Method for separating phycobiliprotein from laver processing wastewater
A technology for processing wastewater and phycobiliproteins, which is applied in the field of separation of phycobiliproteins, can solve problems such as increasing environmental burdens and wasting resources, and achieve the effects of repeated utilization, improved utilization, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] 1. Measure 200ml of laver processing wastewater, filter out laver residue, sludge and other impurities with a sieve to obtain a crude protein solution, put it in a 250ml blue cap bottle, and put it in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
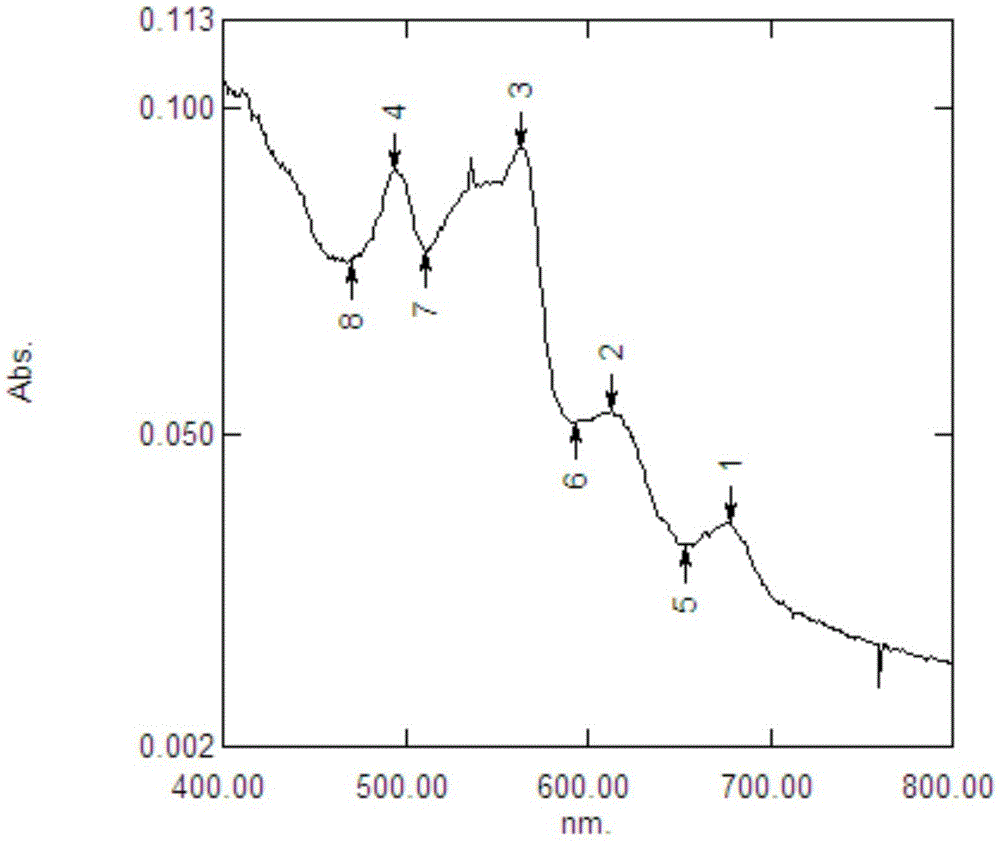
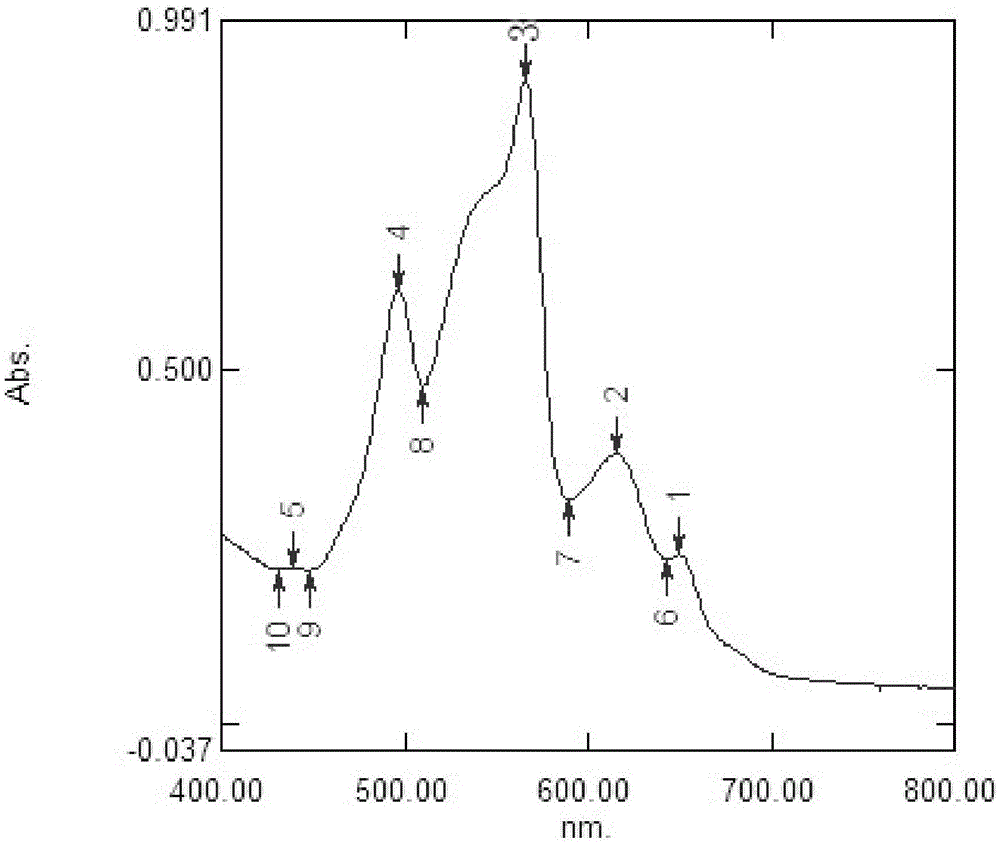
[0032] 2. According to the formula protein (Pro) = OD 562 / 0.0157, the calculated protein content in the crude protein solution is 4.39mg / L, and adopts the absorption spectrum of the crude protein solution extracted by ultraviolet spectrophotometer at room temperature, figure 1 It is the absorption spectrum of the crude protein solution at 400-800nm. There are many absorption peaks at 400-450nm in the figure, indicating that there are many impurities.
