Protein A domain Z derivative with specific binding effect on antibody and application thereof
A technology of binding action and domain, applied in the field of affinity chromatography in biotechnology, can solve the problems of reduction, destruction of the three-dimensional structure of the chromatographic ligand of protein A, loss of antibody binding ability, etc., and achieves good chemical stability and high chemical stability. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
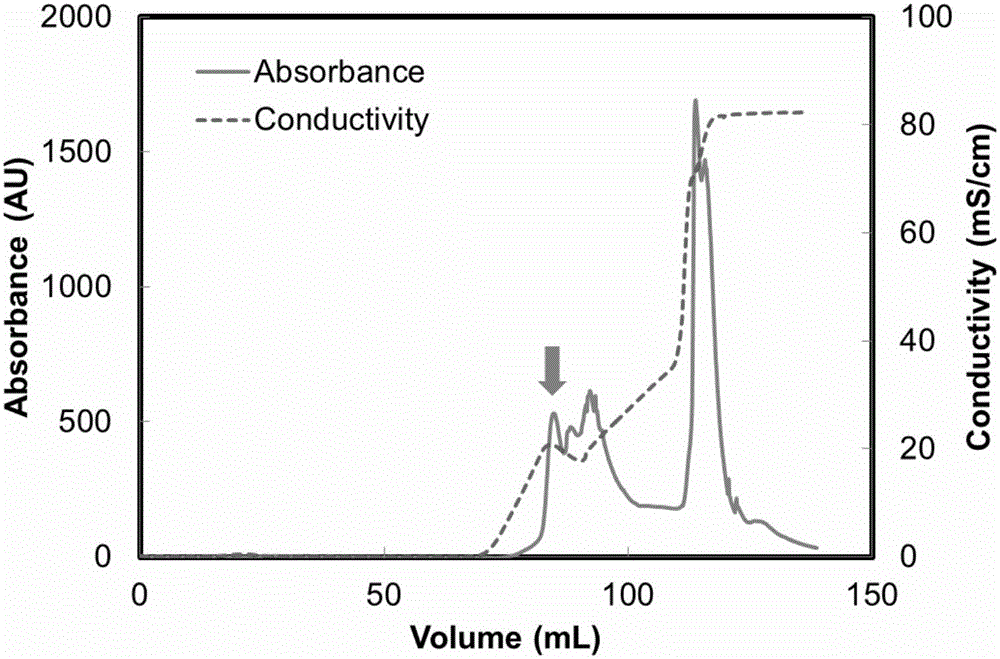
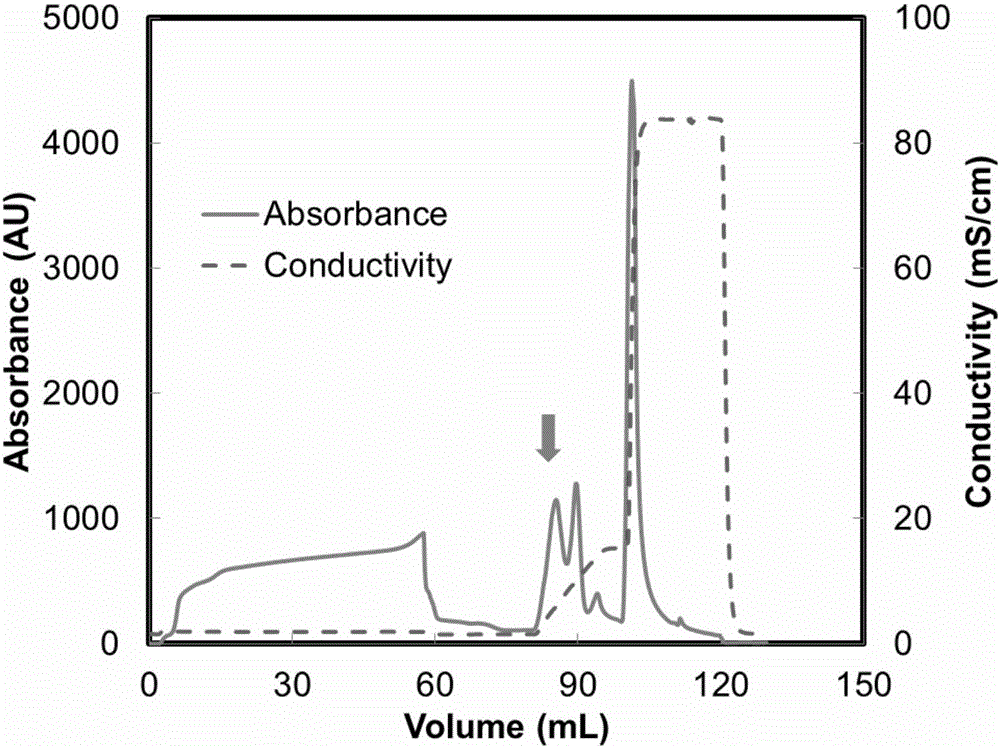
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1 sequence number is the preparation and stability of the domain Z derivative of SEQ ID No.:2
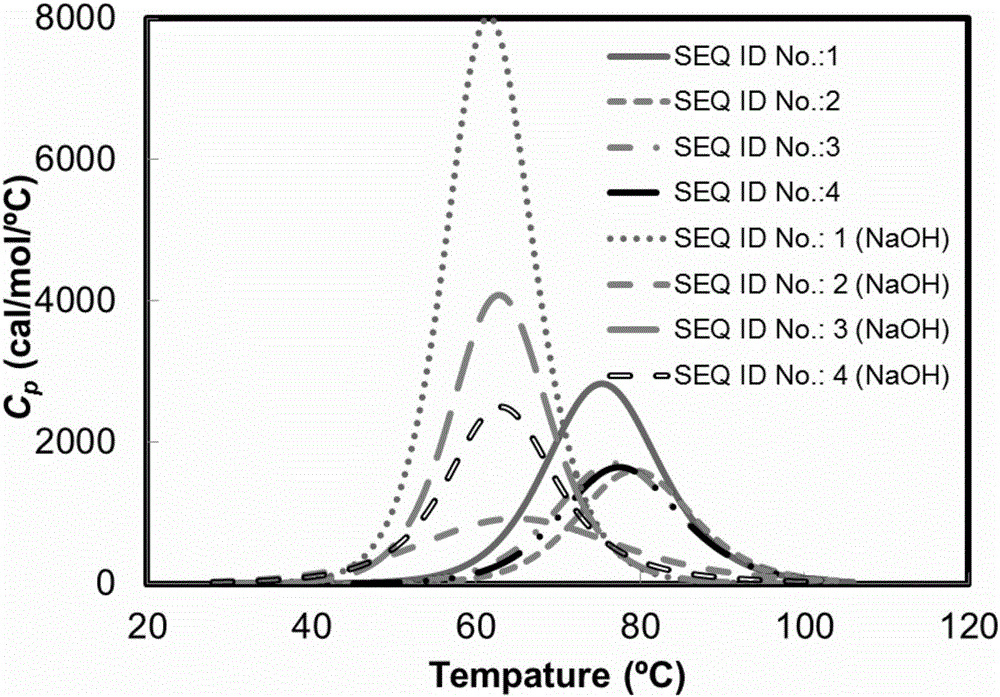
[0029] The structural domain Z with the sequence number of SEQ ID No.: 1 and the protein with the sequence number of SEQ ID No.: 2 were respectively synthesized by using a polypeptide solid-phase chemical synthesis method. The above proteins were dissolved in 20mmol / L PBS buffer (pH 6.0) containing 100mmol / L NaCl to prepare a protein solution with a protein concentration of 1mg / mL. The denaturation temperature of the protein in the above two solutions was carried out in a VP-DSC differential scanning calorimeter. First, after the sample cell and reference cell of VP-DSC were washed with 100mL ultrapure water, the buffer solution (20mmol / L PBS buffer solution containing 100mmol / L NaCl, pH 6.0) and about 0.75 mL of the protein solution were added to the reference pool and the sample pool (the volume of the reference pool and the sample pool was 0.5282 mL). After th...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2 The sequence number is the stability of the domain Z derivative of SEQ ID No.: 2 in alkaline solution
[0031] The preparation method described in Example 1 was used to synthesize the domain Z with the sequence number of SEQ ID No.: 1 and the protein with the sequence number of SEQ ID No.: 2. The above-mentioned protein was dissolved in 0.1 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to prepare a protein solution with a protein concentration of 1 mg / mL. The denaturation temperatures of the proteins in the above two solutions were analyzed using the differential scanning calorimetry method as in Example 1. The solution system is 0.1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution. Inject the 0.1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution that has been vacuum degassed for more than 15 minutes into the reference cell. The temperature scanning range of differential scanning calorimetry is 25-120°C, and the heating rate is 1°C / min. Before heating starts, the test temperature equilibration time is 8min....
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3 The sequence number is the preparation and stability of the domain Z derivative of SEQ ID No.:3
[0033] The protein whose sequence number is SEQ ID No.:3 was synthesized by the preparation method described in Example 1. The denaturation temperature of the above proteins under neutral conditions was analyzed by differential scanning calorimetry as in Example 1. The result is as figure 1 shown. The results show that the denaturation temperature of the domain Z derivative whose sequence number is SEQ ID No.: 3 is 76.9°C. This shows that the domain Z derivative with the sequence number of SEQID No.: 3 is more stable than domain Z under neutral conditions.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com