Preparation method of disodium hydrogen phosphate heat storage system suitable for greenhouses
A disodium hydrogen phosphate heat storage technology, which is applied in the field of agricultural engineering, can solve the problems affecting the production of greenhouse crops and the safe overwintering of greenhouse vegetables, and achieves the effects of low price, high latent heat density, and simple and convenient preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
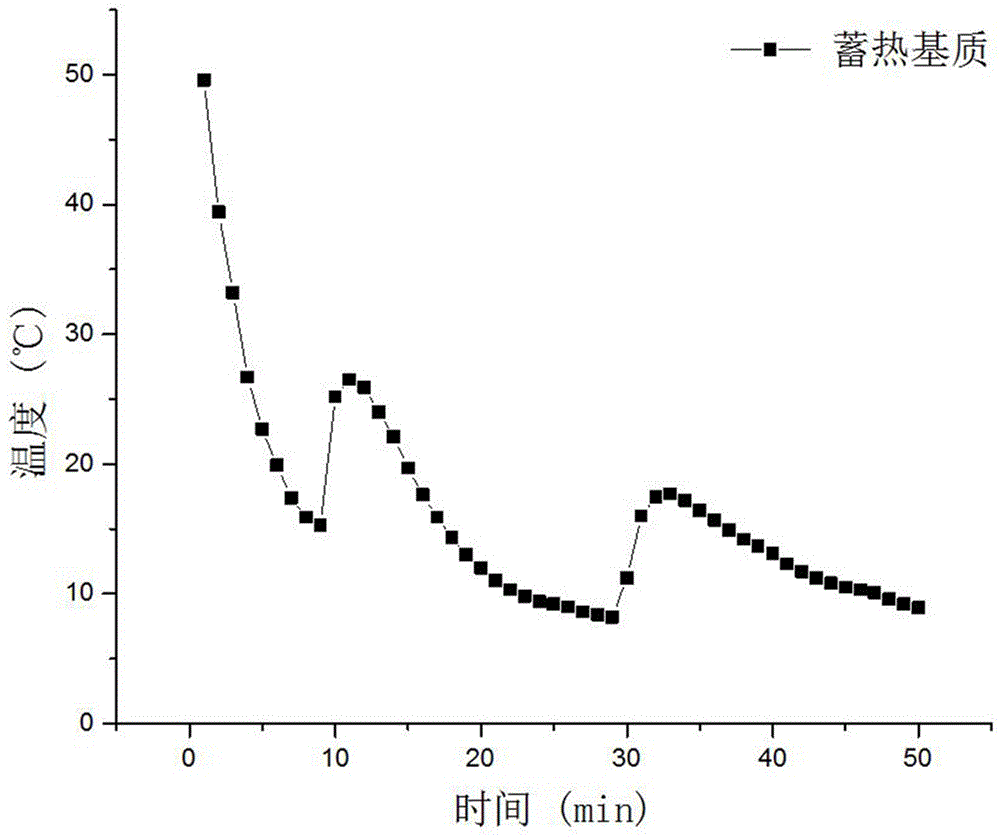
[0014] Embodiment 1: the raw material that this embodiment adopts is Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O crystal (DisodiumHydrogenPhosphate), molecular weight 358.14, relative density 1.52, melting point 35.5°C, solid at room temperature, colorless transparent monoclinic prismatic crystal. Nucleating agent: graphite, stabilizer: sodium silicate nonahydrate. at 100 parts Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O Add 8 parts of KCl, 0.5~02 parts of graphite, and 6 parts of sodium silicate, mix well, heat to 60°C until completely melted, and stir evenly. The homogeneous solution was placed at room temperature to obtain a thermal storage material.
