Application of docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester in preparation of drug for improving excitatory neural toxicity
A technology of ethyl docosahexaenoate and ethyl carbasahexaenoate, which is applied in the field of application of ethyl docosahexaenoate in the preparation of drugs for improving excitatory neurotoxicity, and can solve the protective effect of DHA Few studies, unclear protection mechanism and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Cell Culture and Treatment
[0027] PC12 cells were cultured in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% (v / v) fetal bovine serum, 100 U / mL penicillin and 100 U / mL streptomycin at 37° C. in humidified air with 5% carbon dioxide. Before the experiment, the cells were divided into plates at a density of 2×105 cells per well. PC12 cells were incubated for 24 h in DMEM medium without or with different concentrations of Et-DHA (final concentration: 10, 30 μM). Then KA (final concentration: 30 mM) was added, and cultured for another 12 h to carry out subsequent experiments. In the above steps, the same amount of DMEM was administered to the control culture group. KA was dissolved in DMEM medium. Et-DHA is dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide (DimethylSulfoxide, DMSO). The final concentration of DMSO was less than 0.1% (v / v). The concentrations of KA and Et-DHA in the above steps are selected through our preliminary experiments. All operations were repeated three times (n=3...
Embodiment 2
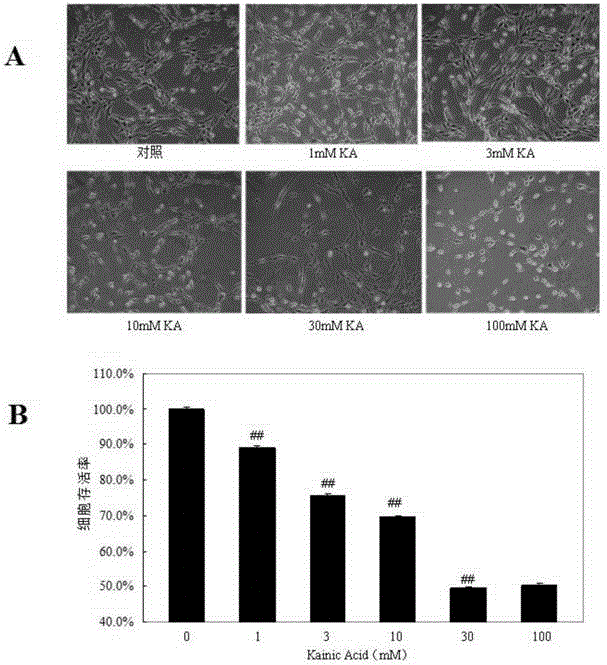
[0028] The cytotoxicity of embodiment 2KA
[0029] PC12 cells were plated at a density of 1 x 105 cells per well. Continue to grow for 24h, then add different concentrations of KA (final concentration: 0, 1, 3, 10, 30 and 100mM) in the medium. All assays were started 12 h after KA treatment of cells. Cytotoxicity of KA was determined by the MTT assay (Mosmann, 1983). like figure 1 As shown in B, the results of cell viability detected by MTT showed that the inhibition of KA on cell viability was concentration-dependent and statistically significant (P<0.01). When the concentration of KA was 100mM, the inhibitory rate of PC12 cells also reached about 50%, but there was no significant difference compared with the 30mM treatment group, so KA30mM was selected as the appropriate injury model dose for PC12 cells in subsequent experiments.
Embodiment 3
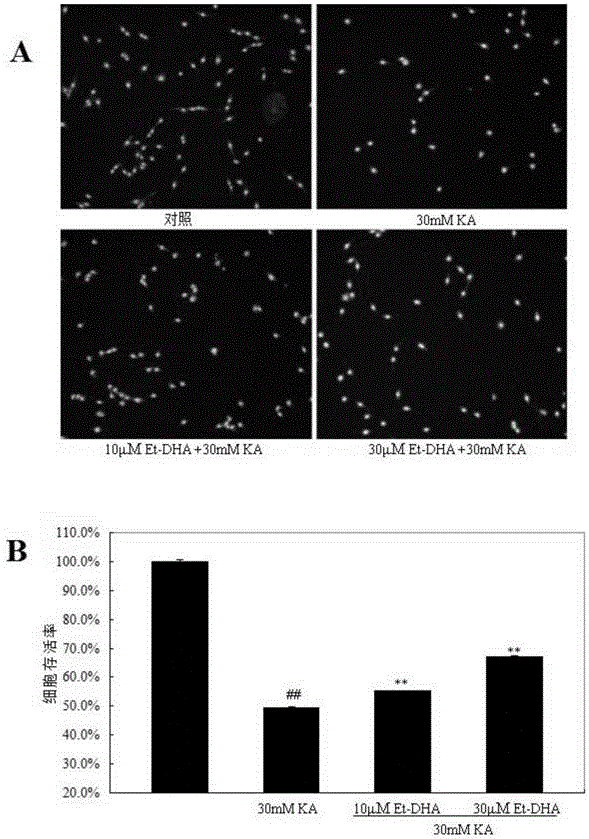
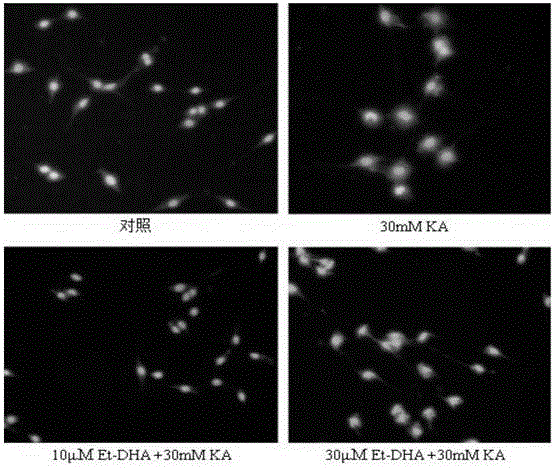
[0030] Determination of the protective effect of embodiment 3Et-DHA on PC12 cells
[0031] PC12 cells with 1×105 cells per well were treated with different concentrations of Et-DHA (final concentration: 0, 10 and 30 μM) on a 96-well plate for 24 hours, and then added KA (final concentration: 30 mM) for 37 hours. Cultivate at ℃ for 12h. Then MTT (0.5mg / mL) was added to each well, and cultured for another 4h. Then, the MTT was discarded, and the obtained dark blue crystals were dissolved with 100 mL DMSO, and finally read at the absorbance value of 550 nm with a microplate reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, USA). Depend on figure 2 B It can be seen that the survival rate of PC12 cells treated with KA (30mM) after pretreatment with different concentrations (10 and 30μM) of Et-DHA for 24h was significantly improved, compared with the single KA treatment group, it rose to 55.2±0.5 % and 67.2±0.6%. Statistical analysis showed that the survival rate of PC12 cells pretreated with 10 and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com