Zinc oxide nanorod based random laser and laser gain medium manufacturing method
A technology of zinc oxide nanorods and random lasers, applied in the field of random lasers, can solve problems such as cumbersome processes, achieve low threshold, non-toxic preparation methods, and environmentally friendly effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The fabrication method of the random laser gain medium based on ZnO nanorods described in this example.
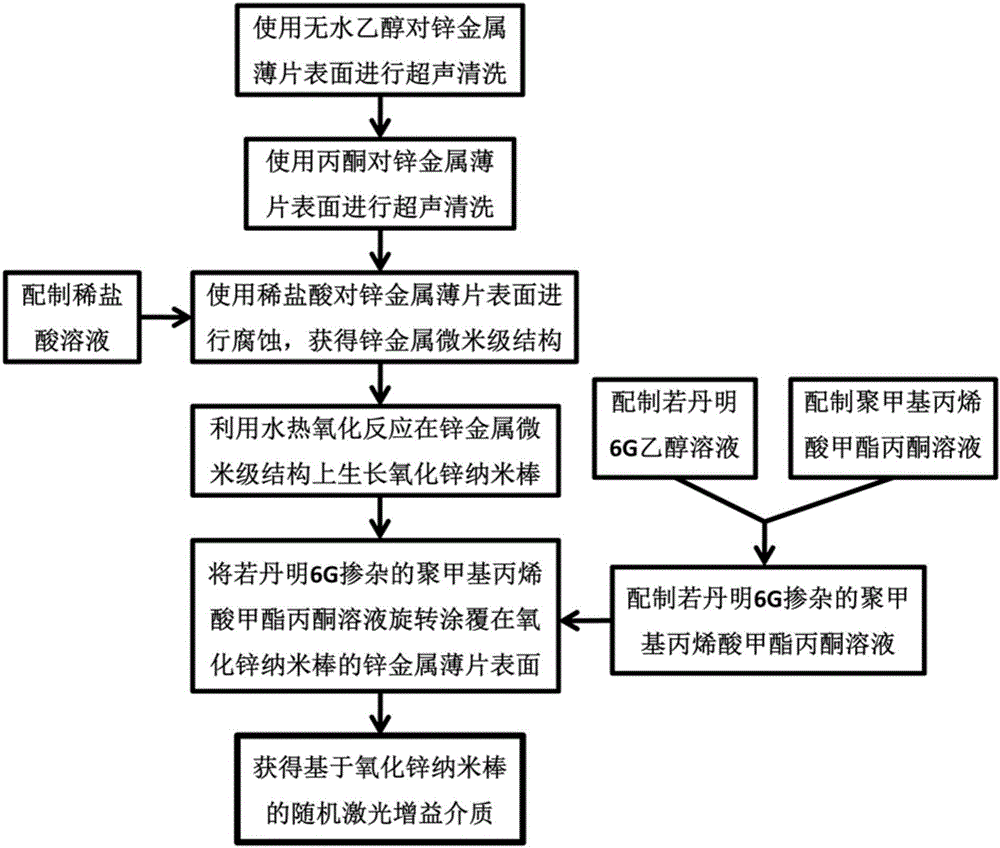
[0037] According to the steps of the method for making a random laser gain medium based on zinc oxide nanorods as described above, the specific operation process is as follows image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0038] (1) Measure 8.33ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid in a volumetric flask, add deionized water, and prepare a 1mol / L dilute hydrochloric acid solution for use;
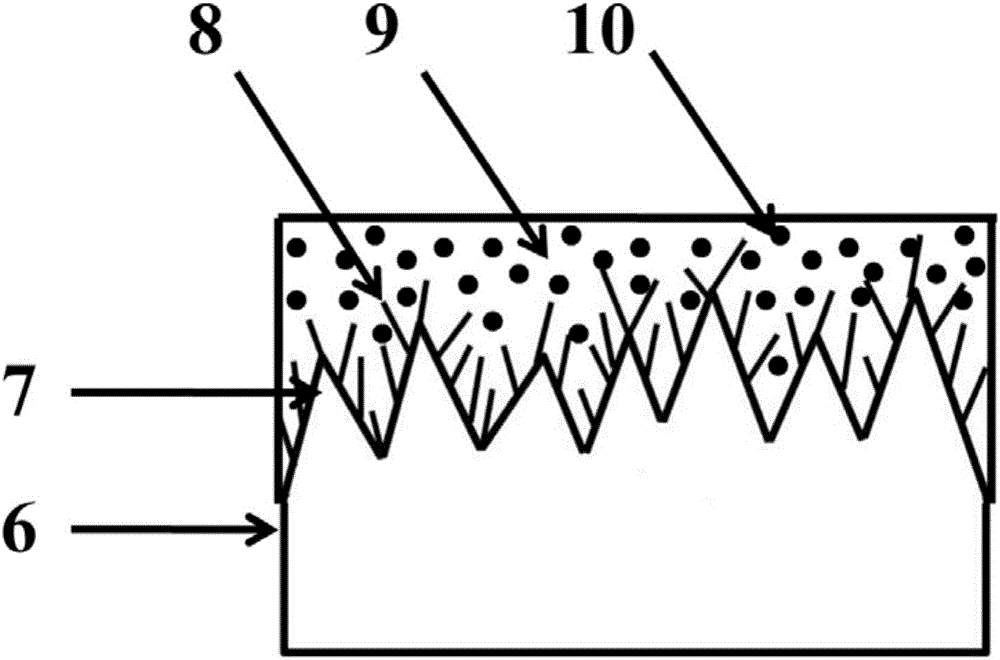
[0039] (2) The zinc metal flakes 6 with a thickness of 1mm are cut and grown into 25mm, and the rectangular flakes with a width of 15mm; the rectangular zinc metal flakes 6 are placed in dehydrated alcohol, ultrasonically cleaned for 30min, and then the zinc metal flakes are cleaned with nitrogen gas. Blow dry with absolute ethanol on the surface;
[0040] (3) Place the rectangular zinc metal flake 6 after cleaning with absolute ethanol described in step (2) in acetone, ultras...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The method for making the random laser gain medium based on zinc oxide nanorods.