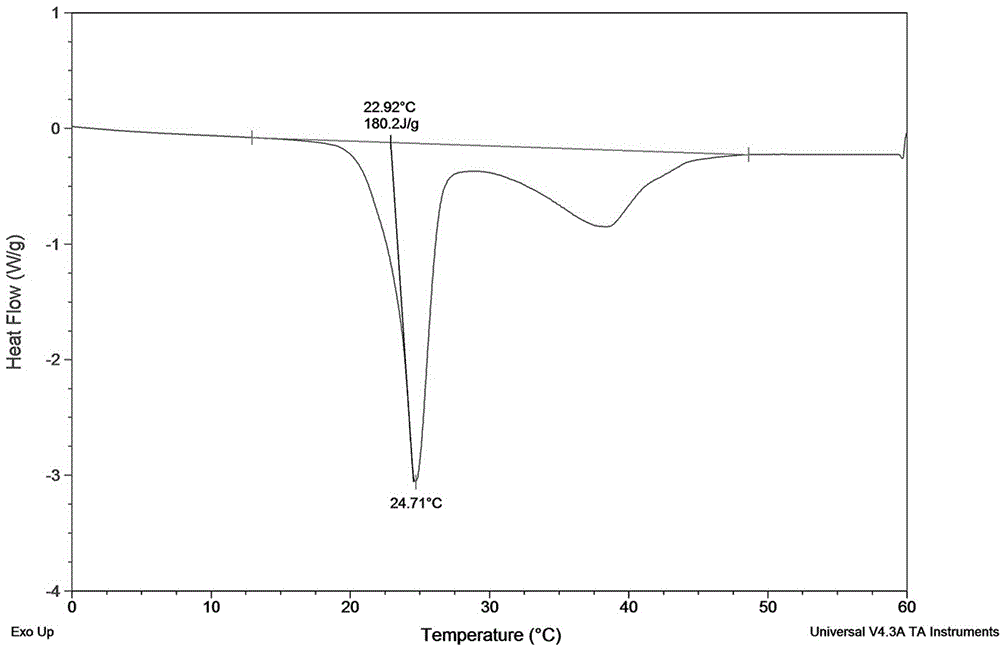
[0015] The calcium chloride hexahydrate heat storage material prepared above was passed through the melting-cooling cycle method, and the phase transition temperature was determined to be 25° C., no supercooling and phase separation occurred, and the performance was stable.
Embodiment 2
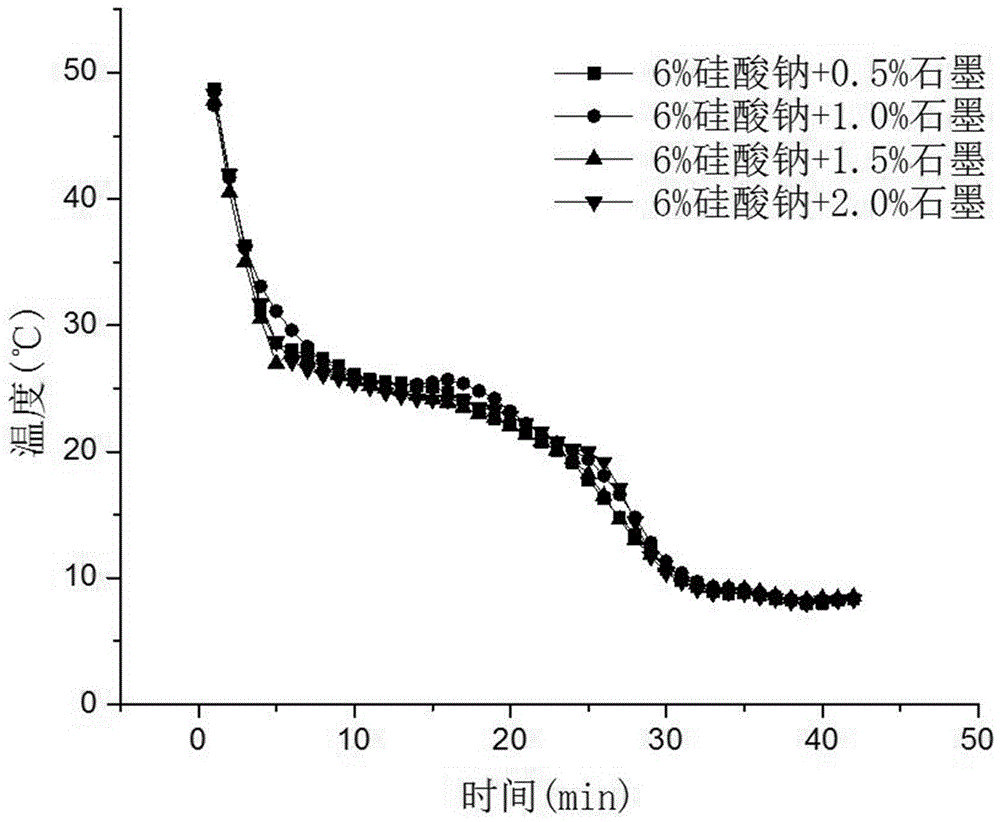
[0016] Embodiment 2: the raw material that this embodiment adopts is Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O crystal, same as example one. Nucleating agent: graphite; Stabilizer: sodium silicate nonahydrate. The difference from Example 1 is 100 parts of Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O Add 8 parts of KCl, 0.5~02 parts of graphite, and 8 parts of sodium silicate, mix well, heat to 60°C until completely melted, and stir evenly. The homogeneous solution was placed at room temperature to obtain a thermal storage material.
[0017] The calcium chloride hexahydrate heat storage material prepared above was passed through the melting-cooling cycle method, and the phase transition temperature was determined to be 25° C., no supercooling and phase separation occurred, and the performance was stable.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com