Dual frequency impedance matching based microstrip rectifier circuit
An impedance matching circuit, rectifier circuit technology, applied in circuit devices, irreversible AC power input conversion to DC power output, electrical components and other directions, can solve the problems of large size, low efficiency, small bandwidth, etc., to reduce circuit size, Efficiently matching the size and improving the effect of output voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
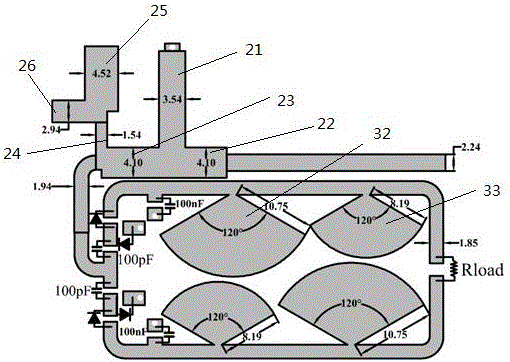
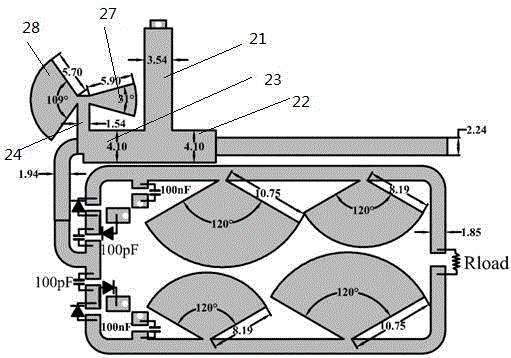
[0030] Such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, the microstrip rectification circuit based on dual-frequency impedance matching includes a rectification circuit 1, and also includes an input connector, a dual-frequency impedance matching circuit 2 and a harmonic suppression circuit 3. The rectification circuit 1 includes two rectification branches 11, The harmonic suppression circuit 3 includes two harmonic suppression branches 31, the output ends of the two rectification branches 11 are respectively connected to the input ends of the two harmonic suppression branches 31; The input end of the impedance matching circuit 2 is connected, and the output end of the dual-frequency impedance matching circuit 2 is respectively connected with the input ends of the two rectification branches 11 .
[0031] In the above solution, due to the addition of the dual-frequency impedance matching circuit 2, the rectification circuit 1 can achieve impedance matching in two frequency bands, so the rectific...
Embodiment 2
[0042] In this embodiment, the S11 parameters of the rectifier circuit provided in Embodiment 1 are tested, and the specific test results are as follows Figure 5 , 6 As shown, it can be seen from the figure that the operating frequency of the dual-frequency microstrip rectifier circuit is 875MHz and 1.83GHz, and the return loss (S11) at these two frequencies can reach a local minimum, that is, the dual-frequency impedance matching network can simultaneously Impedance matching is realized at the corresponding working frequency, and the energy input corresponding to the working frequency is maximized.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com