A novel saccharomycopsis fibuligera strain, a culturing method thereof and uses of the strain
A technology of buttoning capsules, laminating membranes and culturing methods, which is applied in the field of microorganisms and achieves the effect of great application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The screening of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
[0039] In the process of researching traditional liquor brewing, the present invention screens and obtains some bacterial strains from distillery waste. After further research, some strains have high biomass in culture, so they grow well when they are cultured on various agricultural by-products (including various processed residues such as discarded grains) as substrates. It was further found that a strain of bacteria had the effect of reducing the content of toxic substances on the cake raw materials. Name it WNY-2 and conduct further research.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Identification of Example 2 Bacterial Strains——16S rDNA Sequence Analysis
[0041] (1) Total DNA extraction
[0042] After culturing with potato sucrose medium, the cells were collected by centrifugation, washed 3 times with sterile distilled water, dissolved in extraction buffer (100 mM Tris Cl, 100 mM EDTA-Na2, 200 mM NaCl, 2% CTAB, pH 8.0), 37 °C Shake for 45 minutes, add 20% SDS, and bathe in water at 65°C for 1 hour. Centrifuge at 12,000rpm for 10min, and collect the supernatant. The supernatant was extracted twice with an equal volume of phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), added with a final concentration of 0.3M NaAC (pH 5.2) and 2 times the volume of absolute ethanol, and precipitated at room temperature for 1 h . Centrifuge (12,000 rpm) at 4°C for 20 min. The precipitate was washed twice with 70% ethanol, evaporated to dryness and dissolved in 50 μL TE (10 mmTris-Hcl, 1 mmNa2EDTA).
[0043] (2) 16S rDNA amplification and sequencing
[0044] Usi...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3 Morphological characteristics and physiological and biochemical characteristics identification of bacterial strain CGMCC No.12221 of the present invention
[0050] 1. Observation of colony and bacterial morphology
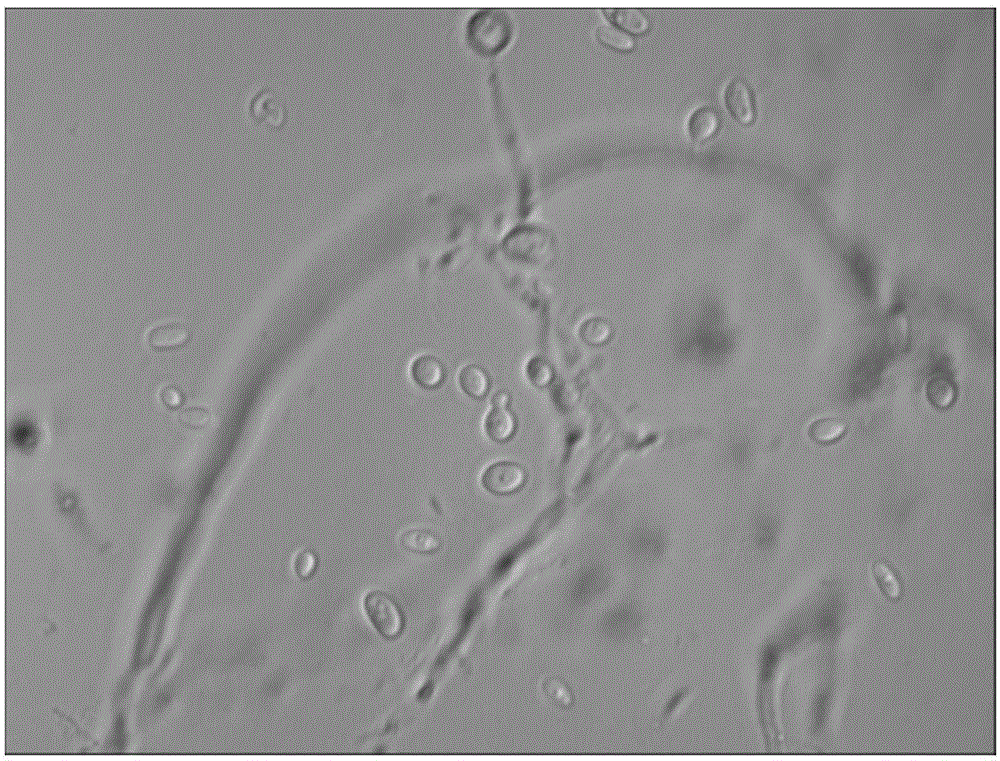
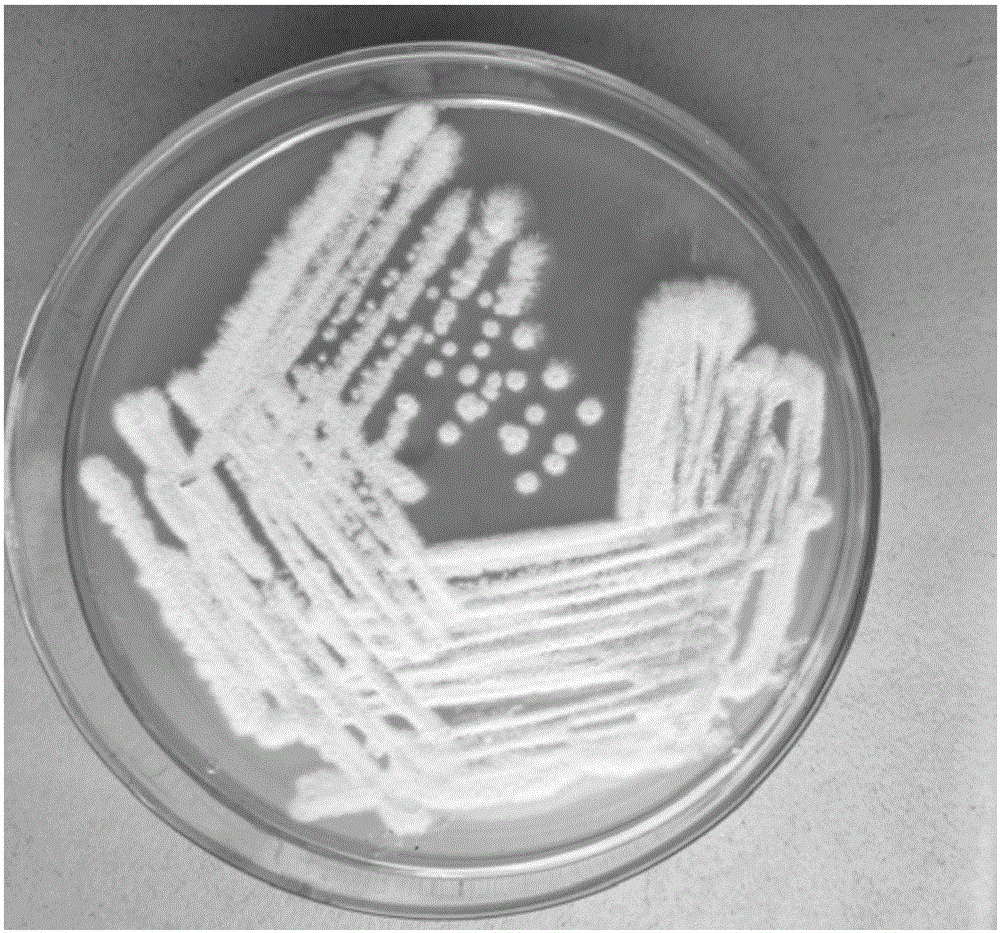
[0051] Streak inoculate this strain on the potato sucrose plate medium, culture at 30°C for 4 days, observe the colony morphology during the culture (see image 3 ); pick a little thalline with an inoculation needle, make slices by soaking in water, and observe the shape of thalli under a microscope (see figure 1 and figure 2 ).
[0052] The results were as follows: under the microscope, the cells were oval, with a length of 5-7.5 μm (average 6.2 μm) and a width of 3.8-5 μm (4.5 μm). Visible cell budding, unilateral budding reproduction. Early growth forms hyphae and produces spores (see figure 1 and figure 2 )
[0053] Colony characteristics:
[0054] The colony is white and flat; the diameter is about 5-10 mm; the surface is rough an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com