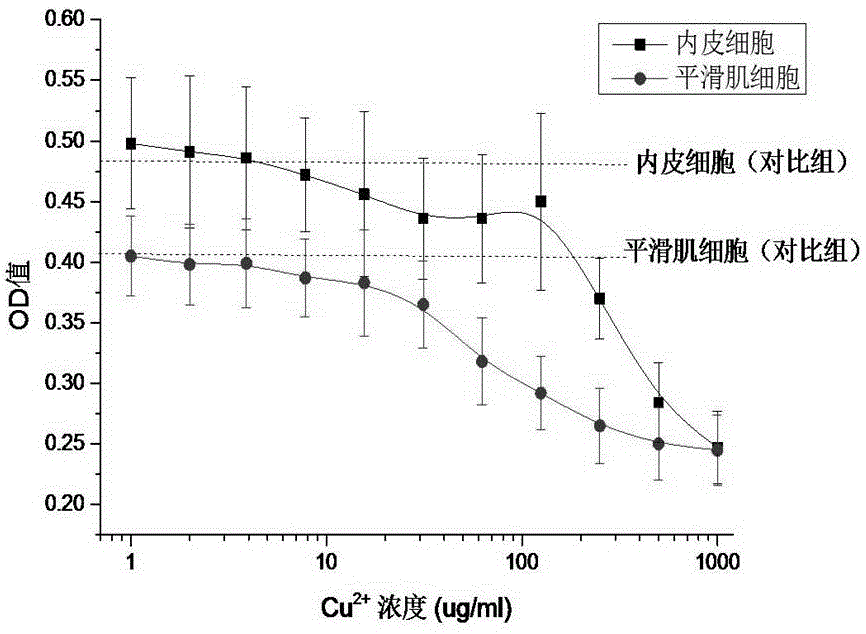
Inorganic nano-coating capable of regulating and controlling cell response and preparation method of inorganic nano-coating
An inorganic nano-coating and coating technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as damage and uncontrollability, and achieve the effects of changing side effects, satisfying mechanical matching, and easily controlling the proportion of coating components.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Preparation of copper-titanium composite thin films.
[0036] Copper-titanium composite films were deposited on the surface of L605 alloy by magnetron sputtering.
[0037] The cathode target materials are high-purity titanium target and high-purity copper target respectively, and the copper-titanium atomic ratio is realized by adjusting the target current, and the copper-titanium combination form can be realized by the deposition process such as deposition temperature, bias voltage, and time.
[0038] L605 alloy was cleaned ultrasonically with acetone. First use cleaning: put a little acetone in the beaker, the liquid level can exceed the sample by a little, and then use ultrasonic cleaning for 5 minutes. Then wash with absolute ethanol. Pour a little absolute ethanol into the beaker until the liquid level exceeds the sample by a little, then clean it with ultrasonic waves for 5 minutes. Finally wash with distilled water. Pour distilled water into the beaker, the li...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Preparation of copper-iron composite thin films.
[0045] Sample pretreatment and sputter cleaning are the same as in Example 1.
[0046] The cathode used in the experiment of the present invention is pure iron, and the arc is ignited under the pulse trigger voltage to generate iron plasma. A magnetic filter elbow is used to filter macroscopic particles and neutral particles. Under the action of sputtering bias, titanium ions and iron ions move to the surface of the substrate material, thereby forming a copper-iron degradable film on the surface of the material.
[0047] Establish a vacuum system, the base vacuum of the vacuum chamber is 1.0×10 -3 At Pa, start the sample rotation at a rotation rate of 30-40rp / m, turn on the sample stage heating system, and ensure that the substrate temperature is 200°C. Introduce argon gas, the gas flow rate is 60-100 sccm, and the vacuum chamber pressure is guaranteed to be 0.5-0.8 Pa. The sputtering power was set to 500W, the pulse...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Preparation of copper-zinc composite thin films.
[0052] Sample pretreatment and sputter cleaning are the same as in Example 1.
[0053] The cathode used in the experiment of the present invention is pure zinc, and the arc is ignited under the pulse trigger voltage to generate iron zinc ions. Under the action of sputtering bias, zinc ions and copper ions move to the surface of the base material, thereby forming a copper-zinc degradable film on the surface of the material.
[0054] Establish a vacuum system, the base vacuum of the vacuum chamber is 1.0×10 -3 At Pa, start the sample rotation at a rotation rate of 30-40rp / m, turn on the sample stage heating system, and ensure that the substrate temperature is 200°C. Introduce argon gas, the gas flow rate is 60-100 sccm, and the vacuum chamber pressure is guaranteed to be 0.5-0.8 Pa. The sputtering power was set to 500W, the pulse duty cycle was 20%, and the negative bias voltage of 200V was applied to the substrate. T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com