[0047] According to the steps of the method for making a random laser gain medium based on zinc oxide nanorods as described above, the specific operation process is as follows image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0048] (1) Measure 8.33ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid in a volumetric flask, add deionized water, and prepare a 1mol / L dilute hydrochloric acid solution for use;
[0049] (2) The zinc metal flakes 6 with a thickness of 1mm are cut and grown into 25mm, and the rectangular flakes with a width of 15mm; the rectangular zinc metal flakes 6 are placed in dehydrated alcohol, ultrasonically cleaned for 30min, and then the zinc metal flakes are cleaned with nitrogen gas. Blow dry with absolute ethanol on the surface;
[0050] (3) Place the rectangular zinc metal flake 6 after cleaning with absolute ethanol described in step (2) in acetone, ultrasonically clean it for 3...
Embodiment 3
[0056] In this embodiment, the random laser gain medium 4 based on zinc oxide nanorods is used to build a random laser.
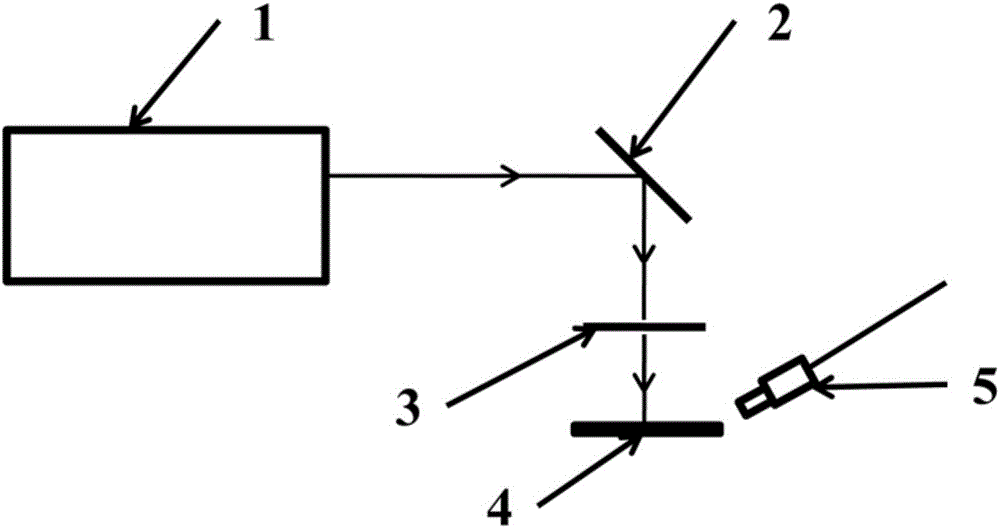
[0057] The pump laser 1 described in the present embodiment selects Nd:YAG laser, the pump wavelength is 532nm, the frequency is 10Hz, and the pulse width is 10ns; the reflector 2 selects a 532nm reflector; the cylindrical lens 3 selects a focal length of 10mm The cylindrical lens; the optical fiber spectrometer probe 5 is an Ocean Optics USB4000 spectrometer with an optical resolution of 1.5nm.
[0058] according to figure 1 The schematic diagram of the optical path of the random laser based on zinc oxide nanorods is shown, and each component is built. Adjust the orientation of the reflector 2 to be 45° to the horizontal direction; place the cylindrical lens 3 horizontally at a distance of 30 mm from the reflector; place the fabricated random laser gain medium 4 based on zinc oxide nanorods horizontally at the distance from the cylindrical lens 3 10 mm; ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com