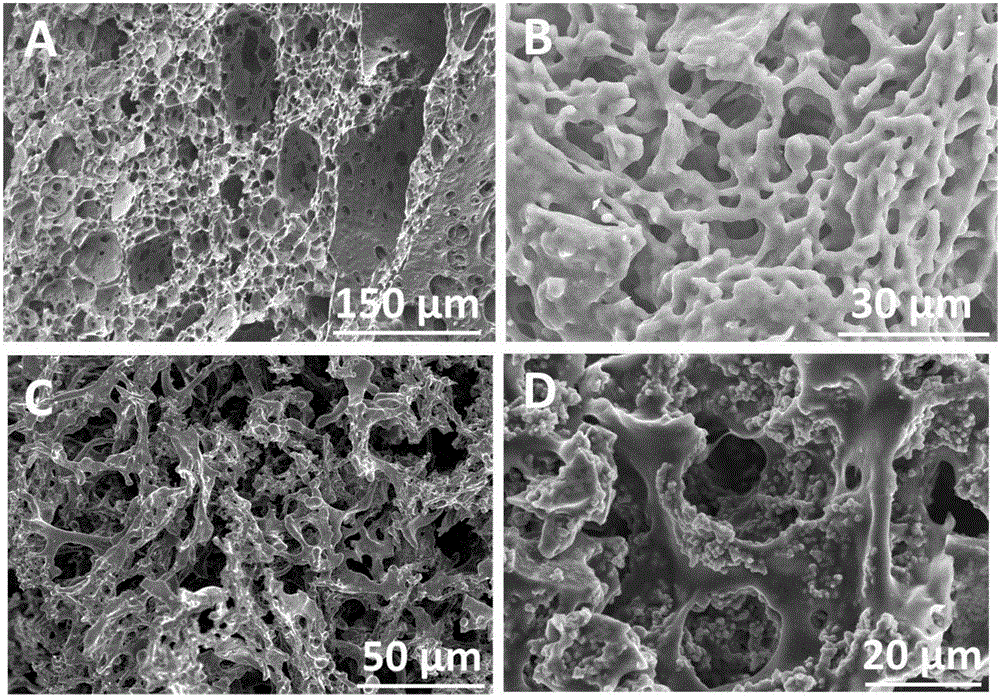
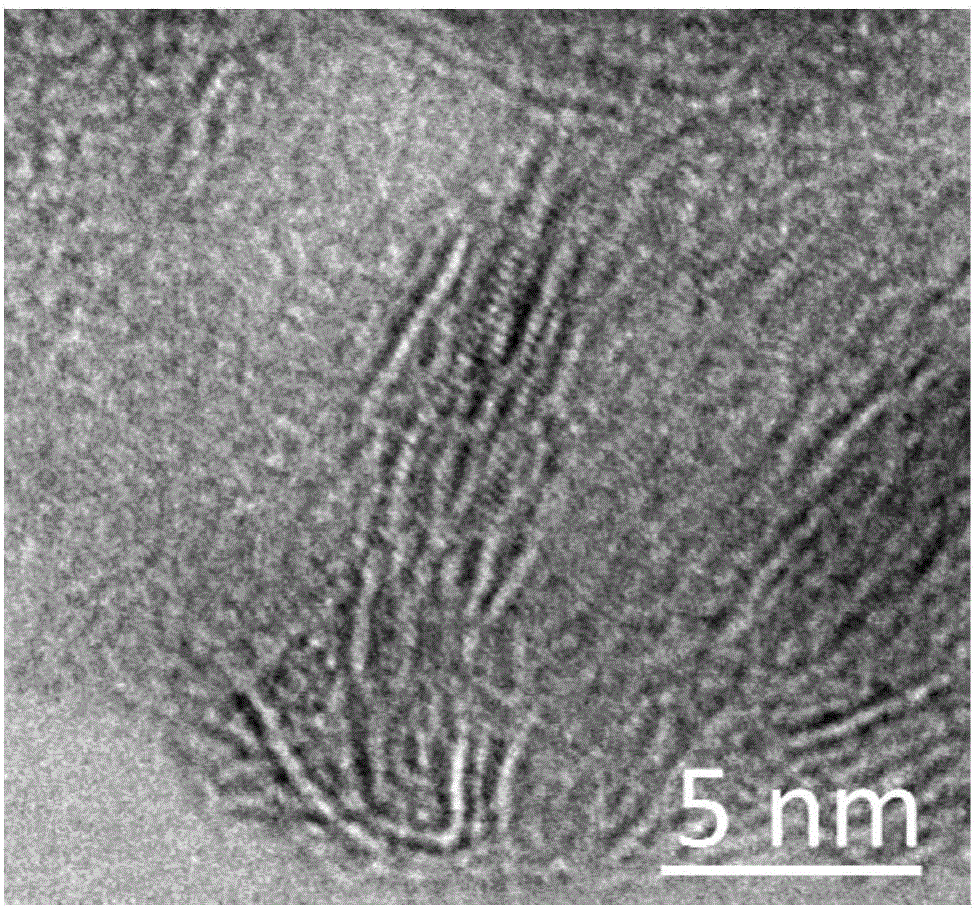
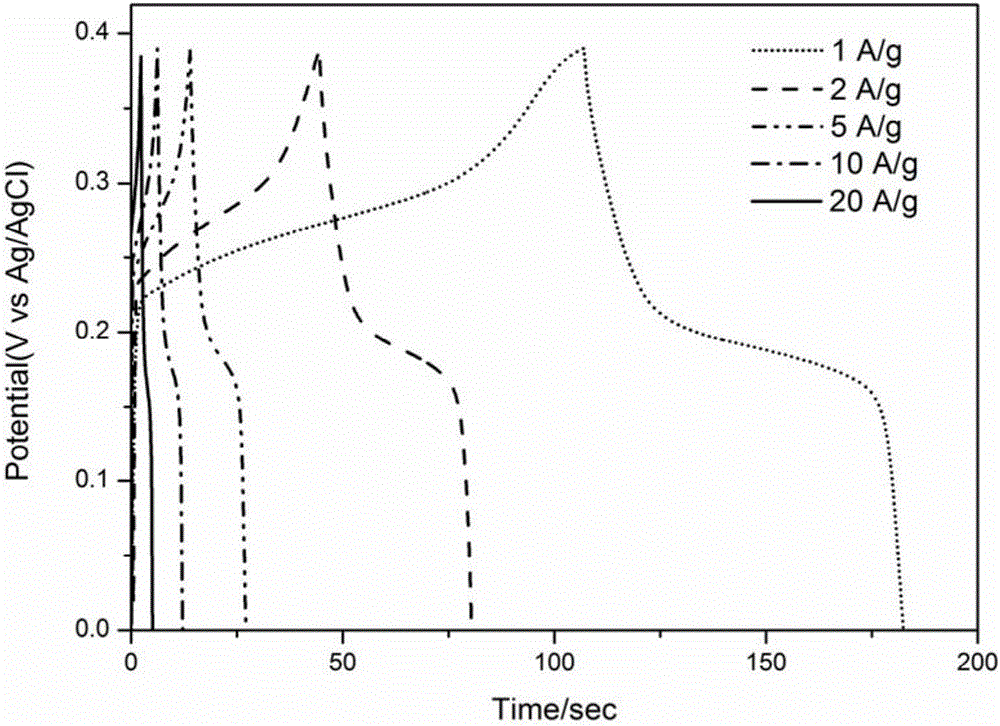
[0027] 0.5 g of sodium molybdate, 1.0 g of thioacetamide and 2 g of agarose were added to the flask, and 20 ml of water was added to dissolve. The flask is immersed in a water bath, and the temperature of the water bath is set to 90 degrees Celsius. After reacting for 3 days, all devices were closed, and the liquid in the flask was poured into a beaker while it was hot to cool. The samples in the beaker were transferred to the refrigerator to freeze, and then transferred to a freeze dryer at minus 40 degrees Celsius for 24 hours to dry. The above samples were calcined in a tube furnace, the experimental conditions were 500 degrees Celsius for 6 hours, and the heating rate was 2 degrees Celsius per minute. The samples prepared as figure 1 As shown in A, the transmission electron micrograph is shown as figure 2 shown. Under the scanning electron microscope, the hierarchical porous structure can be clearly observed without phase separation; while under the transmission elect...
Embodiment 2
[0029] 0.5 g of sodium molybdate, 1.0 g of thioacetamide and 2 g of agarose were added to the flask, and 20 ml of water was added to dissolve. The flask is immersed in a water bath, and the temperature of the water bath is set to 90 degrees Celsius. After reacting for 2 days, all devices were closed, and the liquid in the flask was poured into a beaker while it was hot to cool. The samples in the beaker were transferred to the refrigerator to freeze, and then transferred to a freeze dryer at minus 40 degrees Celsius for 24 hours to dry. The above samples were calcined in a tube furnace, the experimental conditions were 500 degrees Celsius for 6 hours, and the heating rate was 2 degrees Celsius per minute. The samples prepared as figure 1 Shown in B.
Embodiment 3
[0031] 0.5 g of sodium molybdate, 1.0 g of thioacetamide and 2 g of agarose were added to the flask, and 20 ml of water was added to dissolve. The flask is immersed in a water bath, and the temperature of the water bath is set to 90 degrees Celsius. After reacting for 1 day, all devices were closed, and the liquid in the flask was poured into a beaker while it was hot to cool. The samples in the beaker were transferred to the refrigerator to freeze, and then transferred to a freeze dryer at minus 40 degrees Celsius for 24 hours to dry. The above samples were calcined in a tube furnace, the experimental conditions were 500 degrees Celsius for 6 hours, and the heating rate was 2 degrees Celsius per minute. The samples prepared as figure 1 C shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com