Self-adaptive control method for modes of low-voltage microgrid
An adaptive control and micro-grid technology, applied in electrical components, circuit devices, AC network circuits, etc., can solve problems such as operation mode conversion failure, control method switching process impact, control mode conversion delay, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
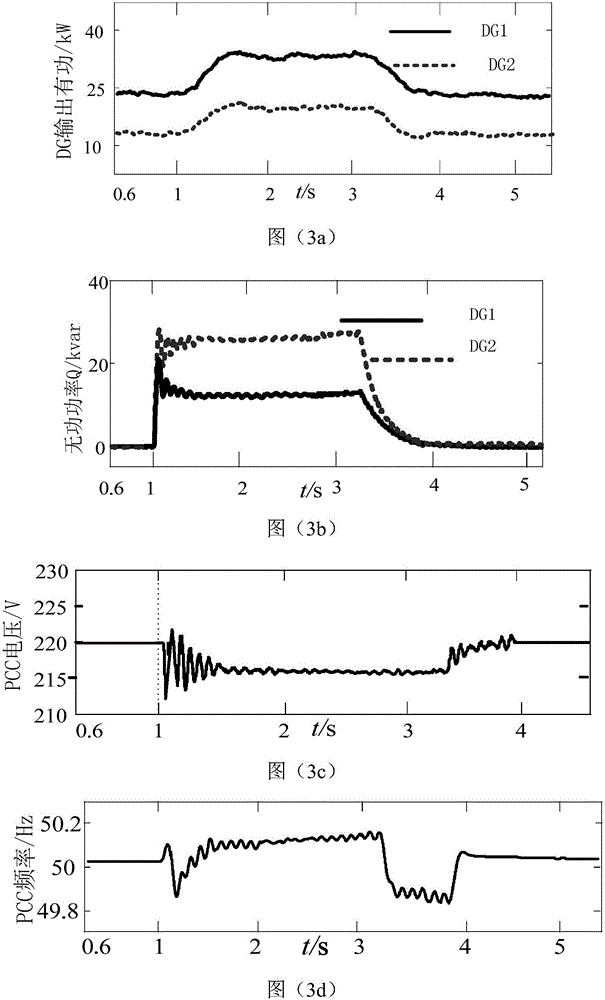
Image
Examples
Embodiment
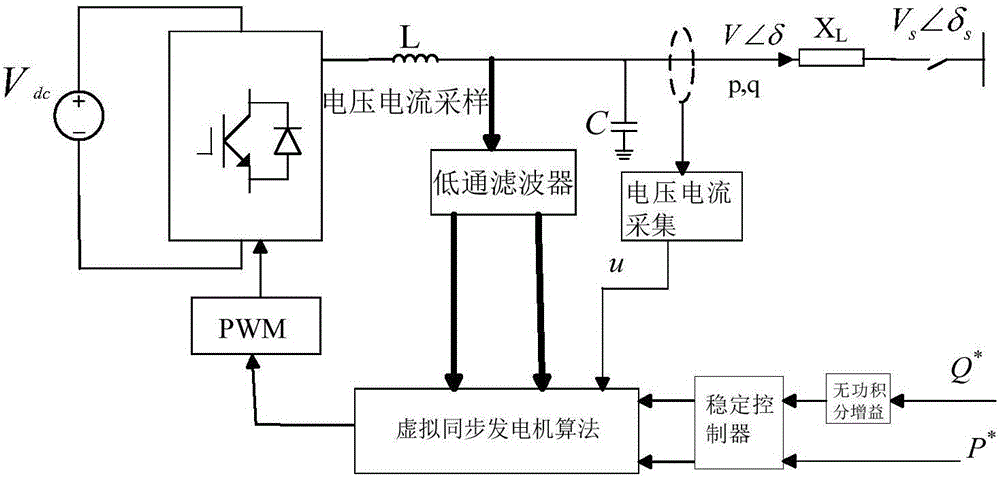
[0038] Such as figure 1 As shown in the figure, the block diagram of the improved low-voltage microgrid droop control is shown.
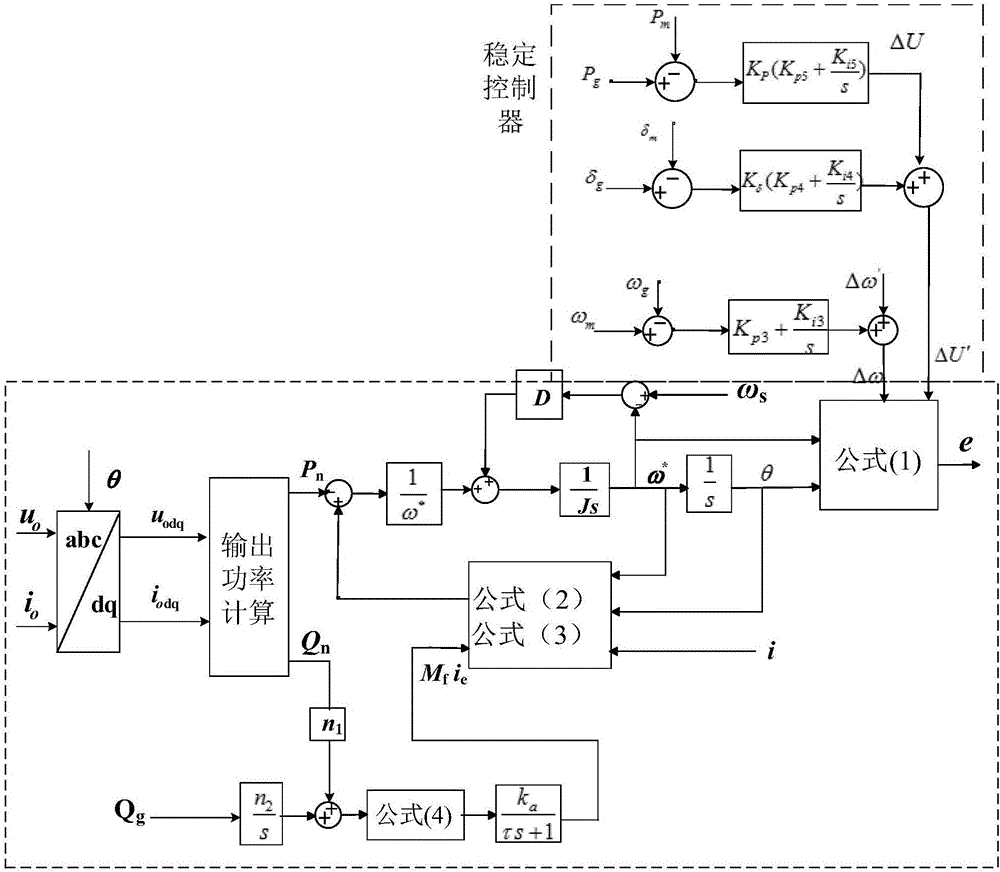
[0039] Such as figure 2 As shown, the figure is the control schematic diagram of the improved low-voltage microgrid droop control, set P T is the mechanical power, P e is the electromagnetic power, J is the moment of inertia of the rotor (kg.m 2 ), ω * is the reference electric angular velocity, D is the constant damping coefficient, e is the induced electromotive force, M f is the maximum inductance between the field winding and the field winding, i e Is the excitation current, θ is the electrical angle of the generator.
[0040] The present invention comprises the following steps:
[0041] A. According to the operating principle of the synchronous generator, the mathematical model of the virtual synchronous generator (VSG) is as follows:
[0042] e = ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com