Extraction process and application of grifolan
A technique of extracting polysaccharides from Grifola frondosa, applied to medical preparations containing active ingredients, plant raw materials, digestive system, etc., to achieve the effects of promoting proliferation, promoting healing and repair, and improving extraction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: Extraction of Grifola frondosa polysaccharide
[0032]Take the dry fruiting body of Grifola frondosa, pass through a 10-mesh sieve after crushing to obtain the fruiting body particles of Grifola frondosa, add 10 times the amount (mass volume ratio) of water and boil for 2 hours; filter, and use 8 times the amount of 2% NaOH for the filter residue The solution was leached for 2 hours; filtered, the filtrate was concentrated to Brix (soluble solids) ≥ 15%, and after being centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes, the supernatant was pumped into ultrafiltration separation components with a molecular weight cut-off of 100kDa, 30kDa, and 5kDa, that is, a molecular weight cut-off of 100kDa The filtrate of the filtration separation module continues to be pumped into the ultrafiltration separation module with a molecular weight cut-off of 30kDa, and the filtrate of the ultrafiltration separation module with a molecular weight cut-off of 30kDa continues to be pumped...
Embodiment 2
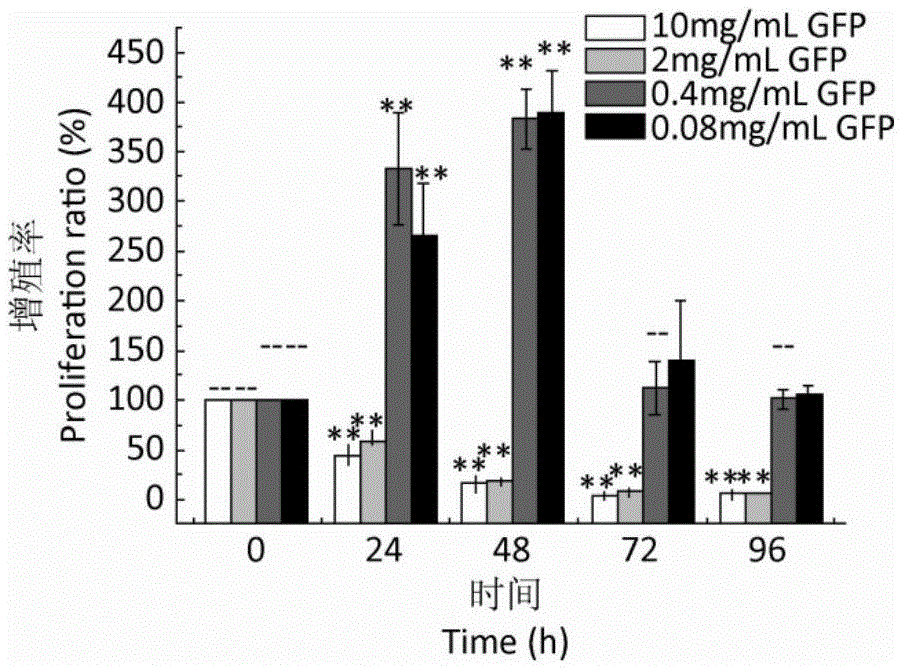
[0035] Example 2: Effects of Grifola frondosa polysaccharides on the proliferation of human gastric mucosal epithelial cells
[0036] 1. Materials
[0037] Cell line: human normal gastric mucosal epithelial cells GES-1 were purchased from Beijing Institute of Cancer Prevention and Control.
[0038] Medium: The basal medium for GES-1 cell culture is DMEM medium (10% FBS, 100U penicillin, 100U streptomycin).
[0039] Grifola frondosa polysaccharide GFP (polysaccharide of Grifola frondosa): the Grifola frondosa polysaccharide prepared in Example 1 was used.
[0040] 2. Method
[0041] The effect of GFP on the proliferation activity of GES-1 was detected by MTS method. GES-1 in the logarithmic growth phase was digested with trypsin and its concentration was adjusted to 2.0×10 4 cells / mL, seeded in a 96-well plate, 100 μL per well, placed at 37°C, saturated humidity, 5% CO 2 After 24 hours of culture in a sterile incubator, the old culture medium was discarded. The experimenta...
Embodiment 3
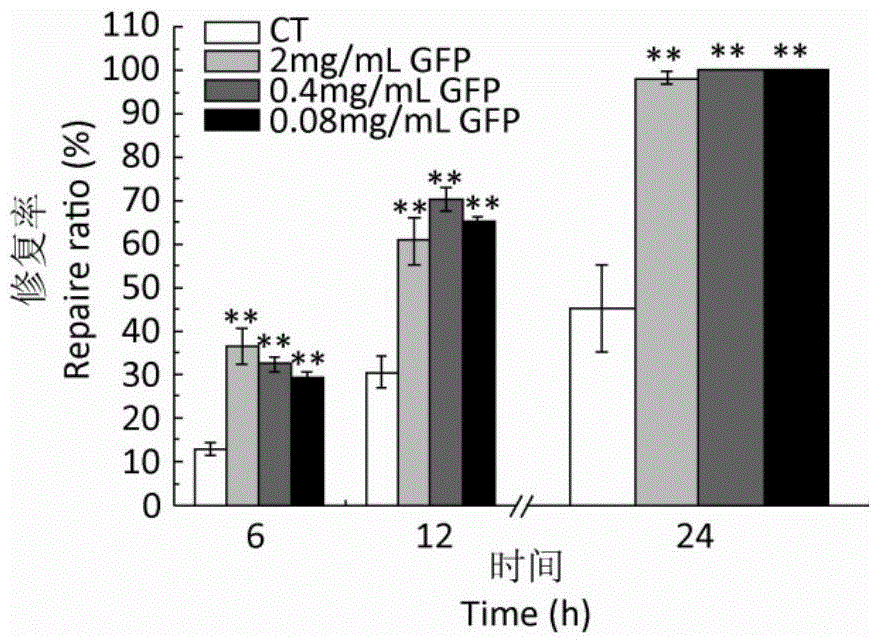
[0047] Example 3: Effects of Grifola frondosa polysaccharides on human gastric mucosal wound healing and repair
[0048] 1. Material: Same as Example 2
[0049] 2. Method
[0050] Select GES-1 in the logarithmic growth phase, and use 6×10 per well 4 Cells were seeded in 24-well plates, 400 μL per well. Set at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate in the incubator for 24 hours. After the cells form a relatively tight connection to form a single layer, use a capillary tube with a diameter of 1.5 mm to draw a vertical trace in the center of each well of the 24-well plate, and the two sides of the wound can be seen under the microscope at the same time. side. Aspirate the original culture medium after scratching, wash each well twice with 1mL PBS to remove non-adherent cells, select the final concentration of GFP as 2, 0.4, 0.08mg / mL according to the results of the proliferation experiment, and culture medium 400μL, the control group only added 400 μL of DMEM basal medium. For each concen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com