OCT-based in-situ three-dimensional printing skin repairing equipment and implementation method thereof
A skin repair and three-dimensional printing technology, applied in the field of biomedical engineering, can solve problems such as limited imaging resolution, long technical measurement time, and large equipment, and meet the requirements of reducing the speed of cell enrichment, instant skin repair, and real-time The effect of monitoring
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described
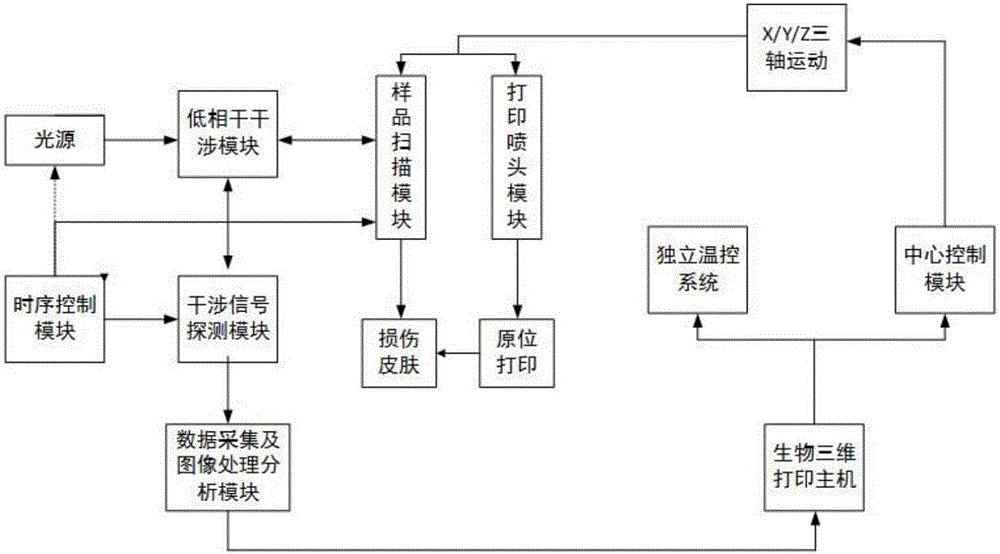
[0042] The in situ three-microbial printing system in vivo includes a 3D bioprinting device based on optical coherence tomography and a 3D bioprinting device with controllable printing parameters. The schematic block diagram is as follows: figure 1 shown.
