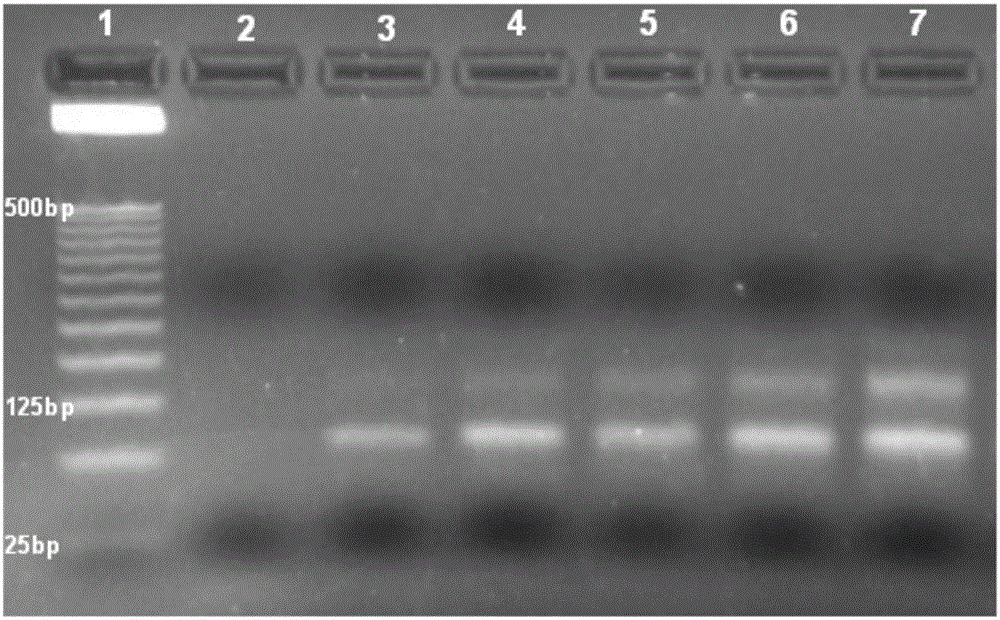
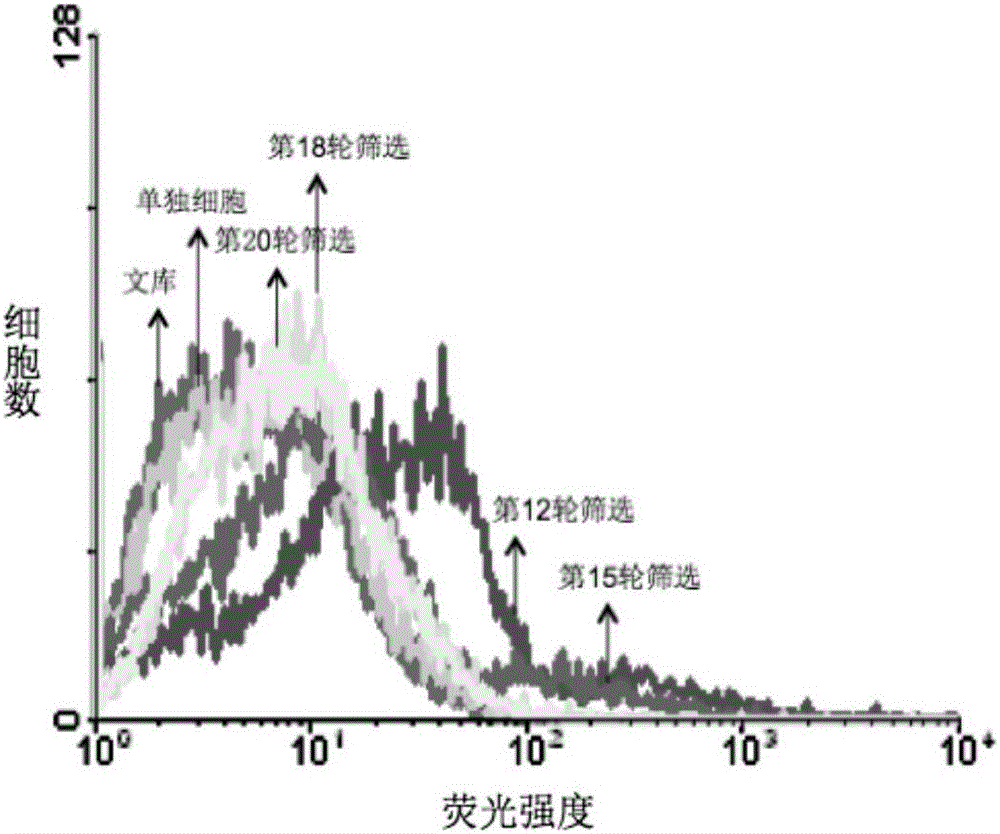
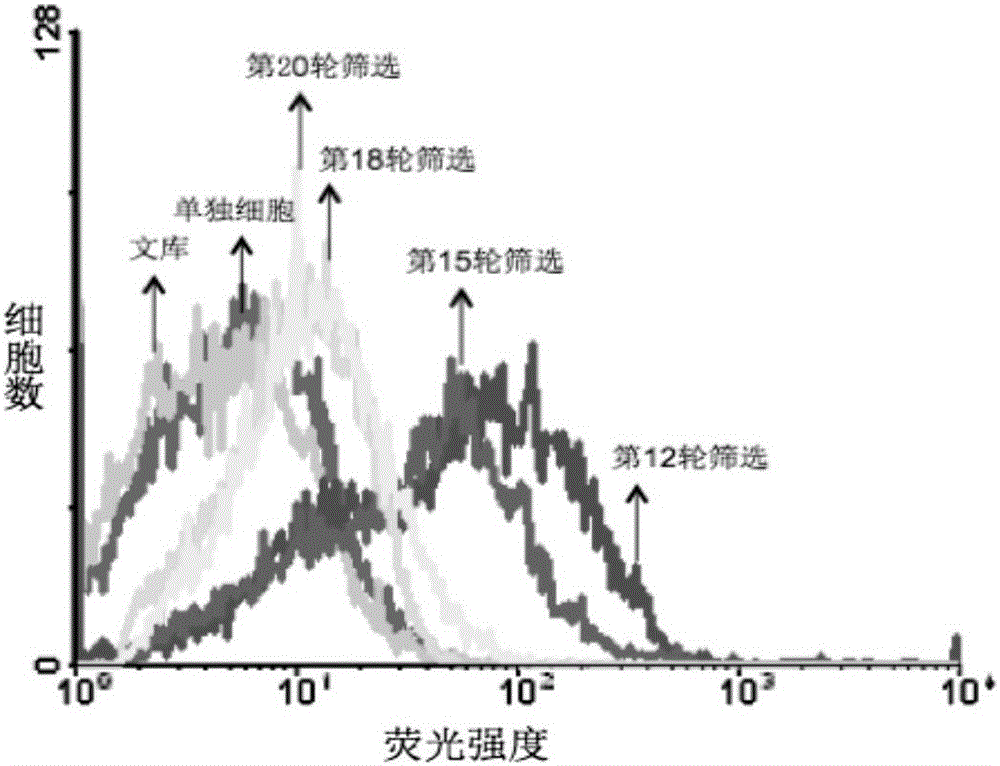
Nonalcoholic fatty liver cell aptamer and application thereof
A non-alcoholic, cellular nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of nucleic acids, can solve problems such as inability to effectively reach the target, achieve easy synthesis and labeling, ensure natural properties, and achieve the effect of small molecular weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1: In vitro screening of nucleic acid aptamers specifically binding to NAFLD cells
[0052] (1) The first round of screening:
[0053] 1.1. Induction and differentiation of NAFLD cells:
[0054] HepG 2 Cells were inoculated on 10 cm culture dishes, using complete culture medium (high glucose DMEM containing 10% FBS, 100 μg / mL penicillin, and 100 μg / mL streptomycin in complete culture medium), at 37 °C, 5% CO 2 Culture under conditions, change the medium once every 2 days, and start to induce differentiation when the cell density reaches 60%-70%. Pour off the original culture solution, and use a final concentration of 100mM oleic acid, 50mM palmitic acid, 1×10 ﹣ 6 M dexamethasone and 1 x 10 ﹣ 12 The induction medium of M insulin continued to culture the cells, changing the medium every 2 days until 1 week, and it could be seen under the microscope that more than 90% of the cells had been induced to differentiate into NAFLD cells.
[0055] 1.2, using 20nmol...
Embodiment 2
[0145] Investigate the effect of temperature on the nucleic acid aptamer NFD-1.
[0146] Because the screening conditions were carried out at 4°C, and the binding test was also carried out at 4°C, but the internal environment temperature of the human body is 37°C, so we studied whether the nucleic acid is suitable for use at 4°C and 37°C. Whether the affinity between the body and the target cell is affected.
