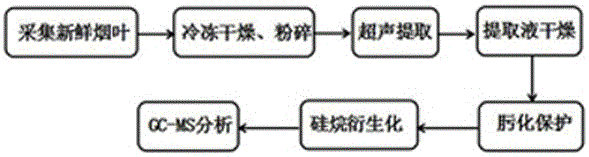
Method for detecting primary metabolites and secondary metabolites in fresh tobacco leaves with GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometer)
A technology of secondary metabolites and fresh tobacco leaves, applied in the field of metabolite detection in fresh tobacco leaves of tobacco metabolomics, can solve imperfect data, affect the accuracy of data preprocessing results, batch analysis data repeatability, narrow linear range, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
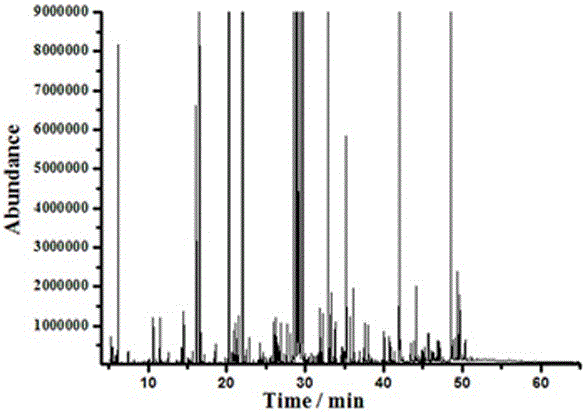
[0028] Example 1: Collect 18 fresh tobacco leaves of the 10th leaf of Honghua Dajinyuan planted in Dali, Yunnan, quickly remove the veins and wrap 3 tobacco leaves with tin foil, freeze them quickly in liquid nitrogen, and take out the samples wrapped in tin foil from liquid nitrogen , crushed and vacuum freeze-dried with a lyophilizer for 72 hours to remove water, and ground to 40-60 mesh. Weigh 20~25mg of crushed tobacco leaves into a 2mL centrifuge tube, add 100μL deuterated tridecanoic acid internal standard solution, 1mL extraction solvent, ultrasonic extraction for 30min, after ultrasonic extraction, centrifuge at 4000r / min for 10min, take 200μL supernatant in Conical vials and blow dry with a nitrogen blower. Add 50 μL of methoxyamine hydrochloride pyridine solution with a concentration of 20 mg / mL to the dried extract, vortex and oscillate and react at 37°C for 90 min, then add 50 μL MSTFA to the injection bottle, vortex and oscillate React at 37°C for 60min and detec...
Embodiment 2
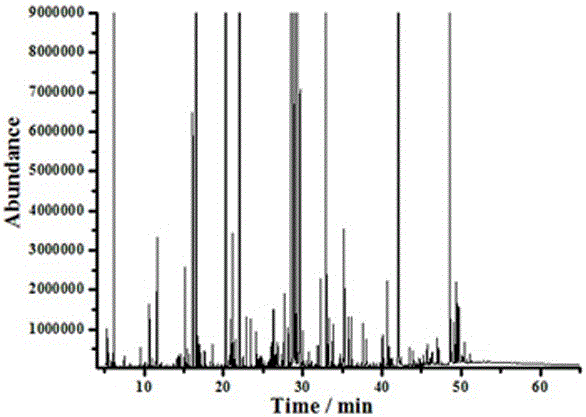
[0036]Example 2: Collect 18 pieces of fresh tobacco leaves at the 10th leaf position of China Tobacco 100 planted in Xiangxian County, Henan Province, quickly remove the trunk and wrap 3 pieces of tobacco leaves with tinfoil paper, freeze them quickly in liquid nitrogen, take out the samples wrapped in tinfoil paper from the liquid nitrogen, Smash it into pieces and vacuum freeze-dry it with a freeze dryer for 72 hours to remove moisture, and grind it to 40-60 mesh. Weigh 20~25mg of crushed tobacco leaves into a 2mL centrifuge tube, add 100μL deuterated tridecanoic acid internal standard solution, 1mL extraction solvent, ultrasonic extraction for 30min, after ultrasonic extraction, centrifuge at 4000r / min for 10min, take 200μL supernatant in a tip Bottom sample bottle and blow dry with nitrogen blower. Add 50 μL of methoxyamine hydrochloride pyridine solution with a concentration of 20 mg / mL to the dried extract, vortex and oscillate and react at 37°C for 90 min, then add 50 μ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com