Application of sinomenine derivatives in the preparation of drugs for treating multiple myeloma
A technology of multiple myeloma and derivatives, applied in the field of medicine, to achieve good medicinal prospects and strong pharmacological effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
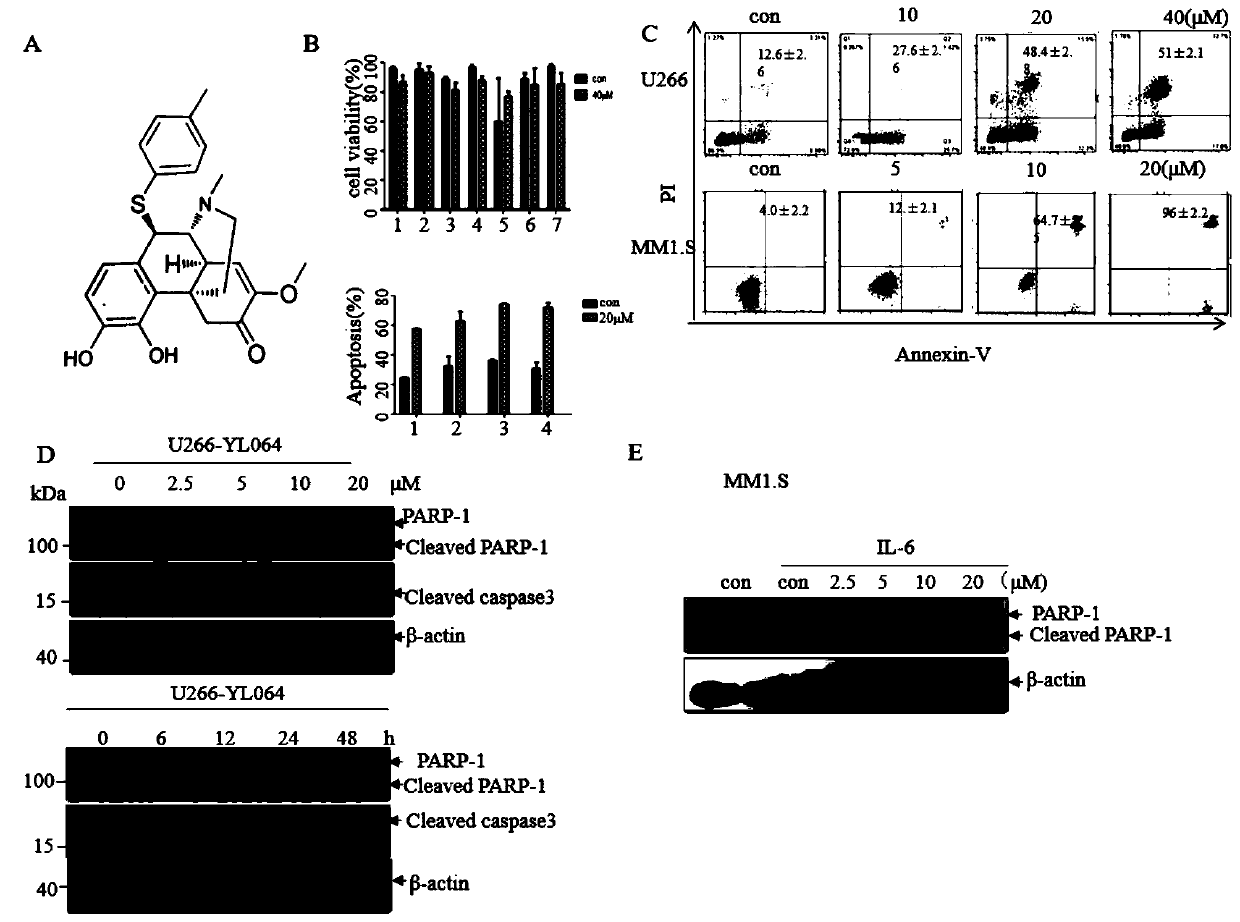
[0050] Example 1. Table 1 YL064 and its series of sinomenine derivatives inhibit the proliferation of myeloma cell line U266
[0051] Multiple myeloma cells U266 were treated with different concentrations of sinomenine derivatives respectively, and the half inhibition rate (IC) of each compound on U266 cells was detected by CCK8 method after 48 h. 50 ). The results showed that sinomenine derivatives could inhibit the proliferation of U266 cells to varying degrees (Table 1.).
