A method for roasting and extracting vanadium in vanadium-bearing shale
A shale and roasting technology, which is applied in the field of decomposition and extraction of vanadium-containing shale, can solve the problems of low vanadium leaching rate, low vanadium leaching rate and high roasting temperature, and achieves no environmental pollution, low raw material cost and low reaction temperature. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
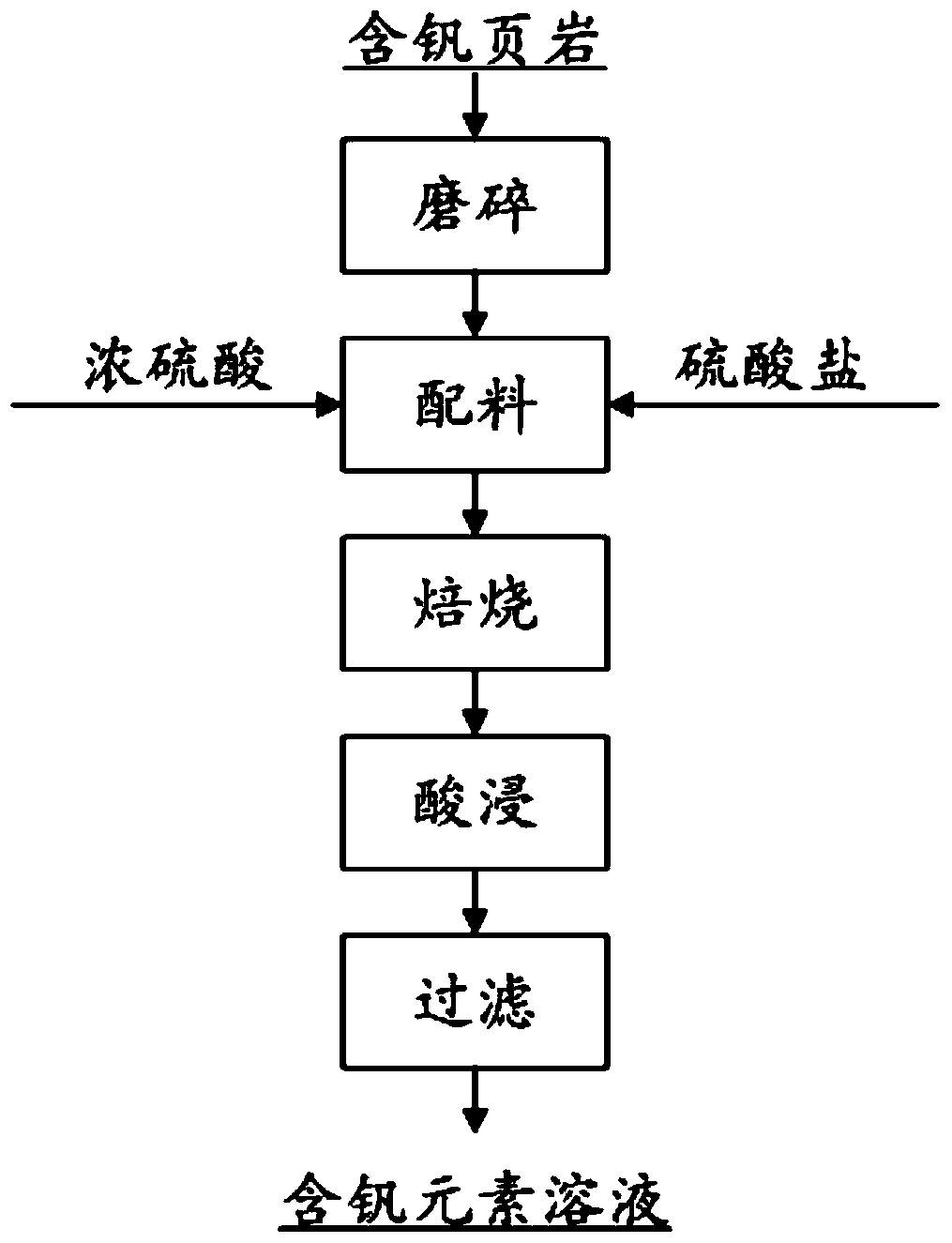
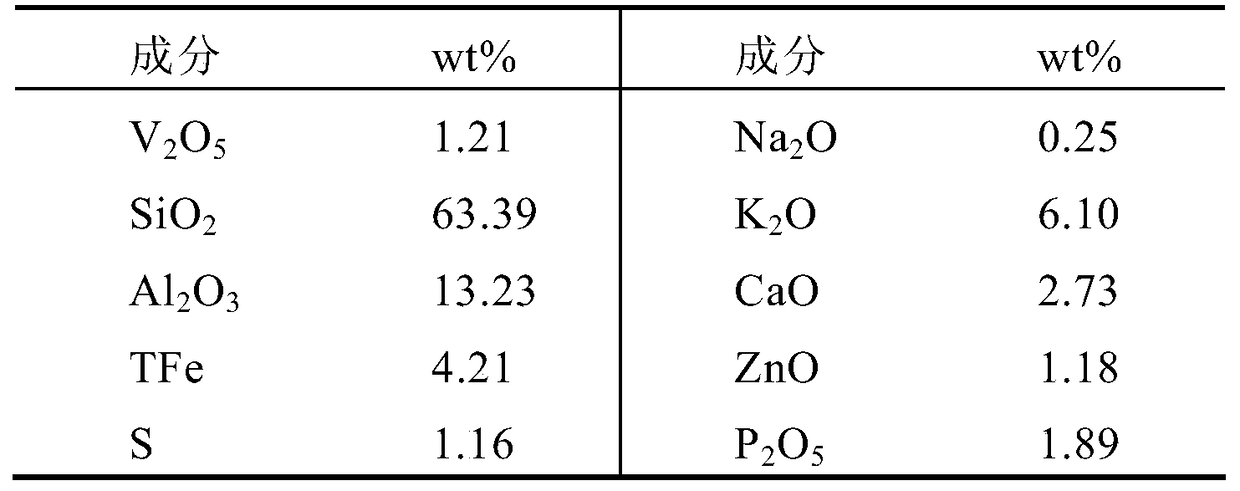
[0024] process such as figure 1 As shown, 100g of a vanadium-bearing shale in Hubei area (the main chemical composition is shown in Table 1) was ground to a particle size of -200 mesh to -400 mesh, and mixed with 10g of concentrated sulfuric acid (content 98%) and 10g of ammonium sulfate And mix evenly, put it into a muffle furnace for roasting, control the roasting temperature to 200° C., and the roasting time to be 1 h. After roasting, the obtained material was added to sulfuric acid solution (concentration ~ 10wt%), the solid-to-liquid ratio (g / mL) was 1:5, stirred at 90°C for 2 hours, and then filtered to obtain a filtrate containing vanadium. The obtained filtrates are respectively transferred to volumetric flasks for constant volume, and the content of vanadium element therein is detected. In addition, the vanadium element in the filter residue also needs to be detected.
