Method for electrochemical etching of surface of copper zinc tin sulfide thin film material without water
A technology of copper-zinc-tin-sulfur and thin-film materials, which is applied in the field of solar cells, can solve problems such as high cost and serious environmental pollution, achieve low production cost, wide electrochemical window, and facilitate the promotion of industrialization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
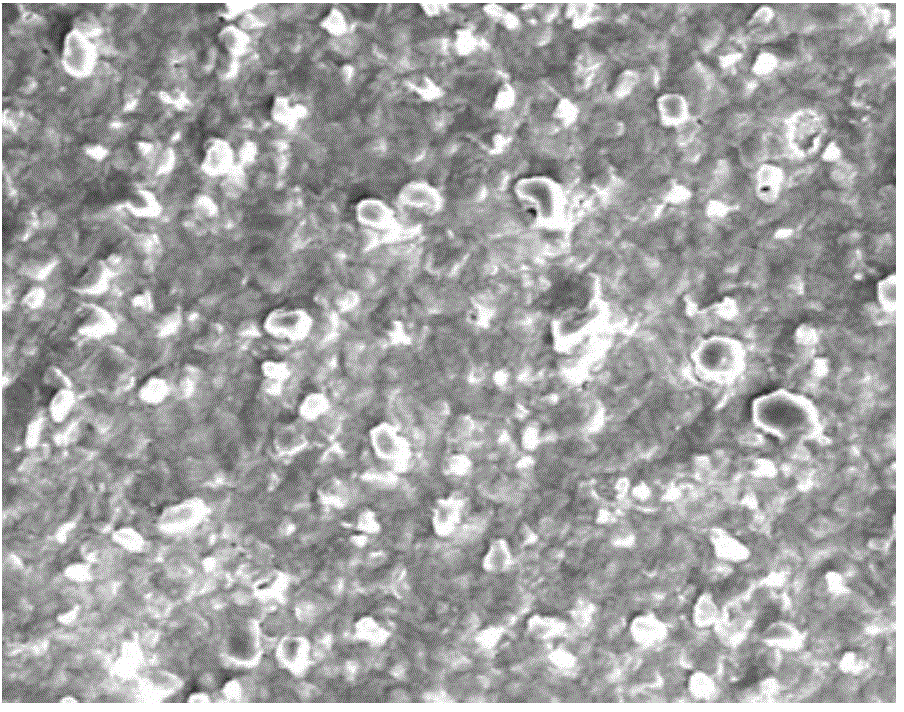
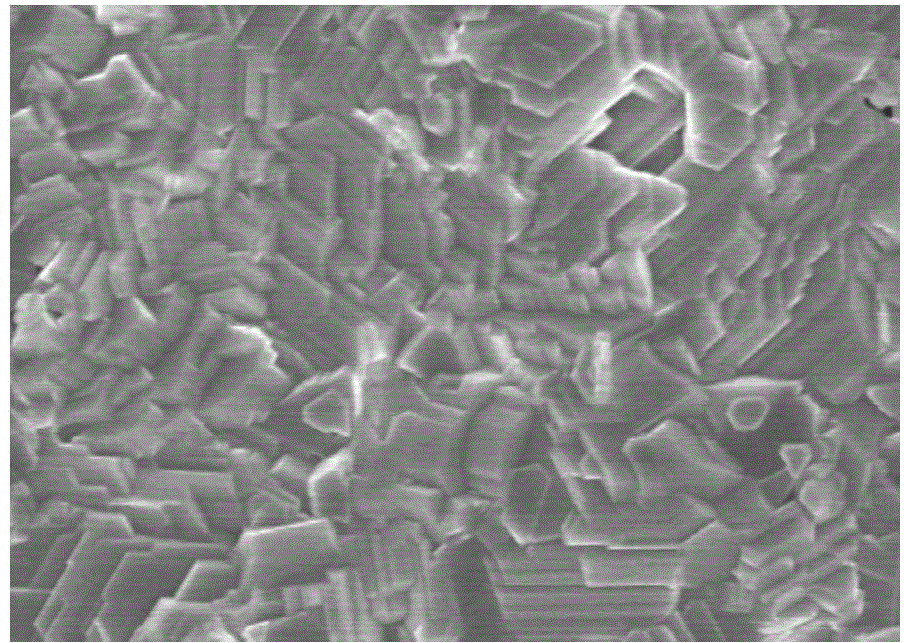
[0042] Example 1 This example is an anhydrous electrochemical method for etching the surface of a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur film
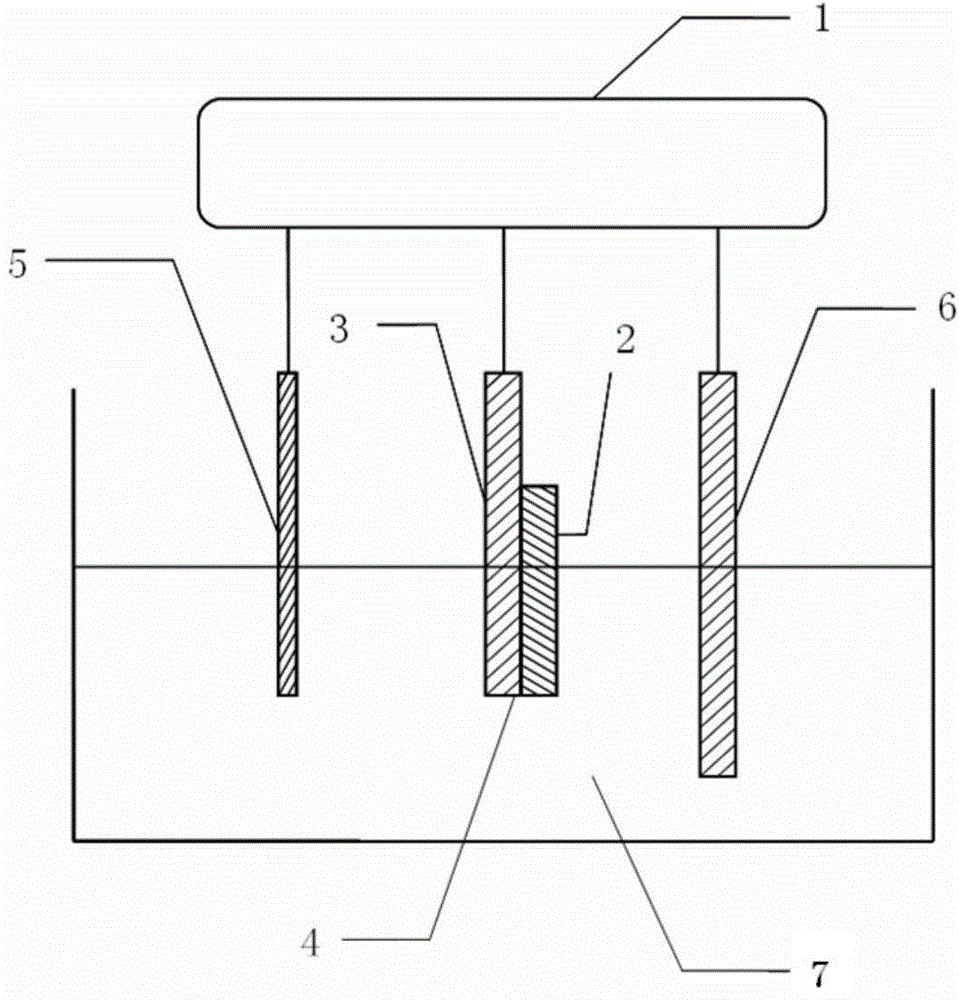
[0043] Metal Mo with a thickness of 1 μm is deposited on the soda-lime glass substrate as a back electrode, and a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film with a thickness of 1-2 μm is deposited on the Mo layer 4 by electrochemical deposition, which is a prefabricated layer.
[0044] Step (1): The copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film material is selenized in a constant temperature tubular annealing furnace, and then placed on the electrochemical workstation, only the substrate 3 and the Mo4 back electrode are connected to the working electrode of the electrochemical workstation 1; Soak in ethanol for 1-2 minutes, remove surface particles and impurities, and blow dry with high-purity nitrogen;
[0045] Step (2) Prepare treatment solution 7. Anhydrous sodium chloride was dissolved in choline chloride and urea solution with a mass ratio of 1:2, and the concentratio...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2 This embodiment is an anhydrous electrochemical method to etch the surface of the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film
