Method for forming aortic stent graft
A molding method and technology of covered stents, which are applied in stents, devices for human tubular structures, medical science, etc., can solve problems such as long process time, poor geometrical compliance of blood vessels, and stress tearing at the distal end of stents.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The experimental methods used in the following examples are conventional methods unless otherwise specified.
[0040] The materials and reagents used in the following examples can be obtained from commercial sources unless otherwise specified.
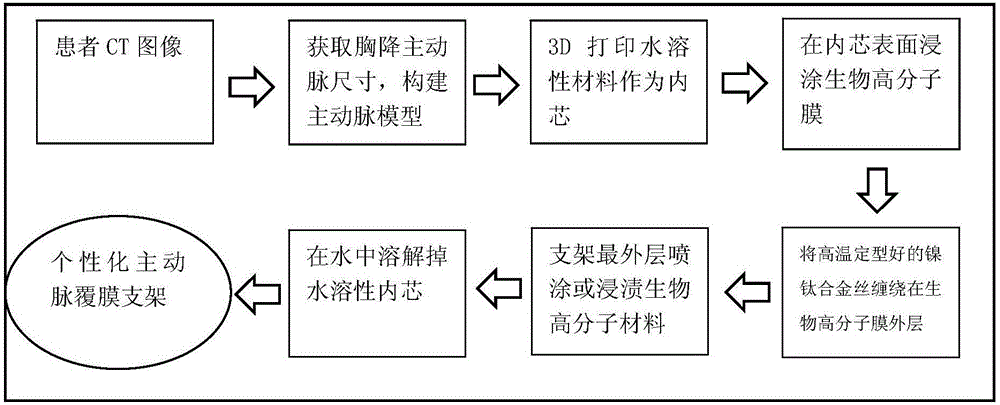
[0041] according to figure 1 The flow chart shown produces the descending thoracic aortic stent graft, and the steps are as follows:
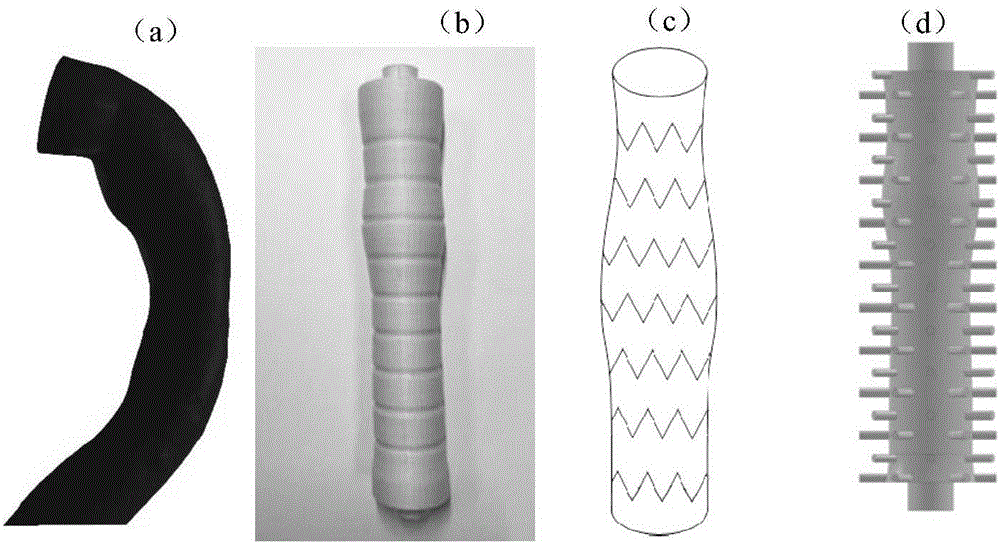
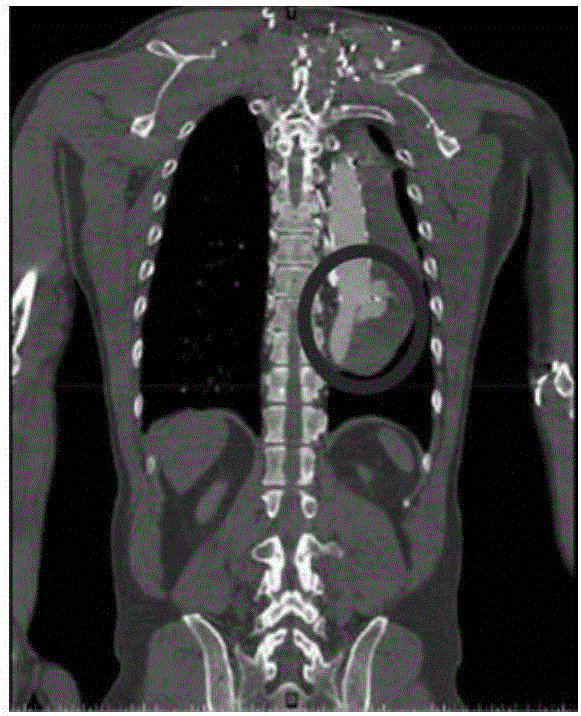
[0042] (1) Obtain a descending thoracic aorta image with a length of about 200 mm according to the patient's CT scan, and use Mimics 10.1 software to extract a three-dimensional model of the vessel, as shown in figure 2 As shown in (a), along the axial direction of the blood vessel, the characteristic diameter of the blood vessel is extracted every 10mm.
[0043] (2) According to the extracted blood vessel data, use CAD software to reconstruct the blood vessel model, and 3D print out the water-soluble blood vessel inner core, such as figure 2 As shown in (b), the water-soluble material is po...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com