[0033] 3. Take 2ml of Q-Sepharose (Q-selpharose) stored in alcohol and fill it into a 50ml centrifuge tube, add 10 times the volume of distilled water, and shake to disperse the Q-Sepharose (Q-selpharose) filler. Let stand to make the Q-sepharose filler sink. Aspirate the supernatant. ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] 1. Measure 1L of seaweed processing wastewater, filter out seaweed residue, sludge and other impurities with a filter cloth to obtain a crude protein solution, put it in a 1L round bottle with a vent at the bottom, and store it in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
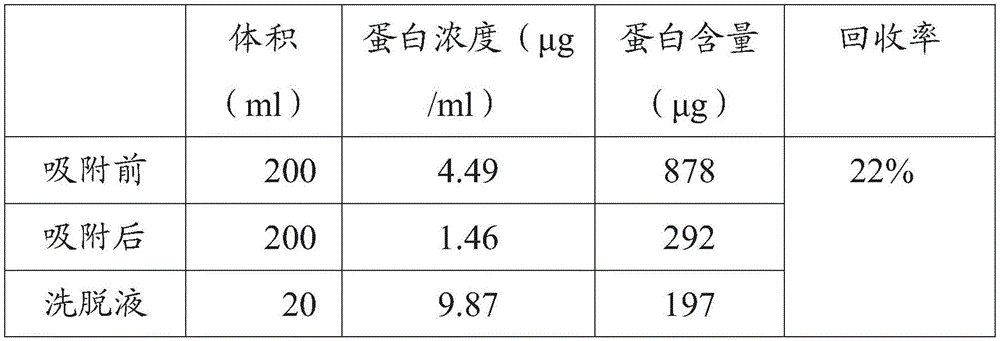
[0041] 2. According to the formula protein concentration (mg / L) = OD 562 / 0.0157, the calculated protein content in the crude protein liquid is 4.39mg / L.
[0042]3. Take 20ml of Q-Sepharose (Q-selpharose) stored in alcohol and stuff it into a 500ml sampling bottle, add 10 times the volume of distilled water, shake to make the Q-Sepharose (Q-selpharose) filler disperse open. Let stand to allow the filling to sink. Aspirate the supernatant. Repeat three times to fully remove the alcohol.
[0043] 4. At 25°C, add the Q-selpharose filler that has been washed off the alcohol into the crude protein solution, and blow the Q-selpharose filler with air at the bottom to make the algae The biliprotein is in full c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com