[0049] Metal Mo with a thickness of 1 μm is deposited on the soda-lime glass substrate as a back electrode, and a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film with a thickness of 1-2 μm is deposited on the Mo layer 4 by electrochemical deposition, which is a prefabricated layer.
[0050] Step (1): The copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film material is selenized in a constant temperature tubular annealing furnace, and then placed on the electrochemical workstation, only the substrate 3 and the Mo4 back electrode are connected to the working electrode of the electrochemical workstation 1; Soak in ethanol for 1-2 minutes, remove surface particles and impurities, and blow dry with high-purity nitrogen;
[0051] Step (2) Prepare treatment solution 7. Anhydrous potassium chloride was dissolved in choline chloride and urea solution with a mass ratio of 1:3, and the ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3 This embodiment is an anhydrous electrochemical method to etch the surface of the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film
[0055] Metal Mo with a thickness of 1 μm is deposited on the soda-lime glass substrate as a back electrode, and a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film with a thickness of 1-2 μm is deposited on the Mo layer 4 by electrochemical deposition, which is a prefabricated layer.
[0056] Step (1): The copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film material is selenized in a constant temperature tubular annealing furnace, and then placed on the electrochemical workstation, only the substrate 3 and the Mo4 back electrode are connected to the working electrode of the electrochemical workstation 1; Soak in ethanol for 1-2 minutes, remove surface particles and impurities, and blow dry with high-purity nitrogen;
[0057] Step (2) Prepare treatment solution 7. Anhydrous magnesium chloride was dissolved in choline chloride and urea solution with a mass ratio of 1:2.5, and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com