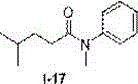
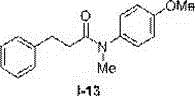
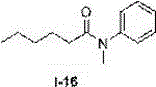
Method for preparing N-aryl amide without solvent and catalyst
A kind of aryl amide and catalyst technology, which is applied in the field of solvent-free and catalyst-free preparation of N-aryl amide, and can solve problems such as expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Embodiment 1, 5-(4-methylbenzyl) Michaelis acid and the influence of the ratio of o-methoxyaniline on the acylation reaction of the present invention (with the I-1 compound shown in the formula as an example)
[0015]
[0016] Add 5-(4-methylbenzyl) Michaelis acid and 2-methoxyaniline (5:1, 2:1, 1:1, 1:2, 1:5) in different molar ratios to the reaction tube in 100 o C reaction, detecting the influence of the molar ratio of (4-methylbenzyl) Michaelis acid and 2-methoxyaniline on the yield of the acylation reaction. After the reaction, the separation yields of the target amides were 96%, 96%, 97%, 95%, and 94%, respectively. This shows that no matter how the molar ratio of (4-methylbenzyl) Michaelis acid and 2-methoxyaniline changes, the yield of the acylation reaction is very stable (based on the insufficient amount of raw materials), and the (4-methylbenzyl) The optimal molar ratio of benzyl) Michaelis acid to 2-methoxyaniline is 1:1.
[0017] 1 H NMR (500 MHz, CD...
Embodiment 2
[0018] The synthesis of I-2 compound shown in embodiment 2, formula
[0019]
[0020] 5-(4-Methylbenzyl) Michaelis acid (0.2 mmol) and 3-methoxyaniline (0.2 mmol) were sequentially added into the reaction flask, and reacted at 100° C. for 5 hours. Water and ethyl acetate were added to the reaction solution, followed by washing with hydrochloric acid (4 mol / L) and saturated aqueous sodium carbonate solution, and the organic phase was dried and desolventized to obtain the target amide as a white solid with a yield of 95%.
[0021] 1 H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ 7.26 (bs, 1H), 7.22 – 7.18 (m, 2H), 7.15 –7.12 (m, 4H), 6.92 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.66 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 3.81(s, 3H), 3.03 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.65 (t, J = 7.8 Hz ,2H), 2.34 (s, 3H). 13 CNMR (125 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ 170.58, 160.11, 139.02, 137.48, 135.92, 129.61, 129.33, 128.27, 111.97, 110.16, 105.58, 55.29, 39.65, 31.12, 21.04.
Embodiment 7
[0022] The synthesis of I-3 compound shown in embodiment 7, formula
[0023]
[0024] Except that the aromatic amine was 2,4-dimethoxyaniline, other reaction conditions were the same as in Example 2 to obtain a white solid with a yield of 98%.
[0025] 1 H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 ) δ 8.26 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.51 (bs, 1H),7.17 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.13 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 6.50 – 6.47 (m, 2H), 3.82(s, 3H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 3.04 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 2.69 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H),2.34 (s, 2H). 13 C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ 169.99, 156.29, 149.11, 137.68, 135.71, 129.22, 128.26, 121.20, 120.73, 103.69, 98.57, 55.64, 55.55, 39.65, 31.20, 21.03.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com