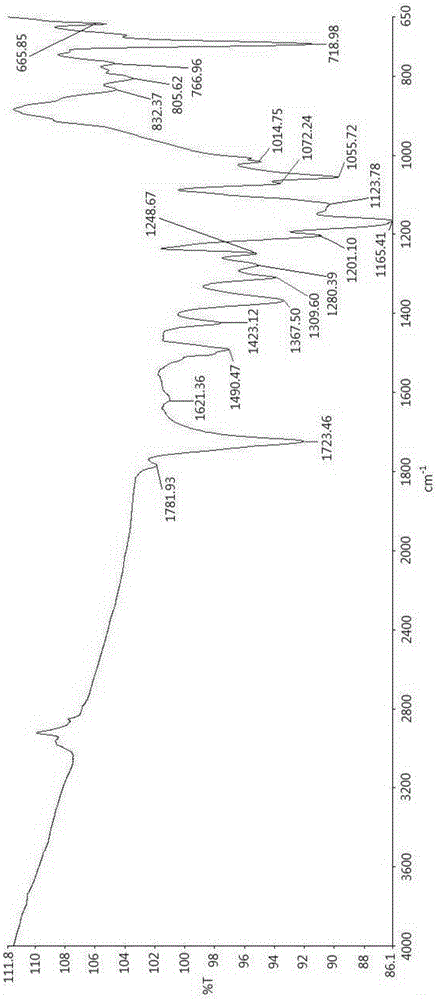
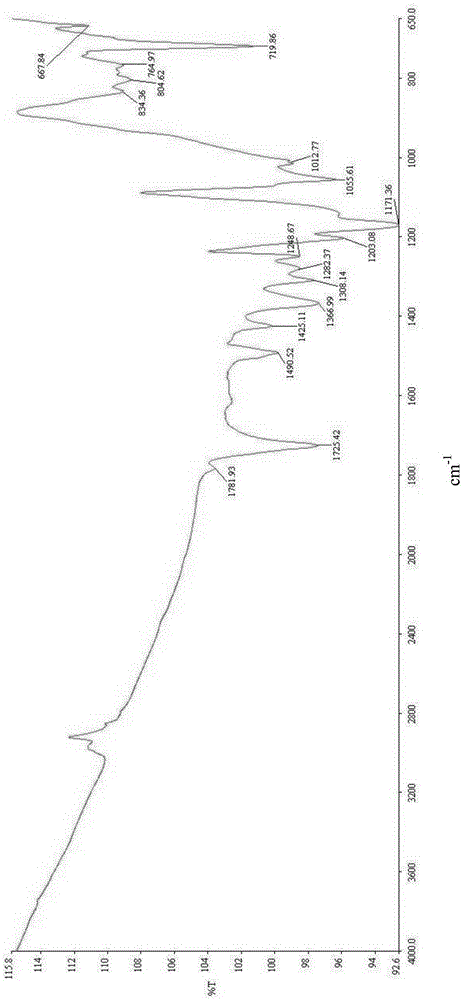
Polymide resin, method for manufacturing the same and thin film thereof
A technology of polyimide resin and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of printed circuits, electrical components, printed circuits, etc., and can solve the problems of LCP film processing and product application limitations, difficulty in controlling dimensional stability, poor mechanical properties, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101]24.20g (0.076mol) of 2,2'-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzidine (TFMB), 1.85g (0.017mol) of p-phenylenediamine (PDA), 2.36g (0.008mol) of 1 , 3-bis(4-aminophenoxy)benzene (TPE-R) and 244.37g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) were put into a three-necked flask. After stirring at 30°C until completely dissolved, add 41.75g (0.091mol) of p-phenylene bis(trimellitate dianhydride) (TAHQ) and 2.83g (0.005mol) of 4,4'- (4,4'-isopropyldiphenoxy)bis(phthalic anhydride) (PBADA), followed by continuous stirring and reaction at 25° C. for 24 hours to obtain the polyamic acid solution of Example 1. In this embodiment, the weight of the dianhydride monomer and the diamine monomer accounts for about 23wt% of the total weight of the reaction solution [(24.20+1.85+2.36+41.75+2.83) / (24.20+1.85+2.36+41.75+2.83+244.37) ×100%=23%].
Embodiment 2
[0103] 26.28g (0.082mol) of 2,2'-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzidine (TFMB), 3.74g (0.009mol) of 2,2'-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy ) phenyl] propane (BAPP) and 215.78g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) were put into a three-necked flask, stirred at 30°C until completely dissolved, then added 39.88g (0.087mol) of p- -Phenyl bis(trimellitate dianhydride) (TAHQ) and 2.02 g (0.005 mol) of 4,4'-(hexafluoropropylene) bis-phthalic anhydride (6FDA), followed by Stir and react at 25° C. for 24 hours to obtain the polyamic acid solution of Example 2. In this embodiment, the weight of the dianhydride monomer and the diamine monomer accounts for about 25 wt% of the total weight of the reaction solution [(26.28+3.74+39.88+2.02) / (26.28+3.74+39.88+2.02+215.78)×100%= 25%].
Embodiment 3
[0105] 29.13g (0.091mol) of 2,2'-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzidine (TFMB), 1.84g (0.017mol) of p-phenylenediamine (PDA), 1.66g (0.006mol) of 1 , Put 3-bis(4-aminophenoxy)benzene (TPE-R) and 271.31g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) into a three-necked flask, stir at 30°C until completely dissolved , and then added 47.12g (0.102mol) of p-phenylene bis(trimellitate dianhydride) (TAHQ) and 5.92g (0.011mol) of 4,4'-(4,4'-isopropyl Diphenoxy) bis(phthalic anhydride) (PBADA), followed by continuous stirring and reaction at 25° C. for 24 hours to obtain the polyamic acid solution of Example 3. In this embodiment, the weight of the dianhydride monomer and the diamine monomer accounts for about 24wt% of the total weight of the reaction solution [(29.13+1.84+1.66+47.12+5.92) / (29.13+1.84+1.66+47.12+5.92+271.31) ×100%=24%].
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| dielectric loss factor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com