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2. YL064 induces apoptosis of human multiple myeloma cell lines and primary myeloma cells
[0053] The multiple myeloma cells U266 and MM1.S cells were treated with different concentrations for 24 hours, and the apoptosis rate was detected by flow cytometry, and the related apoptosis proteins PARP1-1, Caspase3, and Cleaved caspase3 were detected by Westblot. Apoptosis of cell lines was dose- and time-dependent. ( figure 1 C, D, E). Further, we treated the primary cells of 4 cases of myeloma patients with YL064 20μM, and the results showed that YL064 could significantly induce the apoptosis of primary cells, while 40μM YL064 had no effect on normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells ( figure 1 B).
Embodiment 3
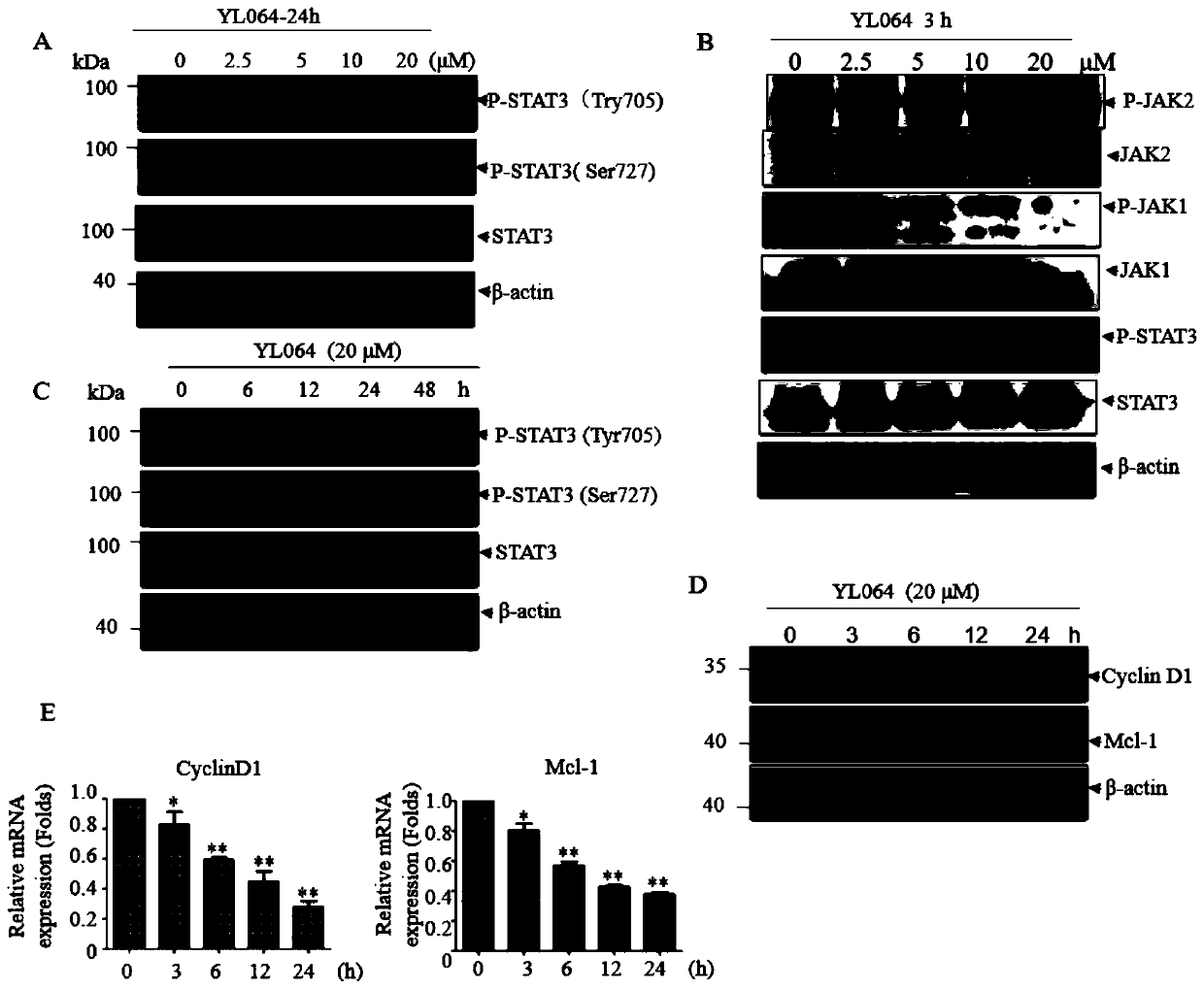
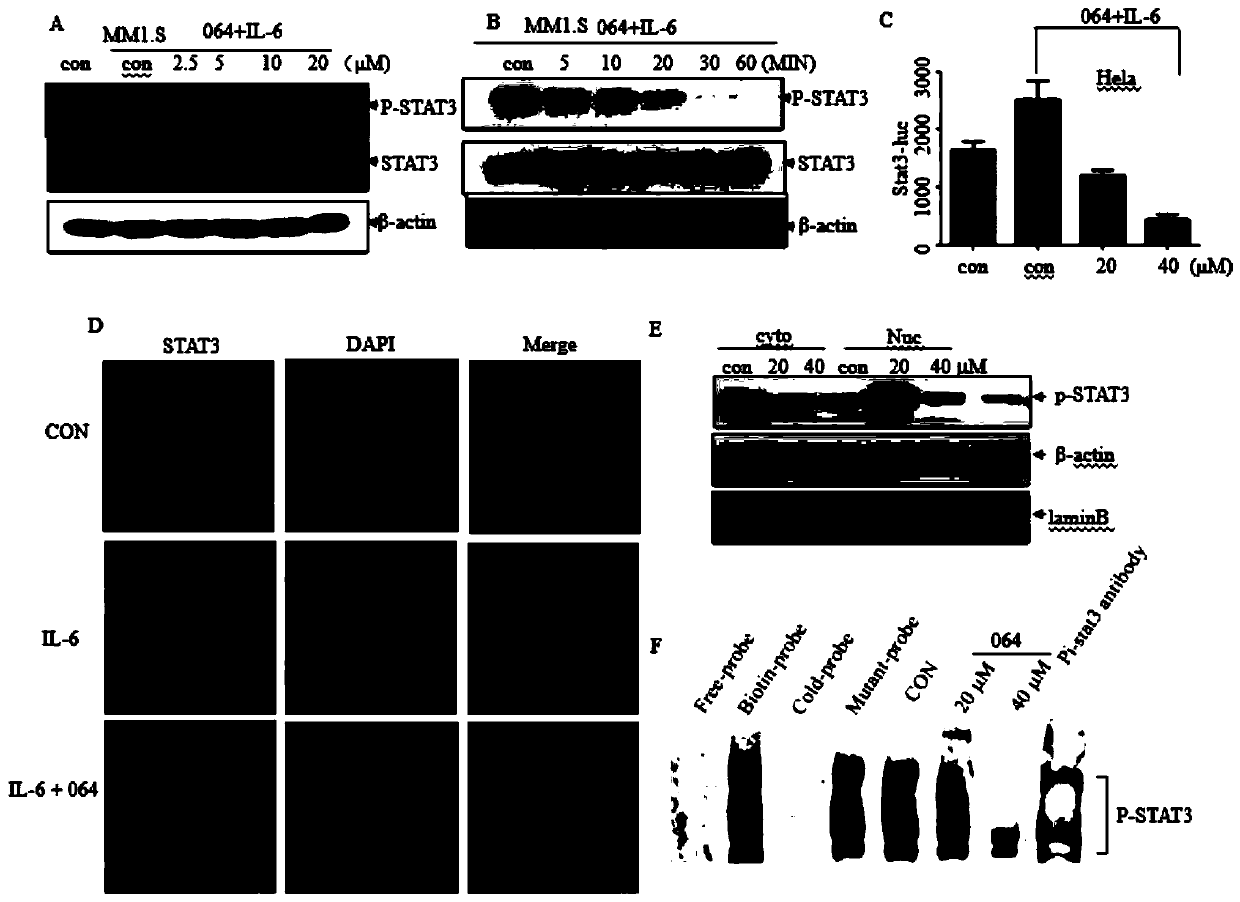
[0054] Example 3. YL064 inhibits activation of STAT3 and inhibits downstream target genes
[0055] In order to study the mechanism of YL06-induced apoptosis in myeloma cells, the effect of YL064 on the STAT3 pathway was observed since the activation of STAT3 signaling pathway mediated by IL-6 is a classical and important pathway involved in the proliferation and invasion of multiple myeloma. U266 cells were treated with different concentrations (2.5, 5, 10, 20 μM) of YL064 for 24 h, and U266 cells were treated with 20 μM of YL064 for different time (6, 12, 24, 48 h), respectively. Among them, p-STAT3 (Tyr705), The expression changes of p-STAT3 (Ser727) and STAT3 showed that YL064 could significantly inhibit the activation of p-STAT3 (Tyr705) in a dose- and time-dependent manner, but did not affect the activation of p-STAT3 (Ser727) ( figure 2 A. figure 2 C). Since the activation of STAT3 is regulated by upstream JAK1 and JAK2, we next examined the effect of YL064 on the JA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com