A torque-driven method for a solid-rotor permanent-magnet synchronous motor with hybrid magnetic circuits, double-stators, field-weakening, and speed-expanding
A technology of permanent magnet synchronous motor and field weakening speed expansion, which is applied to the rotating parts of the magnetic circuit, synchronous motors with stationary armatures and rotating magnets, and magnetic circuits, which can solve the problem of increasing the leakage flux of the motor and weakening the teeth slot torque, reducing the effective flux utilization rate of the motor, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing the speed regulation range and reducing the radial main flux
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
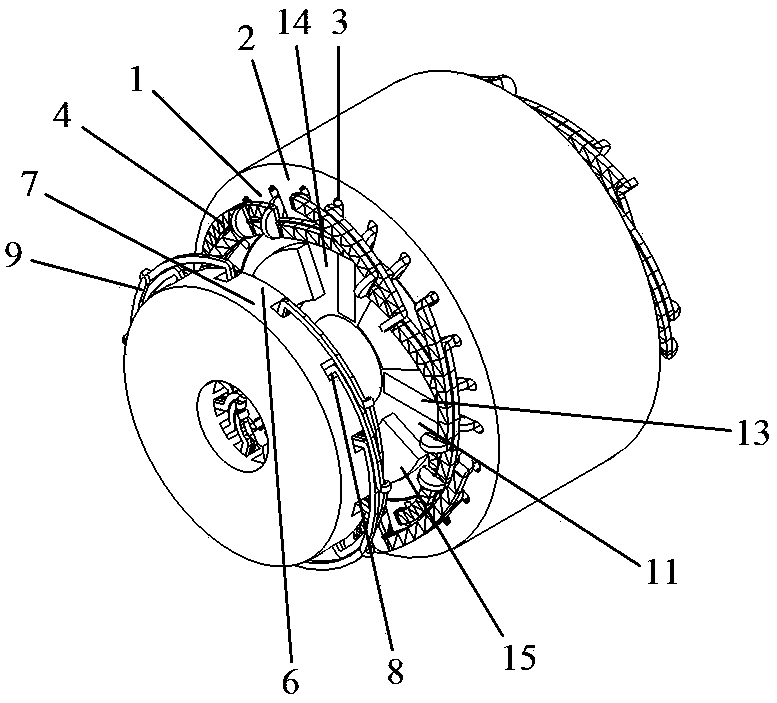
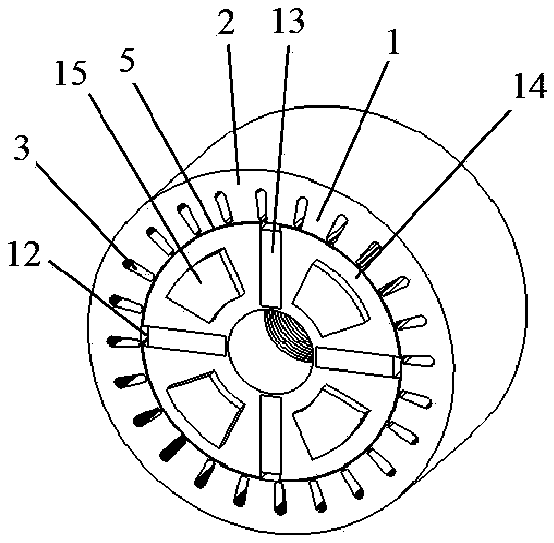
[0061]As shown in Figure 1(a), the overall three-dimensional schematic diagram of the motor, the number of phases of the motor in this embodiment is 3, the number of radial stator teeth is 24, the number of axial stator teeth is 12, the number of rotor slots is 4, and the number of permanent magnet blocks is 4 , the number of radial magnetic poles is 4, and the number of axial magnetic poles is 4. This embodiment includes a radial stator, an axial stator and a rotor. As shown in Figure 1(b), the radial stator is made of laminated silicon steel sheets. The radial stator includes a radial stator tooth 1, a radial stator yoke 2 and a radial stator slot 3, and a radial armature winding 4 is placed in the radial stator slot 3, and the radial armature winding 4 can be a distributed winding, a concentrated winding or The number of poles of the radial armature winding is the same as the number of radial magnetic poles of the rotor, the radial stator and the rotor are coaxial, and there...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The main difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is:
[0064] (1) As shown in Figure 2(a), there are axial stators at both ends of the motor in Example 2, and the two ends of the rotor iron core of the motor are all processed into the shape of fan rings to form axial magnetic poles, The solid rotor is shown in Figure 2(c), while in Example 1, only one end of the motor has an axial stator, and only one end of the motor rotor iron core is processed into the shape of a fan ring to form an axial magnetic pole;
[0065] The motor in Embodiment 2 has two axial air gaps 10, as shown in Fig. 2(e).
[0066] (2) The arrangement of the permanent magnets in Example 2 is different from that in Example 1. The permanent magnets in Example 1 are in a single parallel structure, while in Example 2 the permanent magnets are in a series-parallel hybrid structure. The rest is the same as that of Example 1, as shown in Figure 2(b) and Figure 2(d).
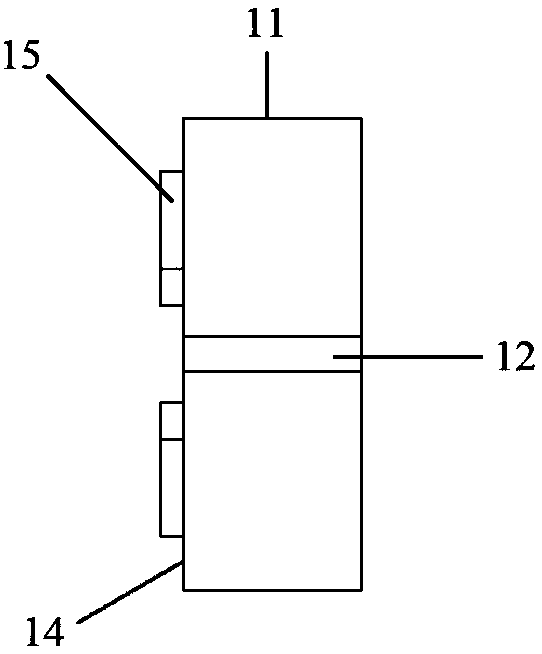
[0067] Among them, in the above...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com