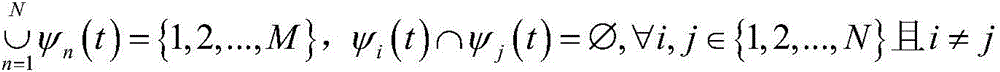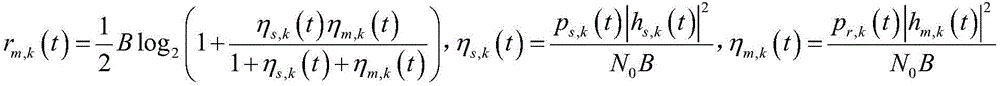Energy efficiency optimization based cooperative communication system resource allocation method
A technology of cooperative communication and system resources, which is applied in the field of resource allocation of cooperative communication systems based on optimal energy efficiency, and can solve problems such as reducing algorithm complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] A resource allocation method for a cooperative communication system based on energy efficiency optimization, including
[0062] Step 1: Build a system model;
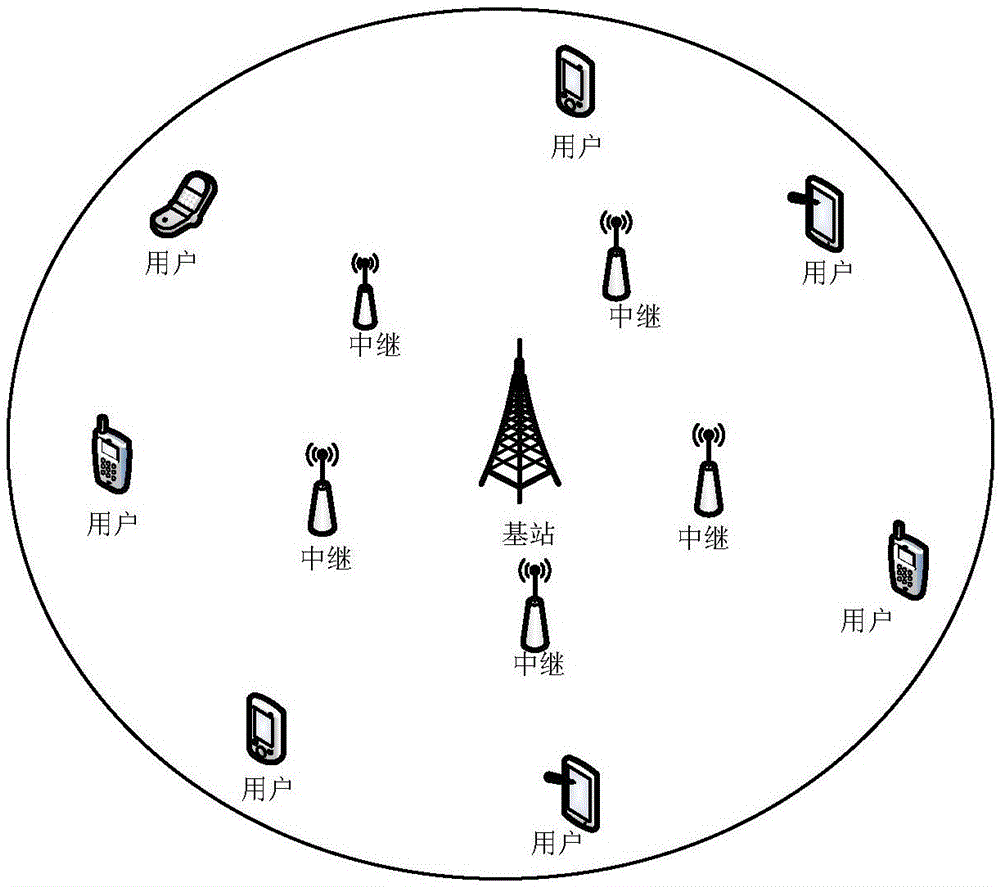
[0063] The present invention is aimed at a special application scene, comes from practical application, and the scene setting is meticulous and reasonable, and has practical guiding significance. Such as figure 1 As shown, the multi-relay multi-user OFDM downlink network, the system consists of base station S, M users (D 1 ,...,D M ) and N relays (R 1 ,...,R N )composition. Users are freely distributed in the ring outside the relay in the cell. Assuming that the user is far away from the base station, the user cannot directly receive the signal transmitted by the base station. The system is in TDD mode, that is, signal transmission is divided into two time slots. In the first time slot, the base station sends a signal to the relay through the subcarrier. In the next time slot, the relay receives the signa...
Embodiment 2
[0089] On the basis of the first embodiment, using the Lagrange multiplier algorithm, we can use the subgradient method in the process of each iteration of the loop, and choose a gradual step length, so that the optimization is more accurate. Specifically, the Lagrangian factor β in the Lagrangian form of the optimization problem P1 k ,β s ,β r,n The iterative update method of the method adopts a subgradient algorithm, which has lower complexity and is more efficient. The iterative update equation of the subgradient algorithm is:
[0090] β k ( τ + 1 ) = [ β k ( τ ) - δ k ( τ ) ...
Embodiment 3
[0097] This embodiment provides a detailed method to solve the most optimization problem P1, specifically:
[0098] It can be seen from the optimization problem P1 that the optimization model of the energy efficiency is a nonlinear mixed integer programming problem, which cannot be solved by the current conventional method. In order to reduce the complexity of the problem, the present invention first uses the Dinkelbach method to optimize the model It becomes a linear convex programming, and then solves the simplified linear programming problem based on the dual programming. At the same time, the optimization problem is divided into two sub-problems to complete: subcarrier allocation and power allocation.
[0099] First, consider the subcarrier allocation;
[0100] Although the exhaustive algorithm as a carrier allocation algorithm can greatly improve the performance of the system, its computational complexity is very high. The present invention adopts a low-complexity carrie...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com