Ceramic drilling method of composite nanosecond-picosecond-femtosecond laser technology
A technology of femtosecond laser and drilling method, which is applied in the direction of laser welding equipment, welding/welding/cutting items, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of short electrode life, slow EDM speed, limited ceramic aperture, etc., to achieve High processing efficiency, improving processing accuracy and processing quality, improving processing accuracy and processing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
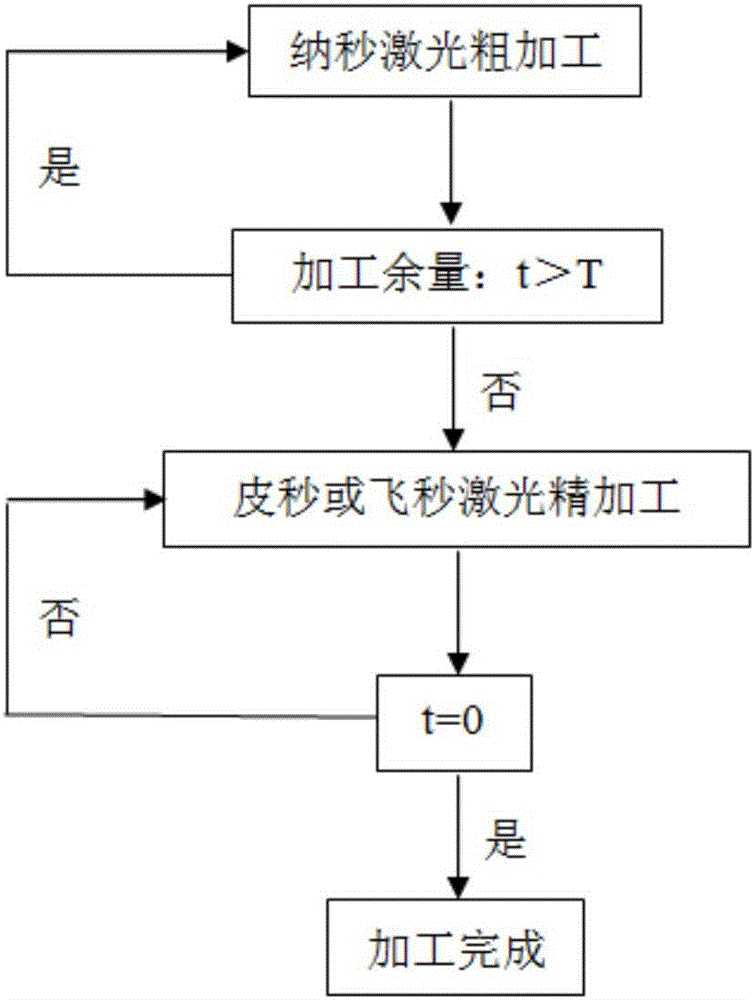
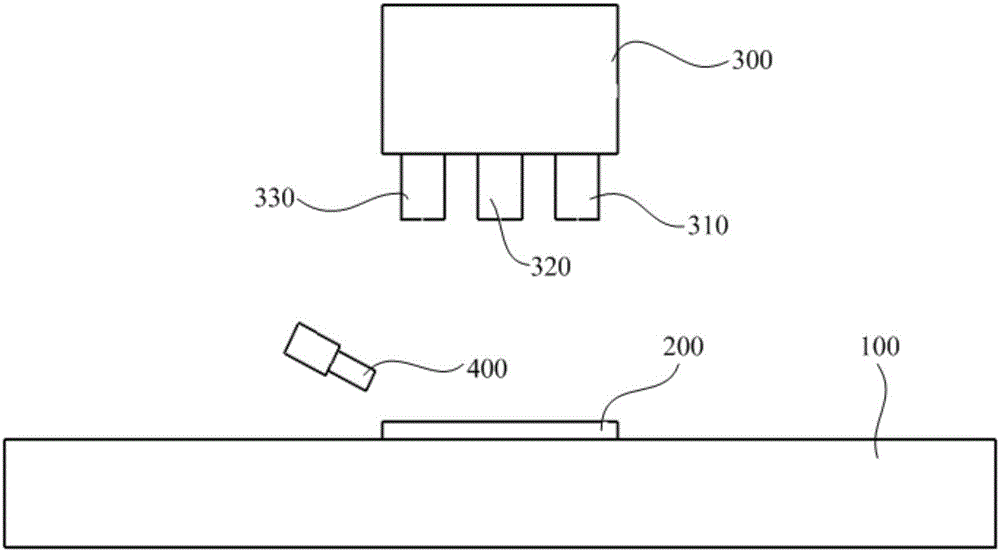
[0039] use as figure 2 The ceramic drilling system of the shown compound nanosecond-picosecond-femtosecond laser technology processes and drills the ceramic workpiece of the present embodiment, and the drilling method is as follows:
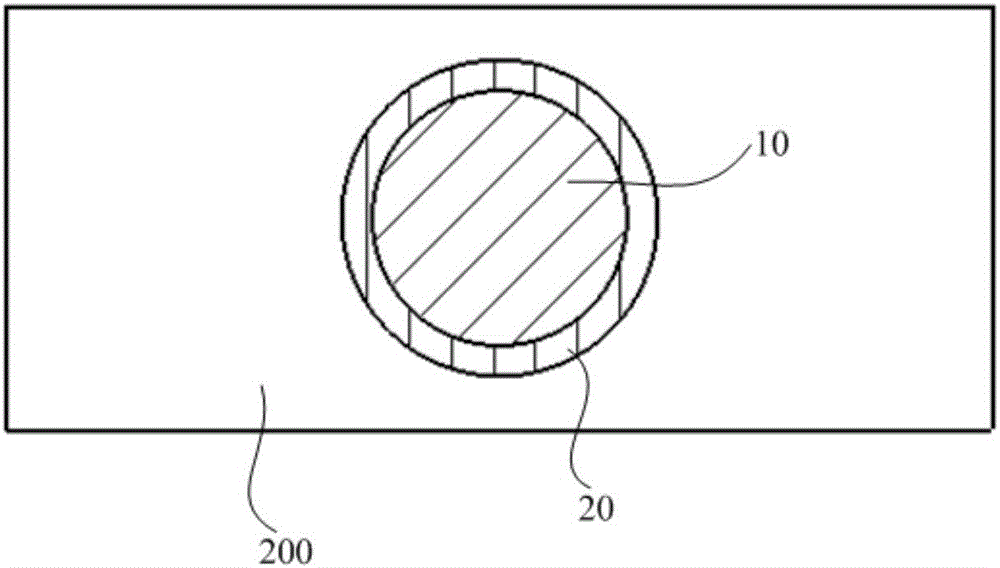
[0040] The ceramic workpiece 200 to be processed is ground and polished, and placed in alcohol for ultrasonic cleaning for 15 minutes. Take it out and fix it on the workbench 100, and adjust the focus of the workbench 100 and the multi-pulse width fiber laser 300 to complete the focus and determine the processing position, such as image 3 As shown, a rough machining area 10 and a finishing area 20 are determined. According to the processing accuracy requirements of the ceramic workpiece 200, the nanosecond laser 310 is used for rough processing first, and the processing path is the helix 1, and the finishing allowance T is reserved according to the data of the dimensional precision measuring instrument, and at the same time, the auxiliary gas ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] use as figure 2 The ceramic drilling system of the shown compound nanosecond-picosecond-femtosecond laser technology processes and drills the ceramic workpiece of the present embodiment, and the drilling method is as follows:
[0043] The ceramic workpiece 200 to be processed is ground and polished, and placed in acetone for ultrasonic cleaning for 30 minutes. Take it out and fix it on the workbench 100, and adjust the focus of the workbench 100 and the multi-pulse width fiber laser 300 to complete the focus and determine the processing position, such as image 3As shown, a rough machining area 10 and a finishing area 20 are determined. According to the processing accuracy requirements of the ceramic workpiece 200, the nanosecond laser 310 is used for rough processing first, and the processing path is a number of first concentric circles 1' from the outside to the inside, and the finishing allowance T is reserved according to the data of the dimensional precision meas...
Embodiment 3
[0045] use as figure 2 The ceramic drilling system of the shown compound nanosecond-picosecond-femtosecond laser technology processes and drills the ceramic workpiece of the present embodiment, and the drilling method is as follows:
[0046] The ceramic workpiece 200 to be processed is ground and polished, and placed in acetone for ultrasonic cleaning for 30 minutes. Take it out and fix it on the workbench 100, and adjust the focus of the workbench 100 and the multi-pulse width fiber laser 300 to complete the focus and determine the processing position, such as image 3 As shown, a rough machining area 10 and a finishing area 20 are determined. According to the processing accuracy requirements of the ceramic workpiece 200, the nanosecond laser 310 is used for rough processing first, and the processing path is a number of first concentric circles 1' from the outside to the inside, and the finishing allowance T is reserved according to the data of the dimensional precision mea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com