A Thermal Residual Stress Repair Method for Fused Silica Laser Damage
A technology of laser damage and residual stress, applied in the field of optical materials and optical components, can solve problems such as unrepairable damage, fused silica microcracks, affecting fused silica, etc., to suppress thermal residual stress, inhibit its growth, and improve damage The effect of the threshold
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
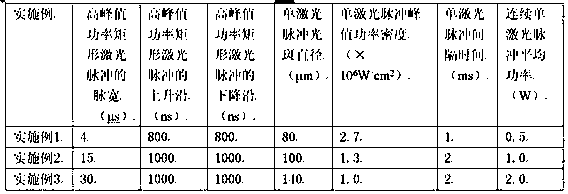
[0024] 1. RF excitation CO with the highest continuous output power of 100W 2 For the laser, the output frequency is set to 1000Hz, the duty cycle is 25%, and the output pulse waveform has a rising edge of 100 microseconds before reaching the power peak value. Since the lower power cannot effectively gasify and strip the damaged material, and will cause the heating of the material and the introduction of thermal residual stress, it is necessary to excite the CO 2 The output pulse of the laser is clipped to obtain the pulse peak segment. Use the AOM to cut the laser pulse waveform, set the AOM and CO 2 The laser is synchronized, the duty cycle is 0.4%, and the high peak power rectangular laser pulse with a pulse width of 4μs is intercepted through the deflection effect of the acousto-optic modulator on the light. The rising edge is 800ns and the falling edge is 800ns;
[0025] 2. Using a 5x beam expander to CO 2 The laser beam is expanded, and a lens with a focal length of 1...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The implementation of this example is basically the same as Example 1, the main difference is that the pulse width of the high peak power rectangular laser pulse is 15 μs, the rising edge is 1000 ns, and the falling edge is 1000 ns; the single laser pulse spot diameter is 100 μm, and the peak power density 1.3×10 6 W / cm 2 , the interval between single laser pulses is 2ms, and the average power of continuous single laser pulses is 1.0W.
Embodiment 3
[0032] The implementation of this example is basically the same as that of Example 1, the main difference being that the pulse width of the high peak power rectangular laser pulse is 30 μs, the rising edge is 1000 ns, and the falling edge is 1000 ns; the single laser pulse spot diameter is 140 μm, and the peak power density 1.0×10 6 W / cm 2 , the interval between single laser pulses is 2ms, and the average power of continuous single laser pulses is 2.0W.
[0033] Table 1
[0034]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com