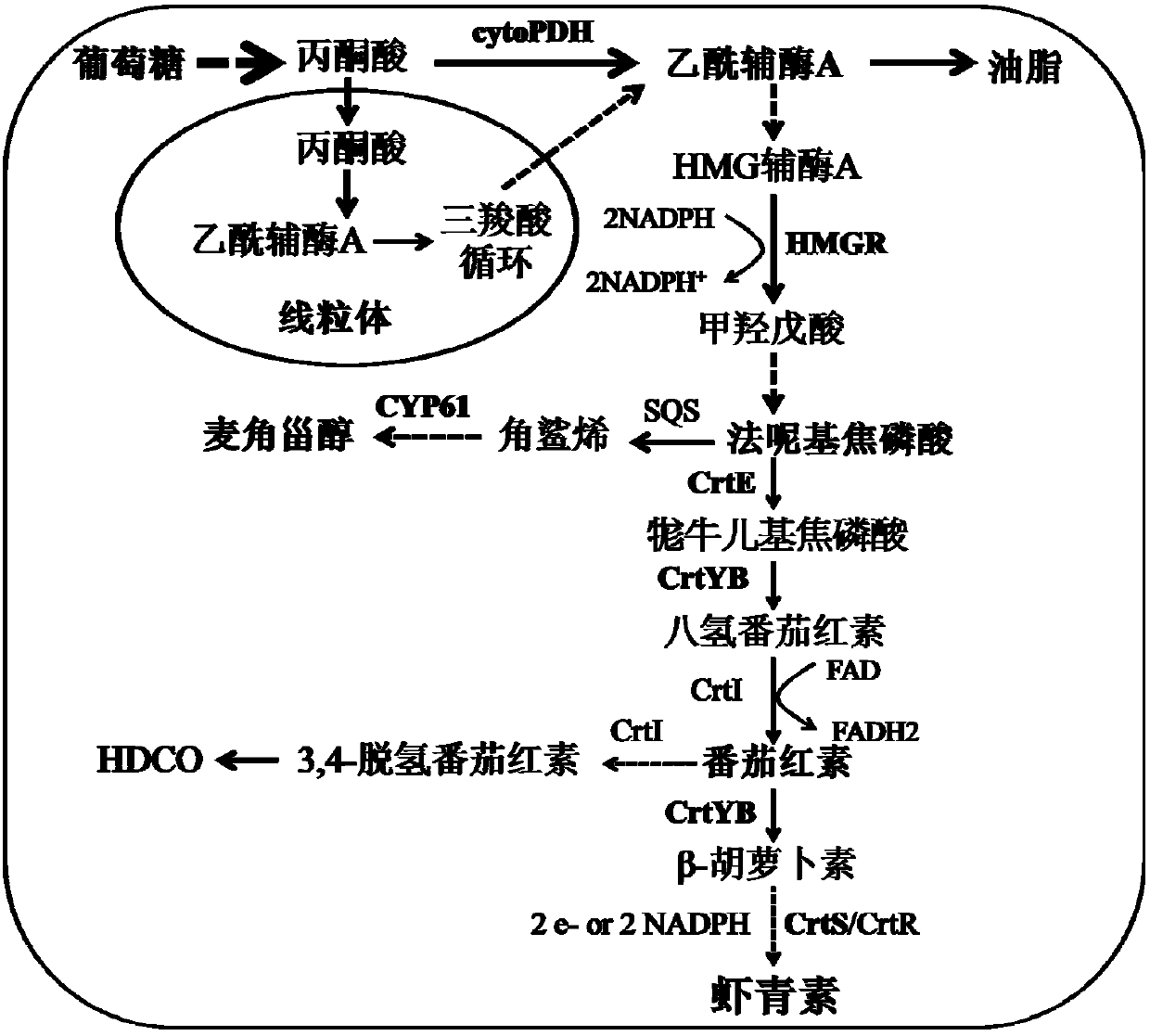
A kind of high-yield astaxanthin Rhodotorula engineering bacteria and its construction method
A technology of red yeast and engineering bacteria, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of high price, unable to meet market demand, limited output, etc., and achieve the effect of improving metabolic flux
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1, plasmid construction
[0025] 1.1 Cloning of genetic elements
[0026] 1) Acquisition of genes ADH2, ALD6, CrtE, CrtYB, CrtS and CrtR:
[0027] The genomic DNA of Phaffia rhodozyme was extracted by the glass bead breaking method, and the genomic DNA of Phaffia rhodozyme was used as a template, and the primer sequences recorded in Table 1 were respectively used as the primer sequences of each gene to be amplified by KAPA HiFi high-fidelity DNA polymerase. Genes were amplified and PCR amplification was performed respectively. The amplification system was 25ul (2×KAPA Mix, 12.5ul; 0.5ul for each 10uM primer; 1ul template; add water to make up to 25ul) to obtain the sequence of each gene.
[0028] The amplification conditions are: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3 minutes; denaturation at 98°C for 20 seconds; annealing at 60-72°C for 15 seconds; minute.
