P-type alpha-MgAgSbSn thermoelectric material with high optimum value and preparation method
A technology of thermoelectric materials and raw materials, which is applied in the direction of thermoelectric device node lead-out materials, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable large-scale commercial application, scarce element reserves, poor mechanical properties, etc., and achieve low raw material prices, simple preparation processes, and mechanical good performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Raw materials were stoichiometrically MgAgSb 0.9975 sn 0.0025 After calculation and weighing, place in a vacuum carbon-coated quartz tube with a vacuum of 10 -4 -10 -1 Pa, smelting at a high temperature of 1000°C for 10 hours to obtain ingots, and then use mechanical ball milling to crush the ingots to obtain micron-sized particles (particle size diameter: 200nm-10.0μm), and then use spark plasma sintering method to sinter at 450°C and 60MPa. 5min, followed by annealing in vacuum at 270°C for 1 week to obtain the final sample.
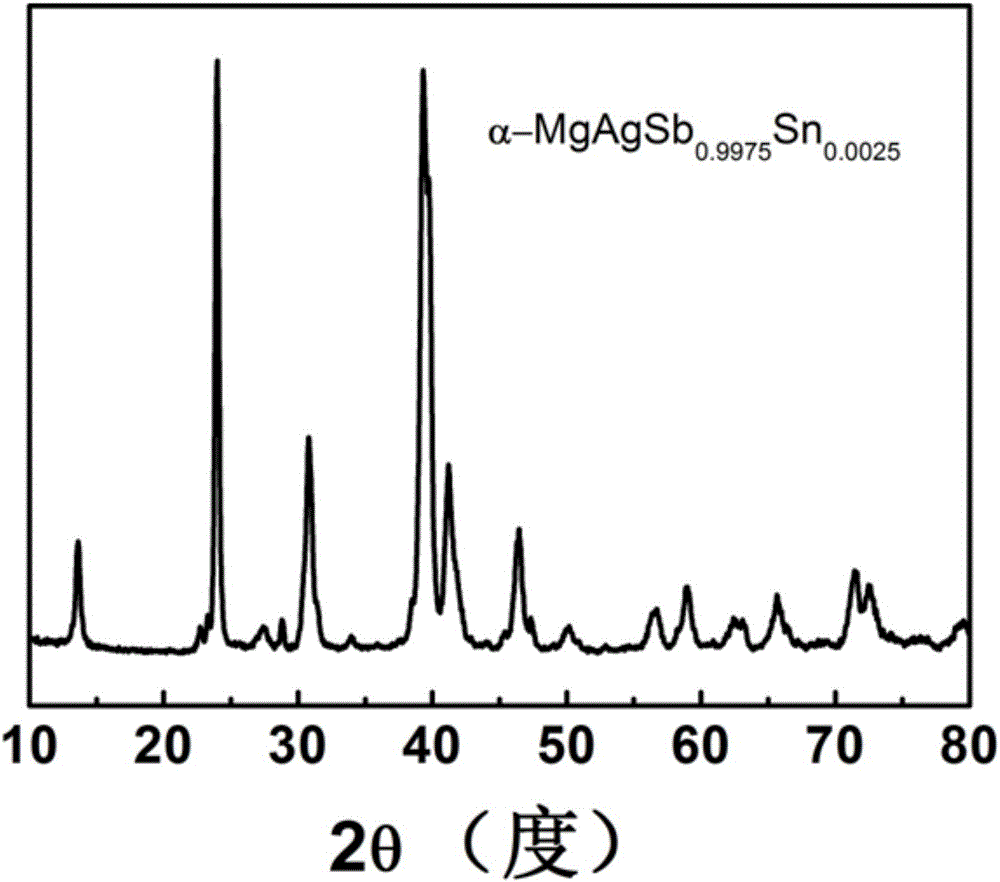
[0027] Adopt RigakuD / MAX-2550PC type X-ray (XRD) to carry out phase analysis to the sample that present embodiment makes, as figure 1 Shown, and confirmed as the α-MgAgSb-based structure, that is, the tetragonal structure (I-4c2), the space group number is 120.
[0028] According to the thermal diffusivity measured by the Netzsch LFA-457 laser pulse thermal analyzer, the thermal conductivity κ was calculated by comparing the measured specifi...
Embodiment 2
[0030] After weighing the raw materials according to the stoichiometric ratio of MgAgSb, place them in a vacuum carbon-coated quartz tube with a vacuum of 10 -4 -10 -1 Pa, smelting at a high temperature of 1000°C for 10 hours to obtain ingots, and then use mechanical ball milling to crush the ingots to obtain micron-sized particles (particle size diameter: 200nm-10.0μm), and then use spark plasma sintering method to sinter at 450°C and 60MPa. 5min, followed by annealing in vacuum at 270°C for 1 week to obtain the final sample.
[0031] The thermal conductivity of the sample prepared in this example is κ=1.01W·m at 525K -1 K -1 , thermoelectric potential coefficient α=193μV / K, electrical conductivity σ=46241S / m, calculated ZT value is 0.89.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Raw materials were stoichiometrically MgAgSb 0.995 sn 0.005 After calculation and weighing, place in a vacuum carbon-coated quartz tube with a vacuum of 10 -4 -10 -1 Pa, smelting at a high temperature of 1000°C for 10 hours to obtain ingots, and then use mechanical ball milling to crush the ingots to obtain micron-sized particles (particle size diameter: 200nm-10.0μm), and then use spark plasma sintering method to sinter at 450°C and 60MPa. 5min, followed by annealing in vacuum at 270°C for 1 week to obtain the final sample.
[0034] The thermal conductivity of the sample prepared in this example is κ=1.06W·m at 525K -1 K -1 , thermoelectric potential coefficient α=186μV / K, conductivity σ=53483S / m, calculated ZT value is 0.91.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com