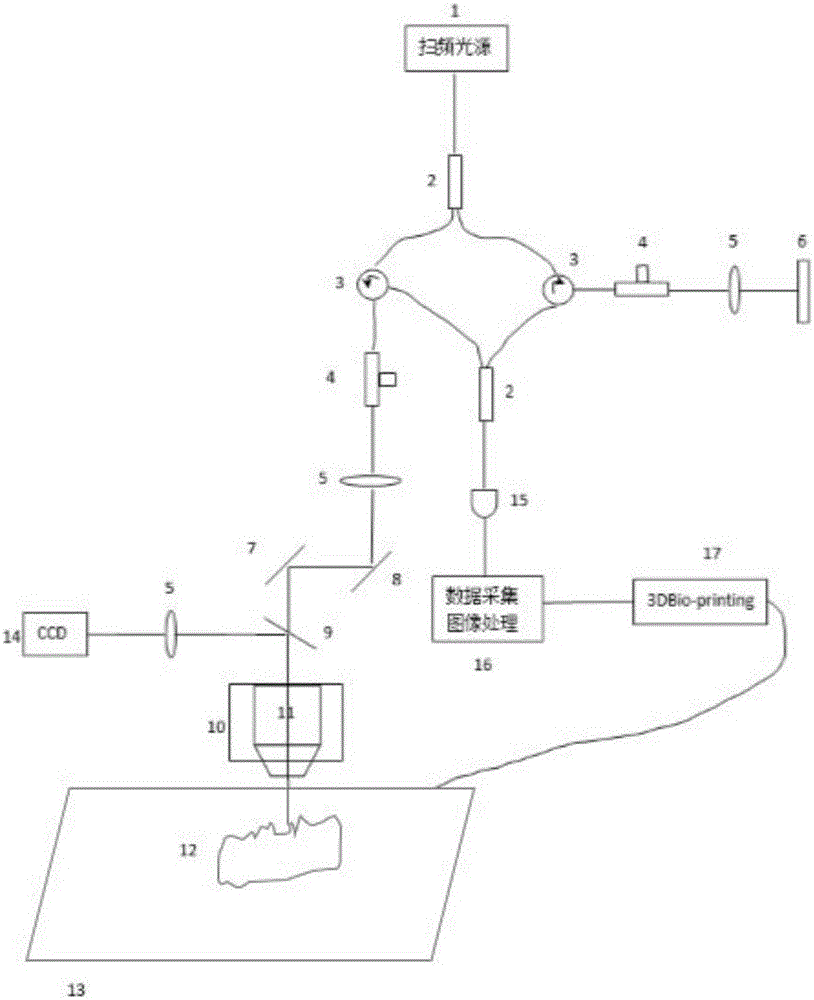
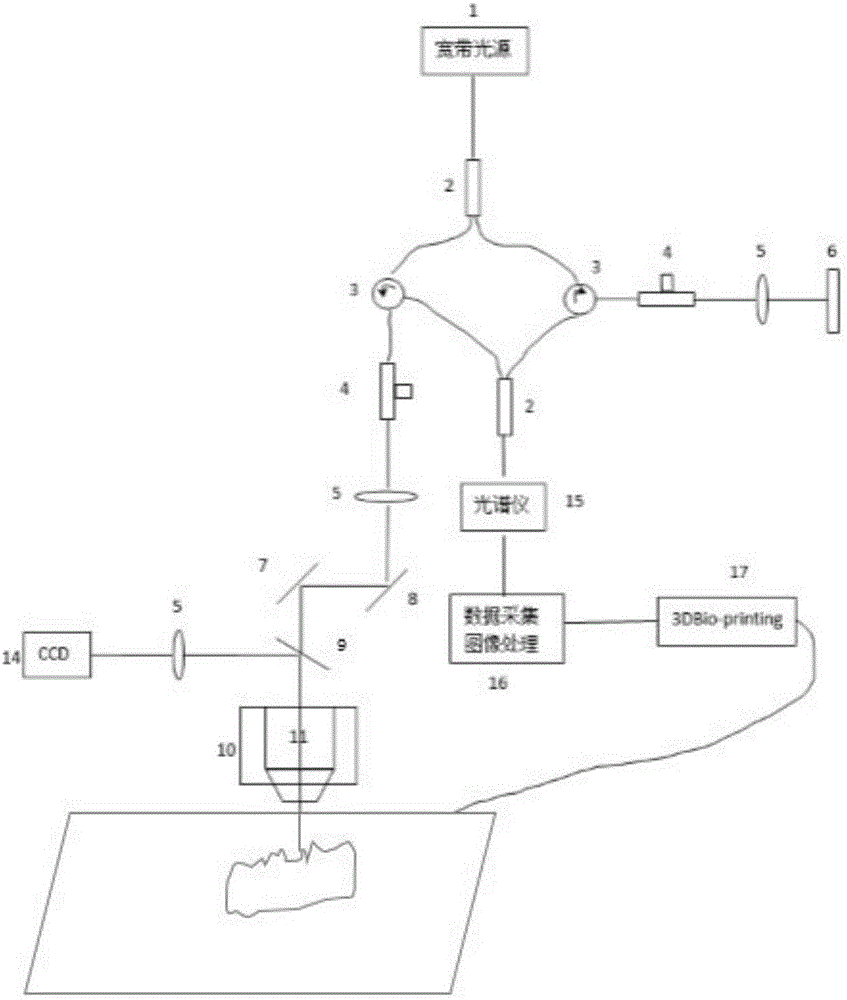
[0043] Figure 2(a) is a detailed view of the in situ 3D bioprinting system based on swept source coherence tomography (SS-OCT), and Figure 2(b) is based on spectral domain coherence tomography (SD-OCT) A detailed view of the in situ 3D bioprinted skin repair system in vivo. The working principle is: the light emitted by light source 1 (Fig. 2(a) is a frequency-sweeping light source, and Fig. 2(b) is a broadband light source) is divided into two paths by a 1×2 fiber coupler 2, one of which is a reference arm, and the light passes through The fiber optic circulator 3, the fiber polarization controller 4 and the collimato...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com