[0025] After calculation, the leaching rate of vanadium is 85.7%.
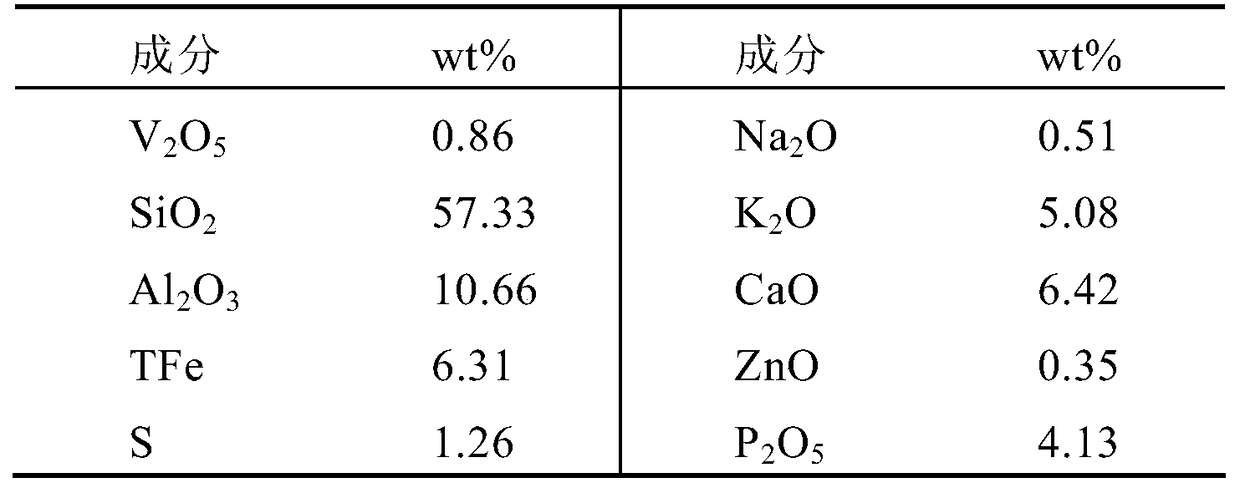
[0026] Table 1. Composition o...
Embodiment 2
[0029] process such as figure 1 As shown, 100g of a vanadium-bearing shale in Hubei area (the main chemical composition is shown in Table 1) was ground to a particle size of -200 mesh to -400 mesh, and mixed with 40g of concentrated sulfuric acid (content 98%) and 40g of magnesium sulfate and mixed evenly, put into a muffle furnace for roasting, the roasting temperature is controlled at 250°C, and the roasting time is 1.5h. After roasting, the obtained material was added to sulfuric acid solution (concentration ~8wt%), the solid-to-liquid ratio (g / mL) was 1:5, stirred at 70°C for 1.5h, and then filtered to obtain a filtrate containing vanadium. The obtained filtrates were respectively transferred to volumetric flasks for constant volume, and the content of vanadium element therein was detected. In addition, it is necessary to detect the vanadium element in the filter residue.
[0030] After calculation, the leaching rate of vanadium is 87.8%.
Embodiment 3
[0032] process such as figure 1 As shown, 100g of a vanadium-bearing shale in Hubei area (the main chemical composition is shown in Table 1) was ground to a particle size of -200 mesh to -400 mesh, and mixed with 70g of concentrated sulfuric acid (content 98%) and 70g of potassium sulfate and mixed evenly, put into a muffle furnace for roasting, control the roasting temperature to 300° C., and the roasting time to be 2 hours. After roasting, the obtained material was added to sulfuric acid solution (concentration ~5wt%), the solid-to-liquid ratio (g / mL) was 1:4, stirred at 60°C for 1 hour, and then filtered to obtain a filtrate containing vanadium. The obtained filtrates were respectively transferred to volumetric flasks for constant volume, and the content of vanadium element therein was detected. In addition, it is necessary to detect the vanadium element in the filter residue.
[0033] After calculation, the leaching rate of vanadium is 92.1%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com