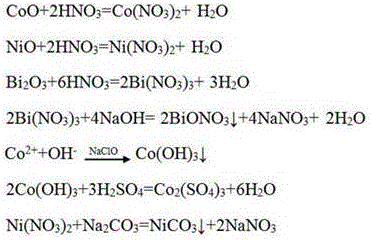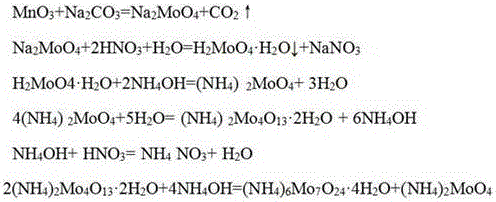Technology for recycling molybdenum, bismuth, cobalt and nickel from dead catalyst
A waste catalyst and process technology, which is applied in the process of cobalt and nickel to recover molybdenum and bismuth at the same time, can solve the problems of large environmental pollution, low recovery rate and high production cost, achieve good separation effect and eliminate environmental pollution Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
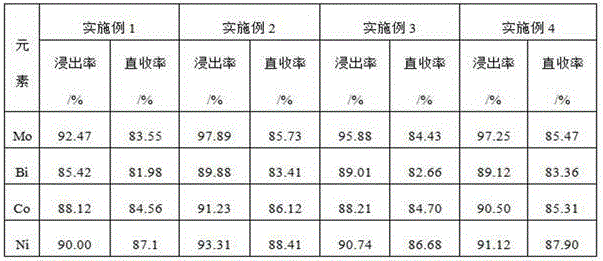
Embodiment 1
[0026] The process of reclaiming molybdenum, bismuth, cobalt and nickel from spent catalyst comprises the following steps:
[0027] (1) Recovery of molybdenum
[0028] a. Alkali leaching: Detect the amount of molybdenum, bismuth, cobalt, and nickel in the spent catalyst, grind the spent catalyst to 100 mesh and heat it, control the liquid-solid weight ratio to 4:1, and add the concentration at 40°C to 200g / L of sodium carbonate solution, the molar ratio of molybdenum and sodium carbonate is 1:1, and the leaching reaction is carried out when the temperature is raised to 80° C., and the leaching time is 60 min, filtered to obtain alkali leaching solution and alkali leaching residue;
[0029] b. Precipitating molybdic acid: After heating the alkali leaching solution to 60°C, add nitric acid to control the pH to 0.5, then boil, filter after 30 minutes, and rinse the obtained molybdic acid with a nitric acid solution with a pH of 0.5.
[0030] c. Transfer to tetramolybdenum: the ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The process of reclaiming molybdenum, bismuth, cobalt and nickel from spent catalyst comprises the following steps:
[0040] (1) Recovery of molybdenum
[0041] a. Alkali leaching: Detect the amount of molybdenum, bismuth, cobalt, and nickel in the spent catalyst, grind the spent catalyst to 150 mesh and heat, control the liquid-solid weight ratio to 5:1, and add the concentration at 50°C to 300g / L of sodium carbonate solution, the molar ratio of molybdenum and sodium carbonate is 1:2, the leaching reaction is carried out when the temperature is raised to 90°C, the leaching time is 90min, and filtering is performed to obtain alkali leaching solution and alkali leaching residue;
[0042] b. Precipitating molybdic acid: After heating the alkali leaching solution to 70°C, add nitric acid to control the pH to 1.0, then boil, filter after 60min, and rinse the obtained molybdic acid with a nitric acid solution with a pH of 1.0;
[0043] c. Transfer to tetramolybdenum: the m...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The process of reclaiming molybdenum, bismuth, cobalt and nickel from spent catalyst comprises the following steps:
[0053] (1) Recovery of molybdenum
[0054]a. Alkali leaching: Detect the amount of molybdenum, bismuth, cobalt, and nickel in the spent catalyst, crush the spent catalyst to 120 mesh, control the liquid-solid weight ratio to 4.5:1, and add a concentration of 250g / L at 45°C Sodium carbonate solution, so that the molar ratio of molybdenum and sodium carbonate is 1:1.5, when the temperature is raised to 85°C, the leaching reaction is carried out, and the leaching time is 75min, filtered to obtain alkali leaching solution and alkali leaching residue;
[0055] b. Precipitating molybdic acid: warming up the alkali leaching solution to 65°C, adding nitric acid, controlling the pH to 0.5, then boiling, filtering after 45min, and rinsing the obtained molybdic acid with a nitric acid solution with a pH of 0.5;
[0056] c. Transfer to tetramolybdenum: the molybden...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com