A heat pump type large temperature difference heat exchange system and method
A technology of heat exchange system and large temperature difference, which is applied in fluid heaters, lighting and heating equipment, energy-saving heating/cooling, etc., and can solve problems such as limiting one network
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
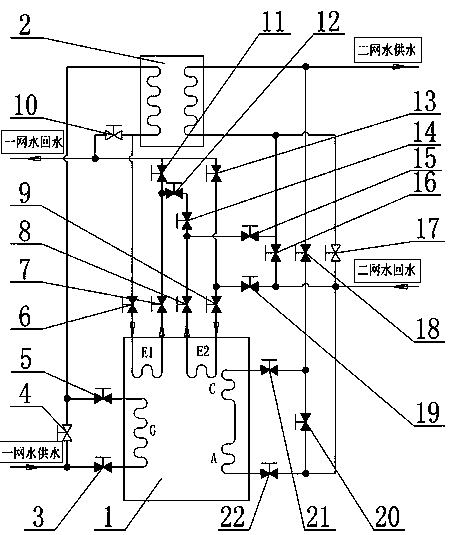
[0041] Example 1 (see figure 1 ): a network of high-temperature water as the driving heat source, enters the heat exchange tube of the heat pump / refrigerator (1) generator (G) through the first valve (3) and heats the dilute lithium bromide solution on the outside of the tube until it boils to generate refrigerant Steam and lithium bromide concentrated solution, the high-temperature water in the first network is cooled by the generator (G) and then enters the water-water heat exchanger (2) through the third valve (5) to heat the water in the second network to achieve further cooling. A network of water enters the heat exchange tube of the 1# evaporator (E1) of the heat pump / refrigerator (1) through the fourth valve (6), and is sprayed by the refrigerant water outside the tube, and the refrigerant water evaporates into refrigerant vapor, absorbing The heat of the return water of the first net of water, after releasing heat and cooling down again, the first net of water flows th...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2 (see figure 2 ): a network of high-temperature water as the driving heat source, enters the heat exchange tube of the heat pump / refrigerator (1) generator (G) through the first valve (3) and heats the dilute lithium bromide solution on the outside of the tube until it boils to generate refrigerant Steam and lithium bromide concentrated solution, the high-temperature water in the first network is cooled by the generator (G) and then enters the water-water heat exchanger (2) through the third valve (5) to heat the water in the second network to achieve further cooling. A network of water flows through the fourth valve (6), the heat exchange tube of the 1# evaporator (E1) of the heat pump / refrigerator (1), the fifth valve (7), the tenth valve (12), and the twelfth valve (14), the sixth valve (8) and the heat exchange tube of the 2# evaporator (E2) of the heat pump / refrigerator (1), the 1# evaporator (E1) and the 2# evaporator of the heat pump / refrigerator (1) (...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3 (see Figure 6 ): a network of high-temperature water as the driving heat source, enters the heat exchange tube of the heat pump / refrigerator (1) generator (G) through the first valve (3) and heats the dilute lithium bromide solution on the outside of the tube until it boils to generate refrigerant Steam and lithium bromide concentrated solution, a net of high-temperature water passes through the generator (G) and then enters a secondary water-water heat exchanger (2.2) and a primary water-water heat exchanger ( 2.1), heating the water in the second network to achieve further cooling, the cooled water in the first network enters the heat exchange tube of the heat pump / refrigerator (1) 1# evaporator (E1) through the fourth valve (6), and is cooled by the cooling tube outside the tube The agent water is sprayed, and the refrigerant water evaporates into refrigerant steam, which absorbs the return water heat of a network of water, and after cooling down again, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com