[0029] 2) Synthesis of genes ACS, PHK and PTA: Escherichia coli acetyl-CoA synthetase gene ACS, Aspergillu...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Embodiment 2, the construction of Phaffia rhodozyme engineering bacteria
[0077] 2.1 Obtaining the expression cassette
[0078] The plasmid pCrtS described in Table 6 was used as a template, the CYPUP-NF and CYPDN-NR described in Table 7 were used as primers, and the CrtS-Hgr-CYP61 expression cassette was amplified by PCR using KAPA HiFi high-fidelity DNA polymerase.
[0079] The plasmid pCrtE described in Table 6 was used as a template, rDNA1-F and rDNA2-R described in Table 5 were used as primers, and the CrtE-G418-rDNA expression cassette was amplified by PCR using KAPA HiFi high-fidelity DNA polymerase.
[0080] The plasmids pStH and pSR described in Table 6 were respectively digested with SmaI to obtain the expression cassette CrtS-tHMGR-Hgr-CYP61 or CrtS-CrtR-Hgr-CYP61.
[0081] Use AflII to digest the plasmids pCrtE, pEYB, pKA, pA3 and pPDH recorded in Table 6, respectively, to obtain the expression cassettes CrtE-G418-rDNA, CrtE-CrtYB-G418-rDNA or PHK-PTA-BLM-...
Embodiment 3
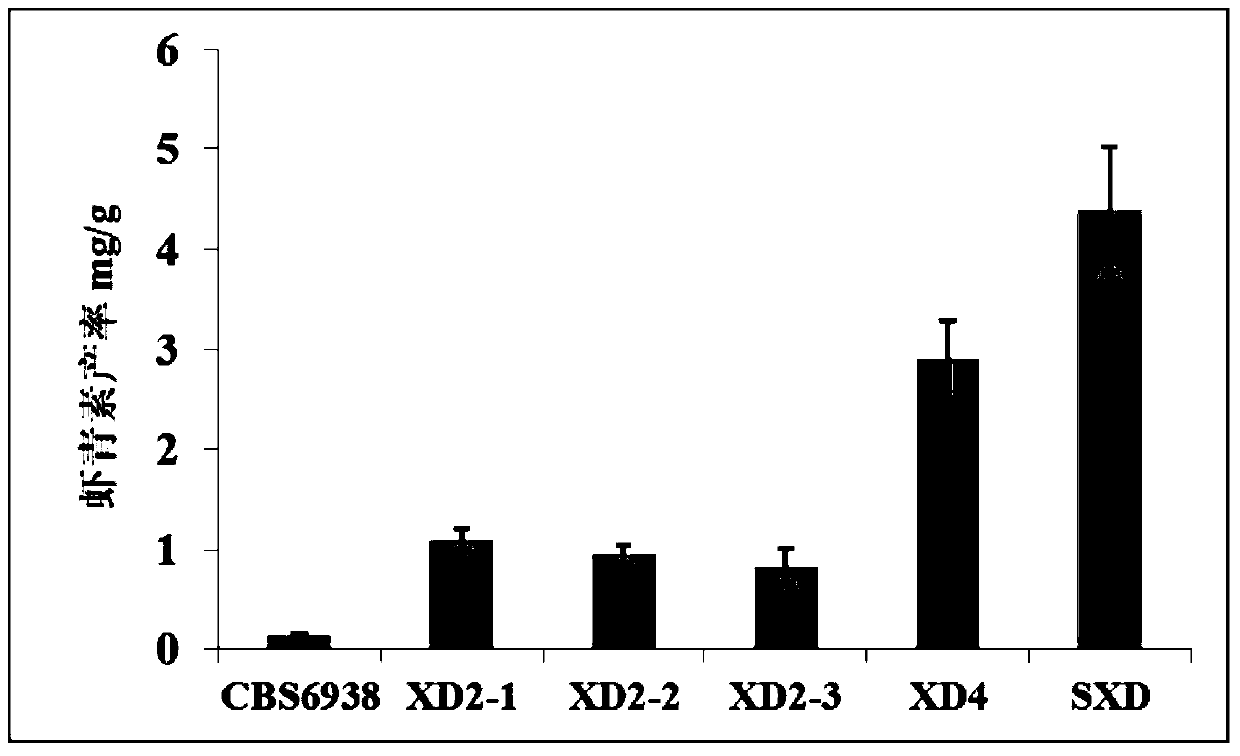
[0092] Embodiment 3, engineering strain culture produces astaxanthin
[0093] 3.1 Strain shake flask culture
[0094] The strains CBS 6938, XD4 and SXD were respectively activated on the YM solid plate and cultured at 22°C for 4 days. Single colonies were picked and inoculated into 250ml shake flasks filled with 20ml CNM medium, cultured at 22°C for 48h, and used as seed culture solution. Then the various seed liquids obtained were inoculated into 250ml shake flasks containing 30ml CNM medium according to the inoculum amount of 8%, respectively, cultivated at 22°C for 3 days, then cultivated at 18°C for 3 days, and set aside.
[0095]Among them, the composition of CNM medium is glucose 40g / L, peptone 3g / L, yeast extract 1.5g / L, corn steep liquor 1g / L, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.8g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5g / L,KH 2 PO 4 1.5g / L, K 2 HPO 4 0.3g / L, CaCl 2 2H 2 O0.1g / L, biotin 1mg / L, soybean oil 2ml / L.
[0096] 3.2 Strain fermenter culture (taking strain SXD as an example)
[009...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com