Method for the ablation cutting of a workpiece by means of a pulsed laser beam
A pulsed laser and ray technology, used in laser welding equipment, glass cutting devices, welding/welding/cutting items, etc., can solve problems such as appearance defects and adverse effects on workpiece stability, and achieve the effect of less material removal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
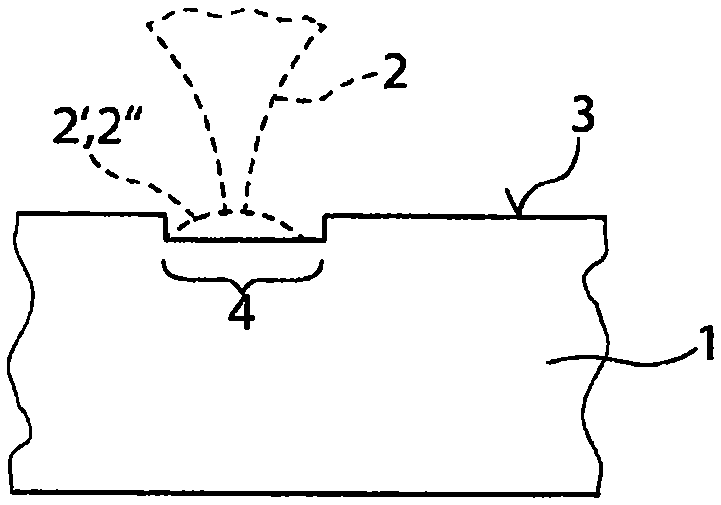
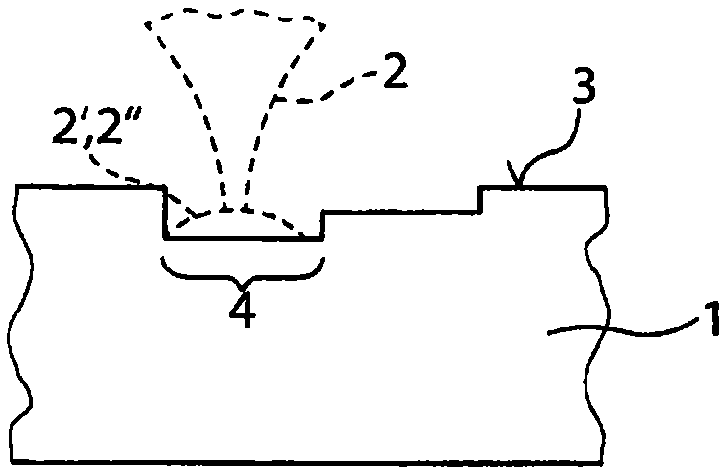
[0031] exist Figures 1a to 1d The individual method steps for performing the material-removing cutting according to the invention of a translucent workpiece 1 by means of a pulsed laser beam 2 are shown in an illustrative manner.
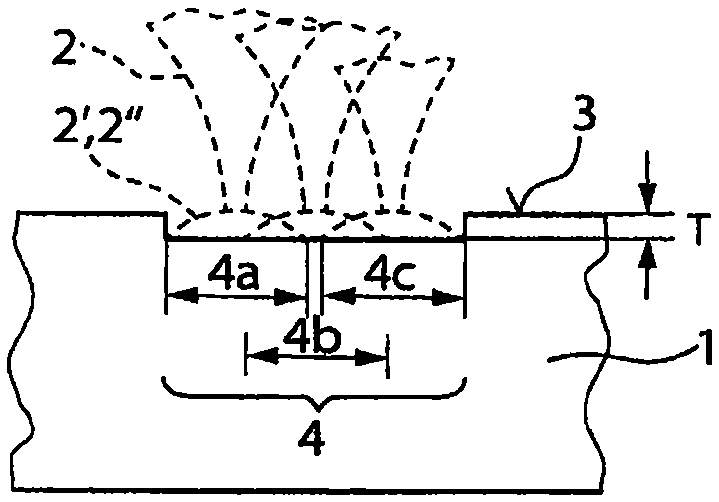
[0032] exist Figure 1a In the first method step shown in , the surface trajectory 4 ( Figure 2a ) through the workpiece surface (the upper side of the workpiece) 3, as the real material removal, the workpiece surface is pretreated. The transmissivity of the workpiece region in the vicinity of the surface is reduced by this pretreatment, for example by roughening the workpiece surface 3 with the aid of the laser beam 2 . Such as Figure 2a As shown, in the first method step, successive laser pulses 2 ′, 2 ″ of the pulsed laser beam 2 have a first pulse overlap 6 of, for example, 95% in the track direction 5 on the workpiece surface 3 1, so that successive pulses 2', 2" largely overlap each other.
[0033] In order to widen the preprocessed su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com