[0147] Specific steps are as follows:
[0148] (1) The synthesized FITC-labeled nucleic acid aptamer and random control library were prepared into a solution with a concentration of 250 nM using a binding buffer and stored at 4°C.
[0149] (2) Select NAFLD cells in good growth state, in the logarithmic growth phase, and whose cell abundance reaches more than 90% to induce differentiation, remove the medium, and wash twice with washing buffer at 4°C.
[0150] (3) Add 3 mL of non-enzymatic digestion solution and digest at 37°C for 5-15 minutes. When the cells become roun...
Embodiment 3
[0158] The effect of protease treatment on the nucleic acid aptamer NFD-1 was investigated.
[0159] (1) Collect differentiated NAFLD cells in good growth state, in the logarithmic growth phase, and with a cell abundance of more than 90%, digest with proteinase K or trypsin at 37°C for 30 min, and wash the cells 3 times with washing buffer.
[0160] (2) Count 1×10 6 Collect the cells in flow cytometry tubes, add 100 μL of 250 nM nucleic acid escape to each tube of cells, and incubate at -4°C for 30 min.
[0161] (3) After the incubation, the cells were washed again 3 times, and the cells were resuspended with 200 μL of washing buffer, and tested on the machine.
[0162] Nucleic acid aptamers screened by Cell-SELEX technology usually bind specifically to proteins on the cell membrane. In order to verify the binding of NFD-1 to cell membrane proteins, we used trypsin and Proteinase K as protease experiments. We used trypsin and Proteinase K. The protease was incubated with the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com